Abstract
Study design:
Cross-sectional study design involving completion of self-report measures.
Objective:
To investigate the relationship between perceived injustice, post-traumatic stress symptoms and depression in a sample of individuals receiving inpatient rehabilitation care following hospitalization for acute spinal cord injury (SCI), as well as the mediating role of anger variables.
Setting:
Inpatient rehabilitation program in a large urban city in the Southwestern United States.
Methods:
A sample of 53 participants with an average of 204.51 days (s.d.=410.67, median=56) post injury occurrence completed measures of perceived injustice, depression and post-traumatic stress symptoms as well as measures of trait anger, state anger, anger inhibition and anger expression.
Results:
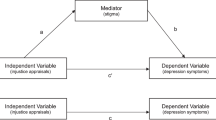
Perceived injustice was significantly correlated with depression and post-traumatic stress symptoms, and accounted for unique variance in depression and post-traumatic stress symptoms when controlling for demographic and injury-related variables. Anger inhibition was found to mediate the relationship between perceived injustice and depression. Trait anger and anger expression were found to mediate the relationship between perceived injustice and post-traumatic stress symptoms.
Conclusions:
Consistent with previous research, perceived injustice was associated with greater depression and post-traumatic stress symptoms. The results support previous findings that anger inhibition mediates between perceived injustice and depression, and provides novel findings regarding mediation of post-traumatic stress symptoms. Results provide preliminary evidence for the role of perceived injustice in SCI and potential mechanisms by which it may exert its effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Kennedy L, Dunstan DA . Confirmatory factor analysis of the injustice experience questionnaire in an australian compensable population. J Occup Rehabil 2014; 24: 385–392.
Sullivan MJL, Adams H, Horan S, Maher D, Boland D, Gross R . The role of perceived injustice in the experience of chronic pain and disability: Scale development and validation. J Occup Rehabil 2008; 18: 249–261.
Sullivan MJ, Scott W, Trost Z . Perceived injustice: a risk factor for problematic pain outcomes. Clin J Pain 2012; 28: 484–488.
Yakobov E, Scott W, Stanish W, Dunbar M, Richardson G, Sullivan M . The role of perceived injustice in the prediction of pain and function after total knee arthroplasty. Pain 2014; 155: 2040–2046.
Scott W, Trost Z, Milioto M, Sullivan MJ . Further validation of a measure of injury-related injustice perceptions to identify risk for occupational disability: a prospective study of individuals with whiplash injury. J Occup Rehabil 2013; 23: 557–565.
Sullivan MJL, Davidson N, Garfinkel B, Siriapaipant N, Scott W . Perceived injustice is associated with heightened pain behavior and disability in individuals with whiplash injuries. Psychol Injury Law 2009; 2: 238–247.
Trost Z, Agtarap S, Scott W, Driver S, Guck A, Roden-Foreman K et al. Perceived injustice after traumatic injury: Associations with pain, psychological distress, and quality of life outcomes 12 months after injury. Rehabil Psychol 2015; 60: 213–221.
Scott W, Sullivan M . Perceived injustice moderates the relationship between pain and depression. Abstract published in The Journal of Pain’s annual meeting supplemental issue 2011; 12: 81.
Scott W, Trost Z, Bernier E, Sullivan MJ . Anger differentially mediates the relationship between perceived injustice and chronic pain outcomes. Pain 2013; 154: 1691–1698.
Rodero B, Luciano JV, Montero-Marín J, Casanueva B, Palacin JC, Gili M et al. Perceived injustice in fibromyalgia: Psychometric characteristics of the Injustice Experience Questionnaire and relationship with pain catastrophising and pain acceptance. J Psychosom Res 2012; 73: 86–91.
Scott W, Trost Z, Milioto M, Sullivan MJL . Barriers to change in depressive symptoms after multidisciplinary rehabilitation for whiplash: the role of perceived injustice. Clin J Pain 2015; 31: 145–151.
Sullivan MJL, Thibault P, Simmonds MJ, Milioto M, Cantin AP, Velly AM . Pain, perceived injustice and the persistence of post-traumatic stress symptoms during the course of rehabilitation for whiplash injuries. Pain 2009; 145: 325–331.
Whiteneck GG, Charlifue SW, Frankel HL, Fraser MH, Gardner BP, Gerhart KA et al. Mortality, morbidity, and psychosocial outcomes of persons spinal cord injured more than 20 years ago. Paraplegia 1992; 30: 617–630.
Mikula G, Scherer KR, Athenstaedt U . The role of injustice in the elicitation of differential emotional reactions. Personal Soc Psychol Bull 1998; 24: 769–783.
Miller DT . Disrespect and the experience of injustice. Annu Rev Psychol 2001; 52: 527–553.
Frijda NH . The Emotions. Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, US; Paris, France. 1986.
