Abstract
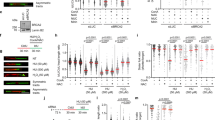
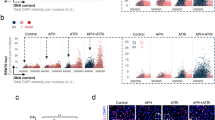
Checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) responds to disruption of DNA replication to maintain the integrity of stalled forks, promote homologous recombination-mediated repair of replication fork lesions, and control inappropriate firing of replication origins. This response is essential for viability as replication inhibitors trigger apoptosis in S-phase cells depleted of Chk1. Given the complex network of cellular responses controlled by Chk1, our aim was to determine which of these protect cells from apoptosis following replication stress. Work with cell-free systems has shown that RPA–ssDNA complex forms following replication inhibition through the uncoupling of replication and helicase complexes. Here we show that replication protein A (RPA) foci form in cells treated with replication inhibitors and that the number of foci dramatically increases together with hyperphosphorylation of RPA34 in Chk1-depleted cells in advance of the induction of apoptosis. RPA foci, RPA34 hyperphosphorylation, and apoptosis were suppressed by siRNA-mediated knockdown of Cdc45, an essential replication helicase cofactor required for both the initiation and elongation steps of DNA replication. In contrast, loss of p21, a negative effector of origin firing, stimulates both the accumulation of RPA foci and apoptosis. Taken together, these results suggest that the loss of control of replication origin firing following Chk1 depletion triggers the accumulation of the RPA–ssDNA complex and apoptosis when replication is blocked.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ATM:
-
Ataxia–Telangiectasia Mutated
- ATR:
-
ATM and Rad3 related
- Chk1:
-
checkpoint kinase 1
- DSB:
-
double strand break
- HR:
-
homologous recombination
- HU:
-
hydroxyurea
- MMR:
-
mismatch repair
- RPA:
-
replication protein A
- siRNA:
-
specific interfering RNA
- ssDNA:
-
single-stranded DNA
References
Zhou B-BS, Elledge SJ . The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature 2000; 408: 433–439.
Kastan MB, Bartek J . Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 2004; 432: 316–323.
Ward IM, Minn K, Chen J . UV-induced ataxia–telangiectasia-mutated and Rad3-related (ATR) activation requires replication stress. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 9677–9680.
Cliby WA, Roberts CJ, Cimprich KA, Stringer CM, Lamb JR, Schreiber SL et al. Overexpression of a kinase-inactive ATR protein causes sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents and defects in cell cycle checkpoints. EMBO J 1998; 17: 159–169.
Brown EJ, Baltimore D . Essential and dispensable roles of ATR in cell cycle arrest and genome maintenance. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 615–628.
Zachos G, Rainey MD, Gillespie DA . Chk1-deficient tumour cells are viable but exhibit multiple checkpoint and survival defects. EMBO J 2003; 22: 713–723.
Byun TS, Pacek M, Yee MC, Walter JC, Cimprich KA . Functional uncoupling of MCM helicase and DNA polymerase activities activates the ATR-dependent checkpoint. Genes Dev 2005; 19: 1040–1052.
Zou L, Elledge SJ . Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA–ssDNA complexes. Science 2003; 300: 1542–1548.
Ball HL, Myers JS, Cortez D . ATRIP binding to replication protein A–single-stranded DNA promotes ATR–ATRIP localization but is dispensible for Chk1 phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 2005; 16: 2372–2381.
Feijoo C, Hall-Jackson C, Wu R, Jenkins D, Leitch J, Gilbert DM et al. Activation of mammalian Chk1 during DNA replication arrest: a role for Chk1 in the intra-S phase checkpoint monitoring replication origin firing. J Cell Biol 2001; 154: 913–923.
Nghiem P, Park PK, Kim Y, Vaziri C, Schreiber SL . ATR inhibition selectively sensitizes G1 checkpoint-deficient cells to lethal premature chromatin condensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 9092–9097.
Maya-Mendoza A, Petermann E, Gillespie DA, Caldecott KW, Jackson DA . Chk1 regulates the density of active replication origins during the vertebrate S phase. EMBO J 2007; 26: 2719–2731.
Sorensen CS, Hansen LT, Dziegielewski J, Syljuasen RG, Lundin C, Bartek J et al. The cell-cycle checkpoint kinase Chk1 is required for mammalian homologous recombination repair. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 195–201.
Cho SH, Toouli CD, Fujii GH, Crain C, Parry D . Chk1 is essential for tumor cell viability following activation of the replication checkpoint. Cell Cycle 2005; 4: 131–139.
Xiao Z, Xue J, Sowin TJ, Rosenberg SH, Zhang H . A novel mechanism of checkpoint abrogation conferred by Chk1 downregulation. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1403–1411.
