Volume 39
-
No. 12 December 2021
High-speed whole-brain imagingReconstruction of nerve bundles in a rhesus monkey brain. Fang Xu et al. present a method to image a whole monkey brain at micrometer resolution in 100 hours.
See Xu et al.
-
No. 11 November 2021
Virus-sensing fabricsNguyen et al. developed a lyophilized synthetic biology circuit embedded in fabric that transmits viral detection signals through a textile-integrated waveguide.
See Nguyen et al.
-
No. 10 October 2021
Bioresorbable, leadless cardiac pacemakerChoi et al. engineer a biodegradable pacemaker without external leads that improves the safety of temporary cardiac pacing.
See Y. S. Choi et al.
-
No. 9 September 2021
MAQC-IV and Sequencing Quality Control 2SEQC2, the final phase of the MAQC consortium, presents the results of several sequencing benchmarking analyses.
SeeEditorial
-
No. 8 August 2021
Imaging-free molecular tomographySchede et al. applied a new tomographic spatial transcriptomic method, STRP-seq—which is able to provide tissue-wide gene expression maps for thousands of genes—to the brain of the bearded dragon (Pogona vitticeps).
See Schede et al.
-
No. 7 July 2021
Single-cell CUT&TagDecoding epigenomic information from individual cells from the mouse brain: with single-cell CUT&Tag, histone modifications and transcription factor binding can now be mapped in tens of thousands of individual cells.
See Bartosovic et al. and Wu et al.
-
No. 6 June 2021
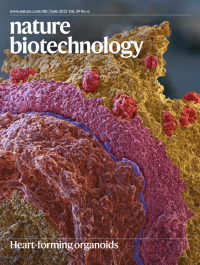
Heart-forming organoidsScanning electron micrograph of a heart-forming organoid showing a myocardial layer (pink) separated by a thin endocardial layer (blue) from an anterior foregut endoderm and vascular layer (cinnamon); the outer layer (yellow) includes liver anlagen (red). The layers were hand colored on the basis of cell shape, cell surface and data from light and confocal microscopy.
See Drakhlis et al.
-
No. 5 May 2021
ChIP-seq of cell-free DNAAn artist's impression of what we can learn from assaying chromatin fragments released from dying cells; the whole body is reflected in a blood sample. Sadeh et al. present a method for assaying these fragments to study cell type and state in health and disease.
See Sadeh et al.
-
No. 4 April 2021
A catalog of Earth’s microbiomesIllustration showing the completion of a genomic catalog of Earth’s microbiomes. Nayfach et al. apply metagenomics to more than ten thousand samples from diverse habitats, extending the known phylogenetic diversity of bacteria and archaea.
See Nayfach et al.
-
No. 3 March 2021
Nature Biotechnology celebrates its 25th anniversaryNature Biotechnology celebrates 25 years of publishing the very best of biotech science and business.
See Editorial
-
No. 2 February 2021
How pain receptors drive inflammationColorized scanning electron micrograph of silicone-encapsulated gold interconnects of a device for epineural optogenetic neuromodulation. Michoud et al. use the device to show how nociceptor activation drives protective pain behavior and inflammation.
See Michoud et al.
-
No. 1 January 2021
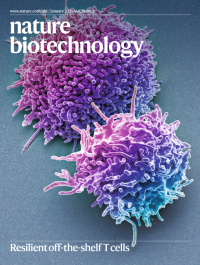
Resilient off-the-shelf T cellsColored scanning electron micrograph of resting human T lymphocytes. Mo et al. present an alloimmune defense receptor that allows allogeneic T cells to resist rejection by the host immune system by deleting activated host T and NK cells.
See Mo et al.