Trost Z, Vangronsveld K, Linton SJ, Quartana PJ, Sullivan MJL . Cognitive dimensions of anger in chronic pain. Pain 2012; 153: 515–517.
Duckro PN, Chibnall JT, Tomazic TJ . Anger, depression, and disability: a path analysis of relationships in a sample of chronic posttraumatic headache patients. Headache 1995; 35: 7–9.
Hull L, Farrin L, Unwin C, Everitt B, Wykes T, David AS . Anger, psychopathology and cognitive inhibition: a study of UK servicemen. Personal Individual Differ 2003; 35: 1211–1226.
Clay DL, Anderson WP, Dixon WA . Relationship between anger expression and stress in predicting depression. J Counsel Dev 1993; 72: 91–94.
Kellner R, Hernandez J, Pathak D . Self-rated inhibited anger, somatization and depression. Psychother Psychosom 1992; 57: 102–107.
Riley WT, Treiber FA, Woods MG . Anger and hostility in depression. J Nerv Ment Dis 1989; 177: 668–674.
Tschannen TA, Duckro PN, Margolis RB, Tomazic TJ . The relationship of anger, depression, and perceived disability among headache patients. Headache 1992; 32: 501–503.
Scott W, Milioto M, Trost Z, Sullivan MJL . The relationship between perceived injustice and the working alliance: a cross-sectional study of patients with persistent pain attending multidisciplinary rehabilitation. Disabil Rehabil 2016; 38: 2365–2373.
Olatunji BO, Ciesielski BG, Tolin DF . Fear and loathing: a meta-analytic review of the specificity of anger in PTSD. Behav Ther 2010; 41: 93–105.
Rodrigues D, Tran Y, Wijesuriya N, Guest R, Middleton J, Craig A . Pain intensity and its association with negative mood States in patients with spinal cord injury. Pain Ther 2013; 2: 113–119.
Craig A, Tran Y, Siddall P, Wijesuriya N, Lovas J, Bartrop R et al. Developing a model of associations between chronic pain, depressive mood, chronic fatigue, and self-efficacy in people with spinal cord injury. J Pain 2013; 14: 911–920.
Wollaars MM, Post MWM, van Asbeck FWA, Brand N . Spinal cord injury pain: the influence of psychologic factors and impact on quality of life. Clin J Pain 2007; 23: 383–391.
Trost Z, Monden KR, Buelow M, Boals A, Scott W . Perceived injustice predicts intention to litigate: findings from a spinal cord injury sample. Psychol Inj and Law 2016; 9: 31–40.
Melzack R . The short-form McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain 1987; 30: 191–197.
Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T, French M . Measures of Adult Pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2011; 63: S240–S252.
Cohen MJ, McArthur DL, Vulpe M, Schandler SL, Gerber KE . Comparing chronic pain from spinal cord injury to chronic pain of other origins. Pain 1988; 35: 57–63.
Finnerup NB, Johannesen IL, Sindrup SH, Bach FW, Jensen TS . Pain and dysesthesia in patients with spinal cord injury: a postal survey. Spinal Cord 2001; 39: 256–262.
Kroenke K, Strine TW, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Berry JT, Mokdad AH . The PHQ-8 as a measure of current depression in the general population. J Affect Disord 2009; 114: 163–173.
Shih R, Schell T, Hambarsoomian K, Marshall G, Belzberg H . Prevalence of PTSD and major depression following trauma-center hospitalization. J Trauma 2010; 69: 1560–1566.
Bombardier CH, Fann JR, Tate DG, Richards JS, Wilson CS, Warren AM et al. An exploration of modifiable risk factors for depression after spinal cord injury: which factors should we target? Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2012; 93: 775–781.
Hanley J, deRoon-Cassini T, Brasel K . Efficiency of a four-item posttraumatic stress disorder screen in trauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2013; 75: 722–727.
Reese C, Pederson T, Avila S, Joseph K, Nagy K, Dennis A et al. Screening for traumatic stress among survivors of urban trauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012; 73: 462–467.
Prins A, Ouimette P, Kimerling R, Cameron RP, Hugelshofer DS, Shaw-Hegwer J et al. The primary care PTSD screen (PC-PTSD): development and operating characteristics. Prim Care Psychiatry 2003; 9: 9–14.
Spielberger C . Manual for the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory (STAXI). Pschological Assessment Resources: Odessa, Florida. 1988.
Azevedo FB de, Wang Y-P, Goulart AC, Lotufo PA, Benseñor IM . Application of the Spielberger’s State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory in clinical patients. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2010; 68: 231–234.
Bailie JM, Cole WR, Ivins B, Boyd C, Lewis S, Neff J et al. The experience, expression, and control of anger following traumatic brain injury in a military sample. J Head Trauma Rehabil 2015; 30: 12–20.
Burns JW, Quartana PJ, Bruehl S . Anger inhibition and pain: conceptualizations, evidence and new directions. J Behav Med 2008; 31: 259–279.
