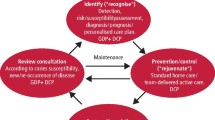
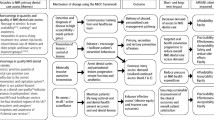
Key Points
-
Highlights a shift in practice from traditional concepts of practice to MI.
-
Suggests that a coherent approach to planning organisational change in practice is required.
-
Provides suggestion of an overall planning process in practice.
Abstract
Minimum intervention dentistry (MID) is the evidence-based delivery of oral healthcare which aims to maximise preservation of tooth structure and longevity of tooth life, improving long-term oral health and wellbeing. In general dental practice implementing such an ethos and approach can require change in the practice structure and processes. Such change in processes requires careful management and planning. Planning should include financial as well as business planning. A detailed understanding of the planning that may be required is described here as a guide to help oral healthcare practice staff and other stakeholders to facilitate the delivery of MID.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Frencken J E, Peters M C, Manton D J, Leal S C, Gordan V V, Eden E . Minimal intervention dentistry for managing dental caries – a review: report of a FDI task group. Int Dent J 2012; 62: 223–243.
Walsh L J, Brostek A M . Minimum intervention dentistry principles and objectives. Aust Dent J 2013; 58 Suppl 1: 3–16.
Domejean-Orliaguet S, Banerjee A, Gaucher C et al. Minimum Intervention treatment Plan (MITP) –practical implementation in general dental practice. J Minim Interv Dent 2009.
Banerjee A, Domejean S . The contemporary approach to tooth preservation: minimum intervention (MI) caries management in general practice. Prim Dent J 2013; 2: 30–37.
Hatton A . The Definitive Guide to Marketing Planning. London: Pearson Education Limited, 2000.
Aaker D . Developing Business Strategies. Sixth Edition. Wiley, 2001.
Hamel G, Prahalad C K . Strategic Intent. Harvard Business Rev 1989: 67: 63–76.
Sinek S . Start With Why. Penguin Random House, 2009.
businessballs.com. tuckman forming storming norming performing model. Bruce Tuckmans 1965 Model. Available at http://www.businessballs.com/tuckmanformingstormingnormingperforming.htm (accessed July 2017).
NHS Leadership Academy. Clinical Leadership Competency Framework. 2011. Available at http://www.leadershipacademy.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/NHSLeadership-Leadership-Framework-Clinical-Leadership-Competency-Framework-CLCF.pdf (accessed November 2016).
Ahmed P K, Rafiq M . Internal Marketing, Tools and Concepts for Customer Focused Management. Oxford: Butterworth – Heinemann, 2002.
Cameron, E, Green, M . Making sense of change management: a complete guide to the models, tools and techniques of organizational change. London: Kogan Page Limited, 2004.
MindTools. Resolving Team Conflicts. Available at https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMM_79.htm (Accessed November 2016).
GDC. Scope of Practice. 2013. Available at https://www.gdc-uk.org/api/files/Scope%20of%20Practice%20September%202013.pdf (accessed November 2016).
Public Health England. Delivering better oral health: an evidence-based toolkit for prevention. Third Edition. Department of Health. Available at https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/605266/Delivering_better_oral_health.pdf (accessed November 2016).
NHS National Workforce Projects. Dental Workforce Resource Pack. Available at https://www.pcc-cic.org.uk/sites/default/files/articles/attachments/dental_workforce_resource_packnational_workforce_projectsaug_07.pdf (accessed November 2016).
Perryer, G . Units of Dental Activity. University of Birmingham. http://www.mecourse.com/ecourse/pages/page.asp?pid=1375 (accessed October 2016).
Page J, Weld J A, Kidd E A . Caries control in health service practice. Br Dent J 2010; 208: 449–450.
Williams S . Small Business Guide. London: Vitesse Media Group, 2002.
Ulhaner L . The Growing Business Handbook: Inspiration and advice from successful entrepreneurs and fast growing UK companies. Twelfth Edition. London: Kogan Page Limited, 2010.
Runkle K . The Business of Dentistry. 2011. Available at http://www.dentaleconomics.com/articles/print/volume-101/issue-1/features/the-business-of-dentistry.html (accessed October 2016).
Fill C . Marketing Communications Contexts, Strategies and Applications. Second edition. London: Pearson Education Limited, 2002.
Fill C, Yeshin T . Integrated Marketing Communications. Oxford: Butterworth – Heinemann, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Refereed Paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dawett, B., Atkins, B. & Banerjee, A. A guide to building 'MI' oral healthcare practice. Br Dent J 223, 223–227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2017.673
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2017.673
This article is cited by
-
Could the minimum intervention oral care framework help improve the quality of oral health delivery and access to NHS primary dental care?
British Dental Journal (2024)
-
Top tips for minimally invasive dentistry in primary care
British Dental Journal (2023)
-
A scoping literature review on minimum intervention dentistry for children with dental caries
British Dental Journal (2022)
-
Dental Policy Lab 1 - towards a cavity-free future
British Dental Journal (2021)