Abstract
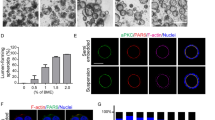
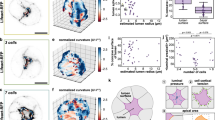
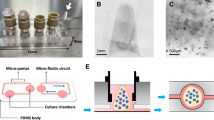
There are two predominant theories for lumen formation in tissue morphogenesis: cavitation driven by cell death, and membrane separation driven by epithelial polarity. To define the mechanism of lumen formation in prostate acini, we examined both theories in several cell lines grown in three-dimensional (3D) Matrigel culture. Lumen formation occurred early in culture and preceded the expression of cell death markers for apoptosis (active caspase 3) and autophagy (LC-3). Active caspase 3 was expressed by very few cells and inhibition of apoptosis did not suppress lumen formation. Despite LC-3 expression in all cells within a spheroid, this was not associated with cell death. However, expression of a prostate-secretory protein coincided with lumen formation and subsequent disruption of polarized fluid movement led to significant inhibition of lumen formation. This work indicates that lumen formation is driven by the polarized movement of fluids and proteins in 3D prostate epithelial models and not by cavitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- 3D:
-
three dimensional
- PSA:
-
prostate-specific antigen
References
Zegers MMP, O'Brien LE, Yu W, Datta A, Mostov KE . Epithelial polarity and tubulogenesis in vitro. Trends Cell Biol 2003; 13: 169–176.
O'Brien LE, Zegers MMP, Mostov KE . Building epithelial architecture: insights from three-dimensional culture models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002; 3: 531–537.
Kroschewski R . Molecular mechanisms of epithelial polarity: about shapes, forces, and orientation problems. News Physiol Sci 2004; 19: 61–66.
Bagnat M, Cheung ID, Mostov KE, Stainier DYR . Genetic control of single lumen formation in the zebrafish gut. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 954–960.
Houghton FD, Humpherson PG, Hawkhead JA, Hall CJ, Leese HJ . Na+, K+, ATPase activity in the human and bovine preimplantation embryo. Dev Biol 2003; 263: 360–366.
Schmiechel KL, Bissell MJ . Modeling tissue-specific signaling and organ function in three dimensions. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 2377–2388.
Mills Shaw KR, Wrobel CN, Brugge JS . Use of three-dimensional basement membrane cultures to model oncogene-induced changes in mammary epithelial morphogenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2004; 9: 297–310.
Debnath J, Mills K, Collins N, Reginato M, Muthuswamy S, Brugge J . The role of apoptosis in creating and maintaining luminal space within normal and oncogene-expressing mammary acini. Cell 2002; 111: 29–40.
Mailleux AA, Overholtzer M, Schmelzle T, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Brugge J . BIM regulates apoptosis during mammary ductal morphogenesis, and its absence reveals alternative cell death mechanisms. Dev Cell 2007; 12: 221–234.
Coucouvanis E, Martin GR . Signals for death and survival: a two-step mechanism for cavitation in the vertebrate embryo. Cell 1995; 83: 279–287..
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S . Another way to die: autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 1528–1534.
Qu X, Zou Z, Sun Q, Luby-Phelps K, Cheng P, Hogan RN et al. Autophagy gene-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells during embryonic development. Cell 2007; 128: 931–946.
Lang SH, Sharrard RM, Stark M, Villette JM, Maitland NJ . Prostate epithelial cell lines form spheroids with evidence of glandular differentiation in three-dimensional Matrigel cultures. Br J Cancer 2001; 85: 590–599.
Lang SH, Smith J, Hyde C, Macintosh C, Stower M, Maitland NJ . Differentiation of prostate epithelial cell cultures by Matrigel/stromal reconstruction.. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2006; 42: 273–280.
Martín-Belmonte F, Yu W, Rodríguez-Fraticelli AE, Ewald A, Werb Z, Alonso MA et al. Cell-polarity dynamics controls the mechanism of lumen formation in epithelial morphogenesis. Curr Biol 2008; 18: 507–513.
Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelivere S, Bissell M, Brugge JS . ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 785–792.
Lang SH, Stark M, Collins A, Paul AB, Stower MJ, Maitland NJ . Experimental prostate epithelial morphogenesis in response to stroma and three-dimensional Matrigel culture. Cell Growth Differ 2001; 12: 631–640.