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF . SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 2004; 36: 717–731.
Agtarap S, Trost Z, Guck AJ, Reynolds M, Foreman ML, Warren AM . Perceived injustice predicts psychological distress in a diverse trauma sample. In: Society of Behavioral Medicine; 23–26 April 2014; Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O, Merikangas KR, Walters EE . Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005; 62: 617–627.
Mischoulon D, Dougherty DD, Bottonari KA, Gresham RL, Sonawalla SB, Fischman AJ et al. An open pilot study of nefazodone in depression with anger attacks: relationship between clinical response and receptor binding. Psychiatry Res 2002; 116: 151–161.
Painuly N, Sharan P, Mattoo SK . Relationship of anger and anger attacks with depression: a brief review. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2005; 255: 215–222.
Van Praag H . Serotonin-related, anxiety/aggression-driven, stressor-precipitated depression. A psycho-biological hypothesis. Eur Psychiatry 1996; 11: 57–67.
Dahlen ER, Martin RC . The experience, expression, and control of anger in perceived social support. Person Individ Differ 2005; 39: 391–401.
Grav S, Hellzèn O, Romild U, Stordal E . Association between social support and depression in the general population: the HUNT study, a cross-sectional survey. J Clin Nurs 2012; 21: 111–120.
Hagerty BM, Williams RA . The effects of sense of belonging, social support, conflict, and loneliness on depression. Nurs Res 1999; 48: 215–219.
Flückiger C, Del Re AC, Wampold BE, Symonds D, Horvath AO . How central is the alliance in psychotherapy? A multilevel longitudinal meta-analysis. J Couns Psychol 2012; 59: 10–17.
Miciak M, Gross DP, Joyce A . A review of the psychotherapeutic ‘common factors’ model and its application in physical therapy: the need to consider general effects in physical therapy practice. Scand J Caring Sci 2012; 26: 394–403.
Blanchard EB, Hickling EJ, Taylor AE, Loos WR, Forneris CA, Jaccard J . Who develops PTSD from motor vehicle accidents? Behav Res Ther 1996; 34: 1–10.
Dunmore E, Clark DM, Ehlers A . A prospective investigation of the role of cognitive factors in persistent posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) after physical or sexual assault. Behav Res Ther 2001; 39: 1063–1084.
Ehlers A, Clark DM . A cognitive model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Behav Res Ther 2000; 38: 319–345.
Castillo DT, Joseph JS, Tharp AT, C’de Baca J, Torres-Sena LM, Qualls C et al. Externalizing and internalizing subtypes of posttraumatic psychopathology and anger expression. J Trauma Stress 2014; 27: 108–111.
Orth U, Wieland E . Anger, hostility, and posttraumatic stress disorder in trauma-exposed adults: a meta-analysis. J Consult Clin Psychol 2006; 74: 698–706.
Chemtob CM, Hamada RS, Roitblat HL, Muraoka MY . Anger, impulsivity, and anger control in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. J Consult Clin Psychol 1994; 62: 827–832.
Foa EB, Riggs DS, Massie ED, Yarczower M . The impact of fear activation and anger on the efficacy of exposure treatment for posttraumatic stress disorder. Behavior Therapy 1995; 26: 487–499.
Bombardier CH, Adams LM, Fann JR, Hoffman JM . Depression trajectories during the first year after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2016; 97: 196–203.
Hatcher MB, Whitaker C, Karl A . What predicts post-traumatic stress following spinal cord injury? Br J Health Psychol 2009; 14: 541–561.
deRoon-Cassini TA, Mancini AD, Rusch MD, Bonanno GA . Psychopathology and resilience following traumatic injury: a latent growth mixture model analysis. Rehabil Psychol 2010; 55: 1–11.
Bryant RA, O’Donnell ML, Creamer M, McFarlane AC, Clark CR, Silove D . The psychiatric sequelae of traumatic injury. Am J Psychiatry 2010; 167: 312–320.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trost, Z., Scott, W., Buelow, M. et al. The association between injustice perception and psychological outcomes in an inpatient spinal cord injury sample: the mediating effects of anger. Spinal Cord 55, 898–905 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2017.39
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2017.39
This article is cited by
-
The effect of justice sensitivity on malevolent creativity: the mediating role of anger and the moderating role of emotion regulation strategies
BMC Psychology (2024)
-
Understanding the association between perceived injustice, depression symptoms, and stigma in individuals with traumatic spinal cord injury
Spinal Cord (2024)
-
Qualitative Examination of the Experience of Perceived Injustice Following Disabling Occupational Injury
Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation (2024)
-
Validation of the Injustice Experience Questionnaire (IEQ) in a spinal cord injury population
Spinal Cord (2021)
-
Perceived injustice after spinal cord injury: evidence for a distinct psychological construct
Spinal Cord (2019)