Abstract
Introduction:
Spinal cord injuries in new born infants following a traumatic delivery or umbilical cord catheterisation due to thromboembolism are well known. Cases with atraumatic acute onset of neonatal paraplegia have also been described in preterm babies or babies born small for gestational age with a stormy postnatal course related to ischaemic aetiology. We describe a rare case of infarction of the spinal cord from a predominant haemorrhagic aetiology.
Case presentation:
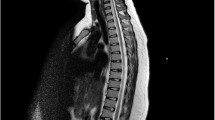
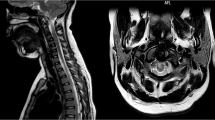
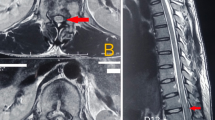
A term female baby, first child of unrelated parents, was born by normal vaginal delivery. She had meconium aspiration at birth, leading to severe respiratory distress, requiring neonatal intensive care admission. At 2 weeks, she developed new flaccid paraplegia. MRI scan of the spine showed haemorrhagic infarction of the spinal cord from the level of thoracic inlet, vertebral level C7–T1. A follow-up MRI scan at 11 months revealed severe atrophy of the cord distal to C6. At 3 years of age, she had good upper-limb function, diaphragmatic breathing and flaccid paralysis of lower limbs.
Discussion:
In an acutely unwell term infant with symptoms of paralysis or spinal cord damage, haemorrhagic infarction needs to be considered in the differential diagnosis. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of spinal cord injury in a term infant with a haemorrhagic lesion, and it helps to understand the pathogenesis of nontraumatic insult.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Vialle R, Piétin-Vialle C, Ilharreborde B, Dauger S, Vinchon M, Glorion C . Spinal cord injuries at birth: a multicenter review of nine cases. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2007; 20: 435–440.
Haldeman S, Fowler GW, Ashwal S, Schneider S . Acute flaccid neonatal paraplegia: a case report. Neurology 1983; 33: 93–95.
Aziz EM, Robertson AF . Paraplegia: complication of umblical artery catheterisation. J Pediatr 1973; 82: 1051–1052.
Brown MS, Phibbs RH . Spinal cord injury in newborns from the use of umblical artery catheters. J Perinatol 1988; 8: 105–110.
Clancy RR, Sladk JT, Rouke LB . Hypoxic-ischemic spinal cord injury following perinatal asphyxia. Ann Neurol 1989; 25: 185–189.
Rehan VK, Seshia MMK . Spinal cord birth injury-diagnostic difficulties. Arch Dis Child 1993; 69: 92–94.
Schneider H, Ballowitz L, Schachinger H, Hanefeld F, Dröszus JU . Anoxic encephalopathy with predominant involvement of basal ganglia, brain stem and spinal cord in perinatal period. Acta Neuropathol 1975; 32: 287–298.
Sladky R, Rorke LB . Perinatal hypoxic/ischemic spinal cord injury. Pediatr Pathol 1986; 6: 87–101.
Singer R, Joseph K, Gilai AN, Meyer S . Nontraumatic, acute neonatal paraplegia. J Pediatr Orthop 1991; 11: 588–593.
Arendar G, Samara E, Palmas C . Neonatal acquired paraplegia: retrospective review of 30 patients. J Pediatr Orthop B 1999; 8: 80–83.
Gilian LA . The arterial blood supply of the human spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 1958; 110: 75–103.
Adamkiewicz A . Die Blutgefasse des mennschlichen Ruckenmarkes. Sitzungsber Kaiserl Akad Wissensch Wien math- naturw CI III. Abt.1881; 83:469–502; 1882; 85:101–130.
Laguna J, Cravioto H . Spinal cord infarction secondary to occlusion of the anterior spinal artery. Arch Neurol 1973; 29: 134.
Duggal N, Lach B . Selective vulnerability of the lumbosacral spinal cord after cardiac arrest and hypotension. Stroke 2002; 33: 116–121.
Ahmann PA, Smith SA, Schwartz JF, Clark DB . Spinal cord infarction due to minor trauma in children. Neurology 1975; 25: 301–307.
Brown MS, Phibbs RH . Spinal cord injury in newborns from use of umbilical artery catheters: report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Perinatol 1988; 8: 105–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulshrestha, R., Chowdhury, J., Lalam, R. et al. Spinal cord infarction in a sick neonate from predominant haemorrhagic aetiology: a case report. Spinal Cord Ser Cases 3, 17038 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/scsandc.2017.38
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/scsandc.2017.38
This article is cited by
-
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy with Cervical Spinal Cord Injury: A Diagnostic Dilemma
Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2024)