Tyson DR, Inokuchi J, Tsunoda T, Lau A, Ornstein DK . Culture requirements of prostatic epithelial cell lines for acinar morphogenesis and lumen formation in vitro: role of extracellular calcium. Prostate 2007; 67: 1601–1613.
Schenk DB, Leffert HL . Monoclonal antibodies to rat Na+, K+-ATPase block enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1983; 80: 5281–5285.
Nejsum LN, Nelson WJ . A molecular mechanism directly linking E-cadherin adhesion to initiation of epithelial cell surface polarity. J Cell Biol 2007; 178: 323–335.
Cohen D, Tian Y, Müsch A . Par1b promotes hepatic-type lumen polarity in MDCK cells via myosin II and E-cadherin-dependent signaling. Mol Biol Cell 2007; 18: 2203–2215.
Bello-DeOcampo D, Kleinman HK, Deocampo ND, Webber MM . Laminin-1 and α6β1 integrin regulate acinar morphogenesis of normal and malignant human prostate epithelial cells. Prostate 2001; 46: 142–153.
Gudjonsson T, Rønnov-Jessen L, Villadsen R, Rank F, Bissell MJ, Petersen OW . Normal and tumor-derived myoepithelial cells differ in their ability to interact with luminal breast epithelial cells for polarity and basement membrane deposition. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: 39–50.
Weaver V, Lelièvre S, Lakins J, Chrenek M, Jones J, Giancotti F et al. 4 integrin-dependent formation of polarized three-dimensional architecture confers resistance to apoptosis in normal and malignant mammary epithelium. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 205–216.
Wodarz A . Molecular control of cell polarity and asymmetric cell division in Drosophila neuroblasts. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2005; 17: 475–481.
Wodarz A, Näthke I . Cell polarity in development and cancer. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 1016–1024.
Kirshner J, Chen CJ, Liu P, Huang J, Shively JE . CEACAM1-4S, a cell-cell adhesion molecule, mediates apoptosis and reverts mammary carcinoma cells to a normal morphogenic phenotype in a 3D culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 521–526.
Abud HE . Shaping developing tissues by apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2004; 11: 797–799.
Yokoyama S, Chen C-J, Nguyen T, Shively JE . Role of CEACAM1 isoforms in an in vivo model of mammary morphogenesis: mutational analysis of the cytoplasmic domain of CEACAM1-4S reveals key residues involved in lumen formation. Oncogene 2007; 26: 7637–7646.
Tawk M, Araya C, Lyons DA, Reugels AM, Girdler GC, Bayley PR et al. A mirror-symmetric cell division that orchestrates neuroepithelial morphogenesis. Nature 2007; 446: 797–800.
Devine WP, Lubarsky B, Shaw K, Luschnig S, Messina L, Krasnow MA . Requirement for chitin biosynthesis in epithelial tube morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 17014–17019.
Husain N, Pellikka M, Hong H, Klimentova T, Choe K, Clandinin TR et al. The agrin/perlecan-related protein eyes shut is essential for epithelial lumen formation in the Drosophila retina. Dev Cell 2006; 11: 483–493.
Debnath J, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS . Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods 2003; 30: 256–268.
Castino R, Lazzeri G, Lenzi P, Bellio N, Follo C, Ferrucci M et al. Suppression of autophagy precipitates neuronal cell death following low doses of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 2008; 106: 1426–1439 (doi: 10.1111/j.1471–4159.2008.05488).
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Norman Maitland for his generous support of the project and provision of Laboratory space. Many thanks to M Stower for providing prostate tissue samples. We also thank the members of the Yorkshire Cancer Research laboratory for their useful discussions and technical help. We are grateful to Dr. Anne Collins for her comments on the paper. This study was supported by the Wellcome Trust (GR076612MA), BBSRC (BB/E021409/1) and Yorkshire Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by D Vaux Best
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pearson, J., Hughes, S., Chambers, K. et al. Polarized fluid movement and not cell death, creates luminal spaces in adult prostate epithelium. Cell Death Differ 16, 475–482 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.181
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.181
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
DNA hypermethylation in prostate cancer is a consequence of aberrant epithelial differentiation and hyperproliferation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)
-
An integrin–ILK–microtubule network orients cell polarity and lumen formation in glandular epithelium
Nature Cell Biology (2013)
-
Stromal upregulation of lateral epithelial adhesions: Gene expression analysis of signalling pathways in prostate epithelium
Journal of Biomedical Science (2011)