Abstract
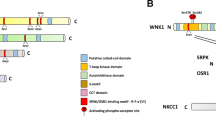
The subfamily of WNK (with no K=lysine) protein kinases has four human members and germline mutations in the WNK1 and WNK4 genes were recently found to cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type II, a familial hypertension disease. Here, we describe cloning and functional analysis of a further WNK member, human WNK3. Endogenous WNK3 protein is an active protein kinase when immunoprecipitated from cells and its overexpression increases the survival of HeLa cells by delaying the onset of apoptosis. Suppression of endogenous WNK3 protein by RNA interference accelerates the apoptotic response and promotes the activation of caspase-3. The mechanism of WNK3 action involves interaction with procaspase-3 and heat-shock protein 70. These results demonstrate a role for WNK3 in promoting cell survival and suggest a mechanism at the level of procaspase-3 activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagci EZ, Vodovotz Y, Billiar TR, Ermentrout GB, Bahar I . (2006). Biophys J (in press).
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T et al. (2000). Nat Cell Biol 2: 469–475.
Boatright KM, Salvesen GS . (2003). Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 725–731.
Ciocca DR, Clark GM, Tandon AK, Fuqua SA, Welch WJ, McGuire WL . (1993). J Natl Cancer Inst 85: 570–574.
Cosulich SC, Savory PJ, Clarke PR . (1999). Curr Biol 9: 147–150.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Cell 116: 205–219.
Dmitrieva NI, Burg MB . (2005). Mutat Res 569: 65–74.
Eischen CM, Alt JR, Wang P . (2004). Oncogene 23: 8931–8940.
Gagnon KBE, England R, Delpire E . (2006). Mol Cell Biol 26: 689–698.
Gamba G . (2005). Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288: F245–F252.
Gotz R, Kramer BW, Camarero G, Rapp UR . (2004). BMC Cancer 4: 85.
Hanks SK, Hunter T . (1995). FASEB J 9: 576–596.
Holden S, Cox J, Raymond FL . (2004). Gene 335: 109–119.
Hunter T . (2000). Cell 100: 113–127.
Igney FH, Krammer P . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 277–288.
Jaattela M . (1999). Exp Cell Res 248: 30–43.
Jaattela M, Wissing D . (1993). J Exp Med 177: 231–236.
Jiang ZY, Zhou QL, Holik J, Patel S, Leszyk J, Coleman K et al. (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 21622–21628.
Jordan P, Matos P, Veríssimo F . (2000). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279: 741–743.
Kahle KT, Gimenez I, Hassan H, Wilson FH, Wong RD, Forbush B et al. (2004b). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 2064–2069.
Kahle KT, Rinehart J, de Los Heros P, Louvi A, Meade P, Vazquez N et al. (2005). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16783–16788.
Kahle KT, Wilson FH, Lalioti M, Toka H, Qin H, Lifton RP . (2004a). Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13: 557–562.
Kaur J, Kaur J, Ralhan R . (2000). Int J Cancer 85: 1–5.
Kim S, Nollen EA, Kitagawa K, Bindokas VP, Morimoto RI . (2002). Nat Cell Biol 4: 826–831.
Komarova EY, Afanasyeva EA, Bulatova MM, Cheetham ME, Margulis BA, Guzhova IV . (2004). Cell Stress Chaperone 9: 265–275.
Kostich M, English J, Madison V, Gheyas F, Wang L, Qiu P et al. (2002). Genome Biol 3 (RESEARCH0043).
Lee BH, Min X, Heise CJ, Xu BE, Chen S, Shu H et al. (2004). Mol Cell 15: 741–751.
Lenertz LY, Lee BH, Min X, Xu BE, Wedin K, Earnest S et al. (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 26653–26658.
Li CY, Lee JS, Ko YG, Kim JI, Seo JS . (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 25665–25671.
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES et al. (1997). Cell 91: 479–489.
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S . (2002). Science 298: 1912–1934.
Mayer MP, Bukau B . (2005). Cell Mol Life Sci 62: 670–684.
Moore TM, Garg R, Johnson C, Coptcoat MJ, Ridley AJ, Morris JD . (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 4311–4322.
