Abstract
Aim
To evaluate the effectiveness of anterior chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris with Botulinum toxin type A (Botox®) to induce temporary ptosis for corneal protection, and assess the incidence of superior rectus underaction.
Methods
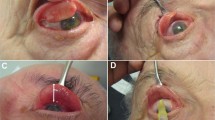
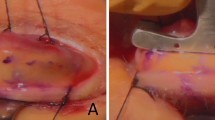
Prospective interventional case series. Patients with ocular surface pathology requiring temporary tarsorrhaphy underwent transcutaneous anterior chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris with Botox®. The onset and duration of ptosis, corneal healing, and superior rectus underaction was evaluated.
Results
Ten eyes of 10 patients underwent transcutaneous anterior chemodenervation of levator muscle. Five patients had Bells palsy with exposure keratopathy, four patients had persistent epithelial defect, and one had neurotrophic ulcer. The median age at presentation was 30 years. Median dose of Botulinum toxin injection was 12.5 U (range 10–15 U). The mean palpebral fissure height of 9 mm (SD±2.1 mm) before injection, reduced to 2.8 mm (SD±1.9 mm) at 1-week post-injection. More than 50% reduction in palpebral fissure height was seen in nine out of 10 eyes (90%, 95% CI 71.4–100%) at 1 week, seven of nine eyes (77.8%, 95% CI 50.6–100%) at 2 weeks, and two of nine eyes (22.2%, 95% CI 0–49.4%) at 4 weeks, and returned to pretreatment level after mean duration of 9.2 weeks (range 5–16 weeks). Superior rectus underaction was not noted in any of the patient (95% CI 0–30%). Corneal pathology improved in all cases.
Conclusion
Anterior chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris with Botulinum toxin type A (Botox®) induces significant temporary ptosis and aids in corneal healing. Anterior placement of the toxin injection may avoid superior rectus underaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adams GG, Kirkness CM, Lee JP . Botulinum toxin A induced protective ptosis. Eye 1987; 1 (Part 5): 603–608.
Kirkness CM, Adams GG, Dilly PN, Lee JP . Botulinum toxin A-induced protective ptosis in corneal disease. Ophthalmology 1988; 95 (4): 473–480.
Ellis MF, Daniell M . An evaluation of the safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin type A (BOTOX) when used to produce a protective ptosis. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2001; 29 (6): 394–399.
Wuebbolt GE, Drummond G . Temporary tarsorrhaphy induced with type A Botulinum toxin. Can J Ophthalmol 1991; 26: 383–385.
Smyth AG . Protective ptosis after parotid surgery induced with Botulinum toxin. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1995; 33: 107–109.
Magoon EH . Botulinum injection for treatment of blepharospasm, corneal exposure and entropion. J Ocul Ther Surg 1985; 4: 133–135.
Heyworth PL, Lee JP . Persisting hypotropias following protective ptosis induced by botulinum neurotoxin. Eye 1994; 8 (Part 5): 511–515.
Bron AJ, Tripathi RC, Tripathi BJ . The extraocular muscles and ocular movements. In: Bron AJ, Tripathi RC, Tripathi BJ (eds). Wolff's Anatomy of the Eye and Orbit, 8th edn. Chapman & Hall: London, 1997, pp 147–152.
Scott AB . Botulinum toxin treatment of strabismus. Focal points 1989: Clinical Modules for Ophthalmologists, Vol 7, Module 12. American Academy of Ophthalmology: San Francisco, 1989, pp 1–11.
Liu M, Lee HC, Hertle RW, Ho AC . Retinal detachment from inadvertent intraocular injection of botulinum toxin A. Am J Ophthalmol 2004; 137 (1): 201–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented in part at the 23rd Annual Meeting of the European Society of Ophthalmic plastics and Reconstructive Surgery, Greece, 15–17 September, 2005
Authors do not have any financial interest in the results presented. This research was funded by Hyderabad Eye Research Foundation, Hyderabad, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, M., Gangopadhyay, N., Fernandes, M. et al. Anterior chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris with botulinum toxin type-A (Botox®) to induce temporary ptosis for corneal protection. Eye 22, 1132–1136 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6702866
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6702866
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A modified transconjunctival technique for botulinum toxin chemodenervation of levator palpebrae superioris for corneal protection
Eye (2022)
-
Adverse Events Associated With Botox as Reported in a Food and Drug Administration Database
Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (2021)
-
Paralytic Lagophthalmos: Comprehensive Approach to Management
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports (2018)
-
Corneal Transplantation in the Setting of Neurotrophic Keratopathy—Risks and Considerations
Current Ophthalmology Reports (2017)
-
Botulinumtoxin bei okulären Folgen nach Fazialisparese
Der Ophthalmologe (2012)