Abstract
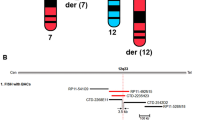
We report on a 2-year-old girl with situs ambiguus comprising right-sided stomach and spleen, left-sided liver and complex cardiac defect. Psychomotor development of this patient was normal, and no other major abnormalities were present. Chromosome analysis revealed a de novo balanced chromosome translocation t(X;1)(q26;p13.1). Molecular cytogenetic investigations identified a breakpoint spanning BAC clone on the X-chromosome containing the ZIC3 gene. Mutations in ZIC3 are associated with situs ambiguus and cardiac defects predominantly in males. This is the first report of a live born girl with an X-autosome translocation involving the ZIC3 region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Zhu L, Belmont JW, Ware SM : Genetics of human heterotaxias. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 17–25.
Gebbia M, Ferrero GB, Pilia G et al: X-linked situs abnormalities result from mutations in ZIC3. Nat Genet 1997; 17: 305–308.
Megarbane A, Salem N, Stephan E et al: X-linked transposition of the great arteries and incomplete penetrance among males with a nonsense mutation in ZIC3. Eur J Hum Genet 2000; 8: 704–708.
Ware SM, Peng J, Zhu L et al: Identification and functional analysis of ZIC3 mutations in heterotaxy and related congenital heart defects. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 93–105.
Ferrero GB, Gebbia M, Pilia G et al: A submicroscopic deletion in Xq26 associated with familial situs ambiguus. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 61: 395–401.
Casey B, Devoto M, Jones KL, Ballabio A : Mapping a gene for familial situs abnormalities to human chromosome Xq24−q27.1. Nat Genet 1993; 5: 403–407.
Fritz B, Kunz J, Knudsen GP et al: Situs ambiguus in a female foetus with balanced (X;21) translocation – evidence for functional nullisomy of the ZIC3 gene? Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: 34–40.
Wirth J, Nothwang HG, van der Maarel S et al: Systematic characterisation of disease associated balanced chromosome rearrangements by FISH: cytogenetically and genetically anchored YACs identify microdeletions and candidate regions for mental retardation genes. J Med Genet 1999; 36: 271–278.
Allen RC, Zoghbi HY, Moseley AB, Rosenblatt HM, Belmont JW : Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet 1992; 51: 1229–1239.
Schmidt M, Du Sart D : Functional disomies of the X chromosome influence the cell selection and hence the X inactivation pattern in females with balanced X-autosome translocations: a review of 122 cases. Am J Med Genet 1992; 42: 161–169.
Sharp AJ, Spotswood HT, Robinson DO, Turner BM, Jacobs PA : Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of the spreading of X inactivation in X; autosome translocations. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 3145–3156.
Acknowledgements
We thank the parents of the patient for their support and Petra Viertel, Hannelore Madle and Susanne Freier for technical assistance. We gratefully acknowledge support from the German National Genome Research Network (NGFN, project number 01GR0105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic database information
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/
Genome Browser, http://www.genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway
Whitehead Institute, http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/cgi-bin/contig/phys_map
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzschach, A., Hoeltzenbein, M., Hoffmann, K. et al. Heterotaxy and cardiac defect in a girl with chromosome translocation t(X;1)(q26;p13.1) and involvement of ZIC3. Eur J Hum Genet 14, 1317–1320 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201707
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201707