Rodriguez R, Meuth M . Chk1 and p21 cooperate to prevent apoptosis during DNA replication fork stress. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 402–412.
Johnson RD, Liu N, Jasin M . Mammalian XRCC2 promotes the repair of double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. Nature 1999; 401: 397–399.
Hinz JM, Helleday T, Meuth M . Reduced apoptotic response to camptothecin in CHO cells deficient in XRCC3. Carcinogenesis 2003; 24: 249–253.
Li J, Stern DF . DNA damage regulates Chk2 association with chromatin. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 37948–37956.
Lundin C, Erixon K, Arnaudeau C, Schultz N, Jenssen D, Meuth M et al. Different roles for nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination following replication arrest in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 5869–5878.
Bolderson E, Scorah J, Helleday T, Smythe C, Meuth M . ATM is required for the cellular response to thymidine induced replication fork stress. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 2937–2945.
Zou L, Mitchell J, Stillman B . CDC45, a novel yeast gene that functions with the origin recognition complex and Mcm proteins in initiation of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 553–563.
Pacek M, Walter JC . A requirement for MCM7 and Cdc45 in chromosome unwinding during eukaryotic DNA replication. EMBO J 2004; 23: 3667–3676.
Pacek M, Tutter AV, Kubota Y, Takisawa H, Walter JC . Localization of the MCM2-7, Cdc45, and GINS to the site of DNA unwinding during eukaryotic DNA replication. Mol Cell 2006; 21: 581–587.
Wang X, Ira G, Tercero JA, Holmes AM, Diffley JF, Haber JE . Role of DNA replication proteins in double-strand break-induced recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 6891–6899.
Syljuasen RG, Sorensen CS, Hansen LT, Fugger K, Lundin C, Johansson F et al. Inhibition of human Chk1 causes increased initiation of DNA replication, phosphorylation of ATR targets, and DNA breakage. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 3553–3562.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM et al. WAF1, publisher: a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993; 75: 817–825.
Meuth M . The molecular basis of mutations induced by deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate pool imbalances in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res 1989; 181: 305–316.
Zou Y, Liu Y, Wu X, Shell SM . Functions of human replication protein A (RPA): from DNA replication to DNA damage and stress responses. J Cell Physiol 2006; 208: 267–273.
Dodson GE, Shi Y, Tibbetts RS . DNA replication defects, spontaneous DNA damage, and ATM-dependent checkpoint activation in replication protein A deficient cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 34010–34014.
Takai H, Tominaga K, Motoyama N, Minamishima YA, Nagahama H, Tsukiyama T et al. Aberrant cell cycle checkpoint function and early embryonic death in Chk1−/− mice. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1439–1447.
Niida H, Tsuge S, Katsuno Y, Konishi A, Takeda N, Nakanishi M . Depletion of Chk1 leads to premature activation of Cdc2–cyclinB and mitotic catastrophe. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 39246–39252.
Hong Y, Stambrook PJ . Restoration of an absent G1 arrest and protection from apoptosis in embryonic stem cells after ionizing radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 14443–14448.
Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K et al. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature 2005; 434: 864–870.
Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV, Karakaidos P, Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T et al. Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature 2005; 434: 907–913.
Chimploy K, Tassotto ML, Mathews CK . Ribonucleotide reductase, a possible agent in deoxyribonucleotide pool asymmetries induced by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 39267–39271.
Hammond EM, Dorie MJ, Giaccia AJ . ATR/ATM targets are phosphorylated by ATR in response to hypoxia and ATM in response to reoxygenation. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 12207–12213.
Mohindra A, Hays LE, Phillips EN, Preston BD, Helleday T, Meuth M . Defects in homologous recombination repair in mismatch-repair-deficient tumour cell lines. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 2189–2200.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Helen Bryant, Cyril Sanders, and Kirsteen Maclean for their comments concerning the paper. This work was supported by a programme grant from Yorkshire Cancer Research to MM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by S Kornbluth
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodriguez, R., Gagou, M. & Meuth, M. Apoptosis induced by replication inhibitors in Chk1-depleted cells is dependent upon the helicase cofactor Cdc45. Cell Death Differ 15, 889–898 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
UQCRFS1 serves as a prognostic biomarker and promotes the progression of ovarian cancer
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals potential mechanisms underlying differential heart development in fast- and slow-growing broilers under heat stress
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
Apoptosis and failure of checkpoint kinase 1 activation in human induced pluripotent stem cells under replication stress
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2016)
-
Aldh1 Expression and Activity Increase During Tumor Evolution in Sarcoma Cancer Stem Cell Populations
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Enhancement of hypoxia-activated prodrug TH-302 anti-tumor activity by Chk1 inhibition
BMC Cancer (2015)