Moriguchi T, Urushiyama S, Hisamoto N, Iemura S, Uchida S, Natsume T et al. (2005). J Biol Chem 280: 42685–42693.
Mosser D, Caron AW, Bourget L, Meriin AB, Sherman MY, Morimoto RI et al. (2000). Mol Cell Biol 20: 7146–7159.
Mosser DD, Caron AW, Bourget L, Denis-Larose C, Massie B . (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 5317–5327.
Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA . (1997). Trends Biochem Sci 22: 299–306.
Nollen EA, Morimoto RI . (2002). J Cell Sci 115: 2809–2816.
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P . (2003). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 552–565.
Parcellier A, Gurbuxani S, Schmitt E, Solary E, Garrido C . (2003). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304: 505–512.
Rinehart J, Kahle KT, de Los Heros P, Vazquez N, Meade P, Wilson FH et al. (2005). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 16777–16782.
Roy N, Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC . (1997). EMBO J 16: 6914–6925.
Saleh A, Srinivasula SM, Balkir L, Robbins PD, Alnemri ES . (2000). Nat Cell Biol 2: 476–483.
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS . (2002). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 401–410.
Tewari M, Quan LT, O'Rourke K, Desnoyers S, Zeng Z, Beidler DR et al. (1995). Cell 81: 801–809.
Vaux DL, Strasser A . (1996). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 2239–2244.
Veríssimo F, Jordan P . (2001). Oncogene 20: 5562–5569.
Vitari AC, Deak M, Collins BJ, Morrice N, Prescott AR, Phelan A et al. (2004). Biochem J 378: 257–268.
Vitari AC, Deak M, Morrice NA, Alessi DR . (2005). Biochem J 391: 17–24.
Wei YQ, Zhao X, Kariya Y, Teshigawara K, Uchida A . (1995). Cancer Immunol Immunother 40: 73–78.
Wilson FH, Disse-Nicodeme S, Choate KA, Ishikawa K, Nelson-Williams C, Desitter I et al. (2001). Science 293: 1107–1112.
Xu B, English JM, Wilsbacher JL, Stippec S, Goldsmith EJ, Cobb MH . (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 16795–16801.
Xu B, Stippec S, Lenertz L, Lee B-H, Zhang W, Lee YK et al. (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 7826–7831.
Xu BE, Stippec S, Chu PY, Lazrak A, Li XJ, Lee BH et al. (2005). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 10315–10320.
Acknowledgements
We thank Sónia Pedro for running the automated ABI sequencer, Jeremy Simpson and Brigitte Joggerst-Thomalla (EMBL) for help in the antibody production, Andrew Riddle (EMBL) for support in handling and interpretation of FACS analysis and the Advanced Light Microscopy Facility staff at EMBL, Heidelberg for support with microinjection and in vivo time-lapse microscopy. We are grateful to R Morimoto (Northwestern University Evanston, IL, USA), VM Dixit (University of Michigan) and the Kazusa Human cDNA Project (Chiba, Japan) for providing plasmids used in this study. Visitron and Zeiss companies are acknowledged for instruments provided to ALMF at EMBL. This work was supported by the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (Grant POCTI/33221/99, Programa de Financiamento Plurianual do CIGMH and fellowship BD 19936/99) and an EurALMF short-term visitor fellowship to FV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veríssimo, F., Silva, E., Morris, J. et al. Protein kinase WNK3 increases cell survival in a caspase-3-dependent pathway. Oncogene 25, 4172–4182 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209449
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209449
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transcriptome signature of miRNA-26b KO mouse model suggests novel targets
BMC Genomic Data (2021)
-
Silencing of the lncRNA H19 enhances sensitivity to X-ray and carbon-ions through the miR-130a-3p /WNK3 signaling axis in NSCLC cells
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
The dynamic stress-induced “O-GlcNAc-ome” highlights functions for O-GlcNAc in regulating DNA damage/repair and other cellular pathways
Amino Acids (2011)
-
Emerging roles for WNK kinases in cancer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2010)
-
Identifying cancer genes from cancer mutation profiles by cancer functions
Science in China Series C: Life Sciences (2008)