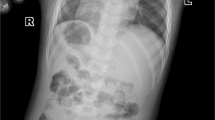
Abstract
Congenital cutis laxa is a genetically heterogeneous condition presenting with loose and redundant skin folds, decreased elasticity of the skin, connective tissue involvement and a highly variable spectrum of associated features. The most common forms are inherited in an autosomal recessive or dominant fashion. Fibulin 5 and elastin mutations were detected in a limited number of patients, but in most cases the etiology is not known. Based on a previous observation of an abnormal transferrin isoelectric focusing pattern in a patient with cutis laxa indicating an N-glycosylation defect, we performed a screening for disorders of protein glycosylation in unrelated children with cutis laxa syndrome, including a recently developed test for defective O-glycosylation. Here, we describe five patients from consanguineous marriages with a cutis laxa syndrome with skeletal and joint involvement, developmental delay and neurological findings. Three of these five children have an inborn error of glycan biosynthesis affecting the synthesis of both N- and O-linked glycans. Two patients had normal glycosylation patterns. All known causes of secondary glycosylation disorders were excluded in the children. No mutations were found in the FBLN5 gene. In conclusion, we have identified a new combined glycosylation defect with a distinct clinical phenotype. Our results suggest that a combined defect of glycosylation might be a causative factor in congenital cutis laxa. This is the first report where abnormal N- and O-linked glycosylation is implicated in the etiology of cutis laxa syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
de Schepper S, Loeys B, de Paepe A, Lambert J, Naeyaert JM : Cutis laxa of the autosomal recessive type in a consanguineous family. Eur J Dermatol 2003; 13: 529–533.
Markova D, Zou Y, Ringpfeil F et al: Genetic heterogeneity of cutis laxa: a heterozygous tandem duplication within the fibulin-5 (FBLN5) gene. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 72: 998–1004.
Loeys B, Van Maldergem L, Mortier G et al: Homozygosity for a missense mutation in fibulin-5 (FBLN5) results in a severe form of cutis laxa. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 2113–2118.
Zhang MC, He L, Giro M, Yong SL, Tiller GE, Davidson JM : Cutis laxa arising from frameshift mutations in exon 30 of the elastin gene (ELN). J Biol Chem 1998; 74: 981–986.
Andiran N, Sarikayalar F, Saraclar M, Caglar M : Autosomal recessive form of congenital cutis laxa: more than the clinical appearance. Pediatr Dermatol 2002; 19: 412–414.
Hashimoto K, Kanzaki T : Cutis laxa. Ultrastructural and biochemical studies. Arch Dermatol 1975; 111: 861–873.
Reisner SH, Seelenfreund M, Ben-Bassat M : Cutis laxa associated with severe intrauterine growth retardation and congenital dislocation of the hip. Acta Paediatr Scand 1971; 60: 357–360.
Beighton P : The dominant and recessive forms of cutis laxa. J Med Genet 1972; 9: 216–221.
Litzman J, Buckova H, Ventruba J, Holcikova A, Mikyska P, Lokaj J : A concurrent occurrence of cutis laxa, Dandy–Walker syndrome and immunodeficiency in a girl. Acta Paediatr 2003; 92: 861–864.
Biver A, De Rijcke S, Toppet V, Ledoux-Corbusier M, Van Maldergem L : Congenital cutis laxa with ligamentous laxity and delayed development, Dandy–Walker malformation and minor heart and osseous defects. Clin Genet 1994; 45: 318–322.
Van Maldergem L, Ogur G, Yuksel M : Facial anomalies in congenital cutis laxa with retarded growth and skeletal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet 1989; 32: 265.
Nakamura T, Lozano PR, Ikeda Y et al: Fibulin-5/DANCE is essential for elastogenesis in vivo. Nature 2002; 415: 171–175.
Kermane A, Tachfouti S, Lezrek M, Mohcine Z : Cutis laxa syndrome. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol 2004; 292: 5–8.
Tuysuz B, Arapoglu M, Ilikkan B, Demirkesen C, Perk Y : Congenital cutis laxa syndrome: type II autosomal recessive inheritance. Turk J Pediatr 2003; 45: 265–268.
Grünewald S, Matthijs G, Jaeken J : Congenital disorders of glycosylation: a review. Pediatr Res 2002; 52: 618–624.
Wopereis S, Grunewald S, Morava E et al: Apolipoprotein C-III isofocusing in the diagnosis of genetic defects in O-glycan biosynthesis. Clin Chem 2003; 49: 1839–1845.
Beltran-Valero de Bernabe D, Currier S, Steinbrecher A et al: Mutations in the O-mannosyltransferase gene POMT1 give rise to the severe neuronal migration disorder Walker–Warburg syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1033–1043.
Okajima T, Fukumoto S, Furukawa K, Urano T, Furukawa K : Molecular basis for the progeroid variant of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 2841–2844.
Wuyts W, Van Hul W : Molecular basis of multiple exostoses: mutations in the EXT1 and EXT2 genes. Hum Mutat 2000; 15: 220–227.
Topaz O, Shurman DL, Bergman R et al: Mutations in GALNT3, encoding a protein involved in O-linked glycosylation, cause familial tumoral calcinosis. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 579–581.
Van Eijk HG, van Noort WL : The analysis of human serum transferrins with the PhastSystem quantitation of microheterogeneity. Electrophoresis 1992; 13: 354–358.
Visconti RP, Barth JL, Keeley FW, Little CD : Codistribution analysis of elastin and related fibrillar proteins in early vertebrate development. Matrix Biol 2003; 22: 109–121.
Yanagisawa H, Davis EC, Starcher BC et al: Fibulin-5 is an elastin-binding protein essential for elastic fiber development in vivo. Nature 2002; 415: 168–171.
Argraves WS, Greene LM, Cooley MA, Gallagher WM : Fibulins: physiological and disease perspectives. EMBO Rep 2003; 4: 1127–1131.
Timpl R, Sasaki T, Kostka G, Chu ML : Fibulins: a versatile family of extracellular matrix proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003; 4: 479–489.
Hansen JE, Lund O, Engelbrecht J, Bohr H, Nielsen JO, Hansen JE : Prediction of O-glycosylation of mammalian proteins: specificity patterns of UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. Biochem J 1995; 308: 801–813.
Wopereis S, Morava E, Grunewald S et al: A combined defect in the biosynthesis of N- and O-glycans in patients with cutis laxa and neurological involvement: biochemical characteristics. Bioch Biophys Acta 2005; in press.
Wu X, Steet RA, Bohorov O et al: Mutation of the COG complex subunit gene COG7 causes a lethal congenital disorder. Nat Med 2004; 10: 518–523.
Acknowledgements
We thank Karin Huijben for the technical assistance and Dr Litzman for providing a serum sample of patient 4 for this study. The authors were supported by EUROGLYCANET 512131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morava, E., Wopereis, S., Coucke, P. et al. Defective protein glycosylation in patients with cutis laxa syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 13, 414–421 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201361
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201361
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetik der kortikalen Fehlbildungen
Medizinische Genetik (2018)
-
Clinical glycomics for the diagnosis of congenital disorders of glycosylation
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2018)
-
Polymicrogyria and myoclonic epilepsy in autosomal recessive cutis laxa type 2A
neurogenetics (2016)
-
Mass spectrometry of transferrin and apolipoprotein C-III for diagnosis and screening of congenital disorder of glycosylation
Glycoconjugate Journal (2016)
-
Glycosylation disorders of membrane trafficking
Glycoconjugate Journal (2013)