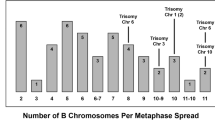
The red viscacha rat is unaffected by having double the usual number of chromosomes.
Abstract
Polyploidy, or having more than a pair of each type of chromosome, is considered to be unlikely in mammals because it would disrupt the mechanism of dosage compensation that normally inactivates one X chromosome in females1. Also, any imbalance in chromosome number should affect the normal developmental processes and therefore constitute an evolutionary end, as in triploid humans2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orr, H. A. Am. Nat. 136, 759–770 (1990).
Niebuhr, E. Humangenetik 21, 103–125 (1974).
Gallardo, M. H. in Chromosomes Today Vol 12 (eds Henríques-Gil, N., Parker, J. S & Puertas, M. J.) 347–365 (Chapman & Hall, London, 1997).
Ojeda, R. A. et al. J. Arid Environ. 41–452 (1999).
Contreras, L. C., Torres-Mura, J. C. & Spotorno, A. E. Experientia 46, 506–508 (1990).
Vinogradov, A. E. Cytometry 31, 100–109 (1998).
Ferrari, M. R., Spirito, S. E., Giuliano, S. M. & Fernández, H. A. Andrologia 30, 85–89 (1998).
Müller, H. Am. Nat. 59 346–353 (1925).
Parkhurst, S. M. & Meneely, P. M. Science 264, 924–932 (1994).
Ohno, S., Kittrell, W. A., Christian, L. C., Stenius, C. & Witts, G. A. Cytogenetics 2, 42–49 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallardo, M., Bickham, J., Honeycutt, R. et al. Discovery of tetraploidy in a mammal. Nature 401, 341 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/43815
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/43815
This article is cited by
-
Polyploidy in liver development, homeostasis and disease
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2020)
-
Derivation and maintenance of mouse haploid embryonic stem cells
Nature Protocols (2019)
-
Centromere inactivation on a neo-Y fusion chromosome in threespine stickleback fish
Chromosome Research (2016)
-
Segmental paleotetraploidy revealed in sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) genome by chromosome painting
Molecular Cytogenetics (2015)
-
The gap in research on polyploidization between plants and vertebrates: model systems and strategic challenges
Science Bulletin (2015)