Abstract
Aim:
Chinese medicine CGA formula consists of polysaccharide from Cordyceps sinensis mycelia (CS-PS), gypenosides and amygdalin, which is derived from Fuzheng Huayu (FZHY) capsule for treating liver fibrosis. In this study we attempted to confirm the therapeutic effects of CGA formula in dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rats, and to identify the mechanisms of anti-fibrotic actions.
Methods:
Rats were injected with DMN (10 mg·kg−1·d−1, ip) for 3 consecutive days per week over a 4-week period. The rats then were orally administered with CGA formula (CS-PS 60 mg·kg−1·d−1, gypenosides 50 mg·kg−1·d−1 and amygdalin 80 mg·kg−1·d−1) daily in the next 2 weeks. CS-PS, gypenosides or amygdalin alone were administered as individual component controls, whereas colchicine and FZHY were used as positive controls. Serum biomarkers were measured. Hepatic injury, collagen deposition and stellate cell activation were examined. The MMP activities, expression of TIMP protein and proteins involved in the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathways in liver tissues were assayed.
Results:
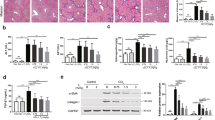
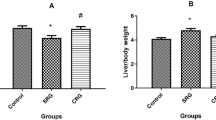
In DMN-treated rats, administration of CGA formula significantly decreased serum ALT, AST and total bilirubin and hepatic hydroxyproline levels, increased serum albumin level, and attenuated liver fibrosis as shown by histological examination. Furthermore, these effects were comparable to those caused by administration of FZHY, and superior to those caused by administration of colchicine or the individual components of CGA formula. Moreover, administration of CGA formula significantly decreased the protein levels of α-SMA, TGF-β1, TGF-β1 receptor (TβR-I), p-TβR-I, p-TβR-II, p-Smad2, p-Smad3, TIMP1 and TIMP2, as well as MMP2 and MMP9 activities in liver tissues of DMN-treated rats.
Conclusion:
Chinese medicine CGA formula ameliorates DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rats, and this effect was likely associated with the down-regulation of MMP2/9 activities, TIMP1/2 protein expression and the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathways in the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Cohen-Naftaly M, Friedman SL . Current status of novel antifibrotic therapies in patients with chronic liver disease. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2011; 4: 391–417.
Lee YA, Wallace MC, Friedman SL . Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: a translational success story. Gut 2015; 64: 830–41.
Friedman SL . Liver fibrosis — from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 2003; 38: S38–53.
Wallace MC, Friedman SL, Mann DA . Emerging and disease-specific mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Semin Liver Dis 2015; 35: 107–18.
Arthur MJ, Fibrogenesis II . Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000; 279: G245–9.
Liu C, Hu Y, Xu L, Liu P . Effect of Fuzheng Huayu formula and its actions against liver fibrosis. Chin Med 2009; 4: 12.
Liu P, Hu YY, Liu C, Xu LM, Liu CH, Sun KW, et al. Multicenter clinical study on Fuzhenghuayu capsule against liver fibrosis due to chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11: 2892–9.
Hassanein T, Box TD, Tong MJ, Pozza R, Lorenzo O, Jeffrey G, et al. A Phase II, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multi-center study to assess the antifibrotic activity of Fuzheng Huayu in chronic hepatitis C patients with hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2014; 146: S261.
Li XM, Hu YY, Duan XH . Uniform designed research on the active ingredients assembling of Chinese medicine prescription for anti-liver fibrosis. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2010; 30: 58–63.
Chen L, Feng Q, Peng JH, Liu L, Liang CG, Hai YM, et al. Effect of CKJ recipe containing serum on activation of rat primary hepatic stellate cells, TGF-beta1 and its receptors. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2015; 35: 210–5.
Chen JC, Tsai CC, Chen LD, Chen HH, Wang WC . Therapeutic effect of gypenoside on chronic liver injury and fibrosis induced by CCl4 in rats. Am J Chin Med 2000; 28: 175–85.
Zhou JH, Yumo W, editors. Chinese Medicine Pharmacology. Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, Shanghai, China; 1986.
Peng J, Li X, Feng Q, Chen L, Xu L, Hu Y . Anti-fibrotic effect of Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide: Inhibiting HSC activation, TGF-beta1/Smad signalling, MMPs and TIMPs. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2013; 238: 668–77.
Bodenheimer H Jr, Schaffner F, Pezzullo J . Evaluation of colchicine therapy in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1988; 95: 124–9.
Kershenobich D, Vargas F, Garcia-Tsao G, Perez Tamayo R, Gent M, Rojkind M . Colchicine in the treatment of cirrhosis of the liver. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1709–13.
Saha SK, Brewer CF . Determination of the concentrations of oligosaccharides, complex type carbohydrates, and glycoproteins using the phenol-sulfuric acid method. Carbohydr Res 1994; 254: 157–67.
