Key Points
-
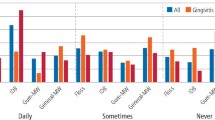
Highlights that diagnosis and effective management of chronic periodontal disease is needed on a daily basis in general dental practice.
-
Suggests there is limited detailed guidance for chronic periodontal disease management in practice.
-
Provides guidance for the management of chronic periodontal disease based around patients' oral hygiene and risk factors so they receive tailored management.
Abstract
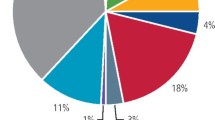
The vast majority of patients will experience gingival-related disease at some point in their life, and up to a quarter of those are susceptible to advanced periodontal disease. This makes its effective management an important part of general dental practice. This paper provides guidance on management which incorporates periodontal assessment, management and recall according to patient's oral hygiene and modifiable risk factors. This has been produced in flow diagram format to aid non-surgical management of chronic gingival and periodontal disease in general dental practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gingivitis and periodontitis. Online information available at www.evidence.nhs.uk/topic/gingivitisandperiodontitis (accessed April 2015).
British Society of Periodontology. Young practitioners guide to periodontology, 2nd edition. Online information available at http://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/downloads/Young_Practitioners_Guide.pdf (accessed April 2015).
Dental Protection. Periodontal monitoring. 2014. Online information available at http://www.dentalprotection.org/new-zealand/publications-resources/clinical-audit-tools/clinical-audit-tools-display/2014/08/27/periodontal-monitoring (accessed April 2015).
Manresa C, Sanz E, Bravo M, Echeverría J J . Interventions for the maintenance of the dentition in patients treated for periodontal disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011; 10: CD009376.
Renz A, Ide M, Newton T, Robinson P, Smith D . Psychological interventions to improve adherence to oral hygiene instructions in adults with periodontal diseases. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007; 2: CD005097.
Lindhe J, Westfelt E, Nyman S, Socransky S S, Haffajee A D . Long-term effect of surgical/non-surgical treatment of periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 1984; 11: 448–458.
Axelsson P, Lindhe J . The significance of maintenance care in the treatment of periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 1981; 8: 281–294.
Westfelt E, Nyman S, Socransky S, Lindhe J . Significance of frequency of professional tooth cleaning for healing following periodontal surgery. J Clin Periodontol 1983; 10: 148–156.
Lindhe J, Nyman S . Long term maintenance of patients treated for advanced periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 1984; 11: 504–514.
Van der Weijden F, Slot D E . Oral hygiene in the prevention of periodontal diseases: the evidence. Periodontology 2000 2011; 55: 104–123.
Schatzle M, Loe H, Lang N.P, Burgin W, Anerud A, Boysen H . The clinical course of chronic periodontitis: IV. Gingival inflammation as a risk factor in tooth mortality. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31: 1122–1127.
Stabholz A, Aubrey Soskolne W, Shapira L . Genetic and environmental risk factors for chronic periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis. Periodontology 2000 2010; 53: 138–153.
British Society of Periodontology. Basic periodontal examination. 2011. Online information available at http://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/downloads/39_143748_bpe2011.pdf (accessed April 2015).
British Society of Periodontology. Periodontology in general dental practice in the United Kingdom. 2001. Online information available at http://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/downloads/64_144208_periodontologyingeneraldentalpracticeinthe-uk.pdf (accessed April 2015).
Armitage G C . Development of a classification system for periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol 1999; 4: 1–6.
Nield-Gehrig J S . Fundamentals of periodontal instrumentation and advanced root instrumentation. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004.
Tunkel J, Heinecke A, Flemmig T F . A systematic review of efficacy of machine-driven and manual subgingival debridement in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 2002; 29 (Suppl 3): 72–81.
Ioannou I, Dimitriadis N, Papadimitriou K, Sakellari D, Vouros I, Konstantinidis A . Hand instrumentation vs ultrasonic debridement in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: a randomized clinical and microbiological trial. J Clin Periodontol 2009; 36: 132–41.
Cobb C M . Clinical significance of non-surgical periodontal therapy: an evidence-based perspective of scaling and root planing. J Clin Periodontol 2002; 29 (Suppl 2): 6–16.
Sanz M, Teughels, Group A of European Workshop on Periodontology. Innovations in non-surgical periodontal therapy: consensus report of the sixth European workshop on periodontology. J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35 (Suppl 8): 3–7.
Needleman I, Nibali L, Di Iorio A . Professional mechanical plaque removal for prevention of periodontal diseases in adults - systematic review update. J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl 16): S12–35.
Jepsen S, Deschner J, Braun A . Schwarz F, Eberhard J . Calculus removal and the prevention of its formation. Periodontology 2000 2011; 55: 167–88.
Kocher T, Fanghanel J, Sawaf H, Litz R . Substance loss caused by scaling with different sonic scaler inserts - an in vitro study. J Clin Periodontol 2001; 28: 9–15.
Darcey J, Ashley M . See you in three months! The rationale for the three monthly periodontal recall interval: a risk based approach. Br Dent J 2011; 211: 379–85.
Scottish Dental Clinical Effectiveness Programme. Prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases in primary care. 2014. Online information available at http://www.sdcep.org.uk/published-guidance/periodontal-management/ (accessed April 2015).
O'Leary T, Drake R B, Naylor J E . Plaque control record. J Periodontol 1972; 43: 38.
Matsunaga M, Setoguchi T, Nakamura M, Yokota M, Sueda T . Relationship between pocket reduction and plaque control in initial treatment. Nihon Shishubyo Gakkai Kaishi 1989; 31: 717–723.
Yokota M, Kubo K, Setoguchi T, Hosaka H, Machigashira M, Sueda T . Influence of residual plaque score during initial treatment on pocket reduction rate at individual tooth surfaces. Nihon Shishubyo Gakkai Kaishi 1989; 31: 1182–1196.
Wennstrom J L, Tomasi C, Bertelle A, Dellasega E . Full-mouth ultrasonic debridement versus quadrant scaling and root planing as an initial approach in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 2005; 32: 851–859.
Ederhard J, Jepson S, Jervoe-Storm P M, Needleman I, Worthington H V . Full mouth disinfection for the treatment of adult chronic periodontitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008; 23: CD004622.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Dental recall: recall interval between routine dental examinations. 2004, revised 2014. Online information available at https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg19 (accessed April 2015).
Acknowledgements
Thank you to Dr M Prideaux, Dr B Ashton and all the staff at Mount Wise Dental Practice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Refereed Paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, G. Producing guidance for the management of patients with chronic periodontal disease in general dental practice. Br Dent J 218, 461–466 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2015.295
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2015.295