Abstract
Study design:
Pilot study.
Objectives:
This study aimed to evaluate an electromechanical stance control (SC) knee joint, 'sensor lock', which could potentially solve the problems of walking parameters and gait symmetry in subjects with poliomyelitis.
Setting:
University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences.
Methods:
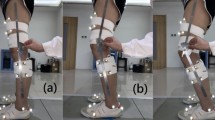
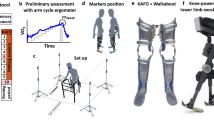
Six subjects with quadriceps weakness were enrolled in this study. A custom-made stance-control knee–ankle–foot orthosis (SCKAFO) with the same set of components was constructed for each participant. A motion analysis system was used for analysis of lower limb kinematics.
Results:
There were no significant differences between the knee–ankle–foot orthoses (KAFOs) and the two types of knee joints with regard to temporal–spatial parameters. Walking speed and cadence reduced and stride length increased in the stance control (SC) mode compared to the knee joint locked mode. The maximum knee flexion angle during swing phase increased when walking with SC mode compared to walking with the KAFO in knee joint lock mode. There was a significant difference between two test conditions with regard to hip flexion. There were only significant differences in the symmetry index of the knee flexion between two test conditions.
Conclusion:
Compared to locked knee mode, SC mode demonstrated a slower speed of walking and increased peak knee flexion during swing. Regarding gait symmetry, the symmetry index of the knee flexion and speed of walking decreased when the KAFO with SC mode was used compared to KAFO with knee joint locked mode.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Yakimovich T, Kofman J, Lemaire ED . Design and evaluation of a stance-control knee-ankle- foot orthosis knee joint. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 2006; 14: 361–369.
Bernhardt K, Oh T, Kaufman K . Stance control orthosis trial in patients with inclusion body myositis. Prosthet Orthot Int 2011; 35: 39–44.
Hwang S, Kang S, Cho K, Kim Y . Biomechanical effect of electromechanical knee-ankle-foot-orthosis on knee joint control in patients with poliomyelitis. Med Biol Eng Comput 2008; 46: 541–549.
Rasmussen AA, Smith KM, Damiano DL . Biomechanical evaluation of the combination of bilateral stance-control knee-ankle-foot orthoses and a reciprocating gait orthosis in an adult with a spinal cord injury. J Prosthet Orthot 2007; 19: 42–47.
Sutherland D, Santi M, Abel M . Treatment of stiff-knee gait in cerebral palsy: a comparison by gait analysis of distal rectus femoris transfer versus proximal rectus release. J Pediatr Orthop 1990; 10: 433–441.
Hebert JS, Liggins AB . Gait evaluation of an automatic stance-control knee orthosis in a patient with postpoliomyelitis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005; 86: 1676–1680.
Irby SE, Bernhardt KA, Kaufman KR . Gait of stance control orthosis users: the dynamic knee brace system. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2005; 29: 269–282.
McMillan AG, Kendrick K, Michael JW, Aronson J, Horton GW . Preliminary evidence for effectiveness of a stance control orthosis. J Prosthet Orthot 2004; 16: 6–13.
Stein RB, Hayday F, Chong S, Thompson AK, Rolf R, James KB et al. Speed and efficiency in walking and wheeling with novel stimulation and bracing systems after spinal cord injury: A case study. Neuromodulation 2005; 8: 264–271.
Rafiaei M, Bahramizadeh M, Arazpour M, Samadian M, Hutchins SW, Farahmand F et al. The gait and energy efficiency of stance control knee–ankle–foot orthoses: a literature review. Prosthet Orthot Int 2016; 40: 202–214.
Portnoy S, Schwartz I . Gait characteristics of post-poliomyelitis patients: Standardization of quantitative data reporting. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 2013; 56: 527–541.
Silver JK, Aiello DD . Polio survivors: falls and subsequent injuries. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2002; 81: 567–570.
Kim CM, Eng JJ . Symmetry in vertical ground reaction force is accompanied by symmetry in temporal but not distance variables of gait in persons with stroke. Gait Posture 2003; 18: 23–28.
Kaufman KR, Irby S, Mathewson J, Wirta R, Sutherland D . Energy-efficient knee-ankle-foot orthosis: a case study. J Prosthet Orthot 1996; 8: 79.
Irby SE, Kaufman KR, Mathewson JW, Sutherland DH . Automatic control design for a dynamic knee-brace system. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 1999; 7: 135–139.
Zissimopoulos A, Fatone S, Gard SA . Biomechanical and energetic effects of a stance-control orthotic knee joint. Journal of rehabilitation research and development. Phys Med Rehab 2007; 44: 503.
Acknowledgements
We thank the iranian National Science Foundation for financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors equally contributed in the preparation of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asadi, F., Arazpour, M., Bani, M. et al. The effect of 'Sensor Lock', a knee–ankle–foot orthosis with an electromechanical stance control knee joint, on walking parameters and gait symmetry of subjects with quadriceps weakness: a pilot study. Spinal Cord Ser Cases 3, 17035 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/scsandc.2017.35
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/scsandc.2017.35