Ala-Kokko L, Pihlajaniemi T, Myers JC, Kivirikko KI, Savolainen ER . Gene expression of type I, III and IV collagens in hepatic fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine in the rat. Biochem J 1987; 244: 75–9.
Scheuer PJ . Classification of chronic viral hepatitis: a need for reassessment. J Hepatol 1991; 13: 372–4.
Mu Y, Liu P, Du G, Du J, Wang G, Long A, et al. Action mechanism of Yi Guan Jian Decoction on CCl4 induced cirrhosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 121: 35–42.
Peng JH, Hu YY, Cheng Y, Han C, Xu LL, Feng Q, et al. Effect of Jianpi Huoxue decoction on inflammatory cytokine secretion pathway in rat liver with lipopolysaccharide challenge. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14: 1851–7.
Kleiner DE, Stetler-Stevenson WG . Quantitative zymography: detection of picogram quantities of gelatinases. Anal Biochem 1994; 218: 325–9.
Friedman SL . Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 2008; 88: 125–72.
Inagaki Y, Okazaki I . Emerging insights into transforming growth factor beta Smad signal in hepatic fibrogenesis. Gut 2007; 56: 284–92.
Jenkins SA, Grandison A, Baxter JN, Day DW, Taylor I, Shields R . A dimethylnitrosamine-induced model of cirrhosis and portal hypertension in the rat. J Hepatol 1985; 1: 489–99.
Li D, Friedman SL . Liver fibrogenesis and the role of hepatic stellate cells: new insights and prospects for therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1999; 14: 618–33.
Friedman SL . Mechanisms of disease: Mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and therapeutic implications. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 1: 98–105.
Friedman SL . Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008; 134: 1655–69.
Bachem MG, Melchior R, Gressner AM . The role of thrombocytes in liver fibrogenesis: effects of platelet lysate and thrombocyte-derived growth factors on the mitogenic activity and glycosaminoglycan synthesis of cultured rat liver fat storing cells. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1989; 27: 555–65.
Bilzer M, Roggel F, Gerbes AL . Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int 2006; 26: 1175–86.
Ghiassi-Nejad Z, Friedman SL . Advances in antifibrotic therapy. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 2: 803–16.
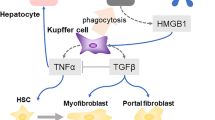
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R . Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med 2006; 10: 76–99.
Gressner AM . Cytokines and cellular crosstalk involved in the activation of fat-storing cells. J Hepatol 1995; 22: 28–36.
Bissell DM, Wang SS, Jarnagin WR, Roll FJ . Cell-specific expression of transforming growth factor-beta in rat liver. Evidence for autocrine regulation of hepatocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 447–55.
Shi Y, Massague J . Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 2003; 113: 685–700.
Piek E, Heldin CH, Ten Dijke P . Specificity, diversity, and regulation in TGF-beta superfamily signaling. FASEB J 1999; 13: 2105–24.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (2012ZX09103-201-048); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81303071); and the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (ZY3-RCPY-2-2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary information is available at the Acta Pharmacologica Sinica's website.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information Figure S1
Generic name and chemical structure of Amygdalin. (DOC 77 kb)
Supplementary Information Figure S2
HPLC chromatograms of gypenosides and the standard compounds. (DOC 81 kb)
Supplementary Information Figure S3
Standard curve of total carbohydrate content determined by phenol-sulfuric acid method. (DOC 35 kb)
Supplementary Information Figure S4
Chemical components of CS-PS (bottom image) and standard (above image, ribose, arabinose, xylose, mannose, glucose, galactose) analyzed by gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) (TRACE-DSQ, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., FL, USA). (DOC 50 kb)
Supplementary Information Figure S5
Semi-quantitation of α-SMA positive area in the immunohistochemical staining sections. (DOC 139 kb)
Supplementary Information Table S1
HPLC mobile phase gradient (DOC 33 kb)
Supplementary Information Table S2
The procedure of reagents admixture in phenol-sulfuric acid method (DOC 34 kb)
Supplementary Information Table S3
Hepatic Hyp in the dosage-effect response test (DOC 34 kb)
Supplementary Information Table S4
Serum ALT, AST and Alb in the dosage-effect response test (DOC 36 kb)
Supplementary Information Table S5
Hepatic fibrosis grading in the dosage-effect response test (DOC 37 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xm., Peng, Jh., Sun, Zl. et al. Chinese medicine CGA formula ameliorates DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rats via inhibiting MMP2/9, TIMP1/2 and the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37, 783–793 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.35
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.35
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelial cells by a retinoic acid receptor-α agonist
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A metabolic mechanism analysis of Fuzheng-Huayu formula for improving liver cirrhosis with traditional Chinese medicine syndromes
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)