Abstract
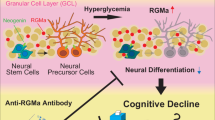
The repulsive guidance molecule (RGM) is a membrane-bound protein that has diverse functions in the developing central nervous system. Identification of neogenin as a receptor for RGM provided evidence of its cell death-inducing activity in the absence of RGM. Here, we show that the serine/threonine kinase death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) is involved in the signal transduction of neogenin. Neogenin interacts with DAPK and reduces DAPK autophosphorylation on Ser308 in vitro. Neogenin-induced cell death is abolished in the presence of RGM or by blocking DAPK. Although neogenin overexpression or RGM downregulation in the chick neural tube in vivo induces apoptosis, coexpression of the dominant-negative mutant or small-interference RNA of DAPK attenuates this proapoptotic activity. Thus, RGM/neogenin regulates cell fate by controlling the DAPK activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- RGM:
-
repulsive guidance molecule
- CNS:
-
central nervous system
- DAPK:
-
death-associated protein kinase
- DCC:
-
deleted in colorectal cancer
- siRNA:
-
small-interference RNA
- TUNEL:
-
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
- CaM:
-
calmodulin
- ICD:
-
intracellular domain
- HEK:
-
human embryonic kidney
- CGN:
-
cerebellar granule neuron
- HH:
-
Hamburger Hamilton
- MLC:
-
myosin light chain
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- PFA:
-
paraformaldehyde
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- DAPI:
-
4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole
References
Stahl B, Muller B, von Boxberg Y, Cox EC, Bonhoeffer F . Biochemical characterization of a putative axonal guidance molecule of the chick visual system. Neuron 1990; 5: 735–743.
Monnier PP, Sierra A, Macchi P, Deitinghoff L, Andersen JS, Mann M et al. RGM is a repulsive guidance molecule for retinal axons. Nature 2002; 419: 392–395.
Matsunaga E, Chedotal A . Repulsive guidance molecule/neogenin: a novel ligand-receptor system playing multiple roles in neural development. Dev Growth Differ 2004; 46: 481–486.
Mueller BK, Yamashita T, Schaffar G, Mueller R . The role of repulsive guidance molecules in the embryonic and adult vertebrate central nervous system. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2006; 361: 1513–1529.
Rajagopalan S, Deitinghoff L, Davis D, Conrad S, Skutella T, Chedotal A et al. Neogenin mediates the action of repulsive guidance molecule. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 756–762.
Vielmetter J, Kayyem JF, Roman JM, Dreyer WJ . Neogenin, an avian cell surface protein expressed during terminal neuronal differentiation, is closely related to the human tumor suppressor molecule deleted in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biol 1994; 127: 2009–2020.
Wilson NH, Key B . Neogenin interacts with RGMa and netrin-1 to guide axons within the embryonic vertebrate forebrain. Dev Biol 2006; 296: 485–498.
Matsunaga E, Nakamura H, Chedotal A . Repulsive guidance molecule plays multiple roles in neuronal differentiation and axon guidance. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 6082–6088.
Fitzgerald DP, Cole SJ, Hammond A, Seaman C, Cooper HM . Characterization of neogenin-expressing neural progenitor populations and migrating neuroblasts in the embryonic mouse forebrain. Neuroscience 2006; 142: 703–716.
Matsunaga E, Tauszig-Delamasure S, Monnier PP, Mueller BK, Strittmatter SM, Mehlen P et al. RGM and its receptor neogenin regulate neuronal survival. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 749–755.
Bredesen DE, Mehlen P, Rabizadeh S . Apoptosis and dependence receptors: a molecular basis for cellular addiction. Physiol Rev 2004; 84: 411–430.
Mehlen P, Fearon ER . Role of the dependence receptor DCC in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 3420–3428.
Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O, Kimchi A . Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev 1995; 9: 15–30.
Cohen O, Inbal B, Kissil JL, Raveh T, Berissi H, Spivak-Kroizaman T et al. DAP-kinase participates in TNF-alpha- and Fas-induced apoptosis and its function requires the death domain. J Cell Biol 1999; 146: 141–148.
Jang CW, Chen CH, Chen CC, Chen JY, Su YH, Chen RH . TGF-beta induces apoptosis through Smad-mediated expression of DAP-kinase. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: 51–58.
Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Yao CC, Chen RH . DAP-kinase induces apoptosis by suppressing integrin activity and disrupting matrix survival signals. J Cell Biol 2002; 159: 169–179.
Cohen O, Feinstein E, Kimchi A . DAP-kinase is a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent, cytoskeletal-associated protein kinase, with cell death-inducing functions that depend on its catalytic activity. EMBO J 1997; 16: 998–1008.
Zhu XJ, Wang CZ, Dai PG, Xie Y, Song NN, Liu Y et al. Myosin X regulates netrin receptors and functions in axonal path-finding. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 184–192.
Shohat G, Spivak-Kroizman T, Cohen O, Bialik S, Shani G, Berrisi H et al. The pro-apoptotic function of death-associated protein kinase is controlled by a unique inhibitory autophosphorylation-based mechanism. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 47460–47467.
Llambi F, Lourenco FC, Gozuacik D, Guix C, Pays L, Del Rio G et al. The dependence receptor UNC5H2 mediates apoptosis through DAP-kinase. EMBO J 2005; 24: 1192–1201.
Green DR, Reed JC . Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 1998; 281: 1309–1312.
Ren XR, Ming GL, Xie Y, Hong Y, Sun DM, Zhao ZQ et al. Focal adhesion kinase in netrin-1 signaling. Nat Neurosci 2004; 7: 1204–1212.
Williams ME, Strickland P, Watanabe K, Hinck L . UNC5H1 induces apoptosis via its juxtamembrane region through an interaction with NRAGE. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 17483–17490.
Tassew NG, Chestopolava L, Beecroft R, Matsunaga E, Teng H, Chedotal A et al. Intraretinal RGMa is involved in retino-tectal mapping. Mol Cell Neurosci 2008; 37: 761–769.
Niederkofler V, Salie R, Sigrist M, Arber S . Repulsive guidance molecule (RGM) gene function is required for neural tube closure but not retinal topography in the mouse visual system. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 808–818.
Schwab JM, Conrad S, Monnier PP, Julien S, Mueller BK, Schluesener HJ . Spinal cord injury-induced lesional expression of the repulsive guidance molecule (RGM). Eur J Neurosci 2005; 21: 1569–1576.
Schwab JM, Monnier PP, Schluesener HJ, Conrad S, Beschorner R, Chen L et al. Central nervous system injury-induced repulsive guidance molecule expression in the adult human brain. Arch Neurol 2005; 62: 1561–1568.
Hata K, Fujitani M, Yasuda Y, Doya H, Saito T, Yamagishi S et al. RGMa inhibition promotes axonal growth and recovery after spinal cord injury. J Cell Biol 2006; 173: 47–58.
Kuo JC, Wang WJ, Yao CC, Wu PR, Chen RH . The tumor suppressor DAPK inhibits cell motility by blocking the integrin-mediated polarity pathway. J Cell Biol 2006; 172: 619–631.
Bialik S, Bresnick AR, Kimchi A . DAP-kinase-mediated morphological changes are localization dependent and involve myosin-II phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ 2004; 11: 631–644.
Mueller BK, Mack H, Teusch N . Rho kinase, a promising drug target for neurological disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2005; 4: 387–398.
Velentza AV, Schumacher AM, Watterson DM . Structure, activity, regulation, and inhibitor discovery for a protein kinase associated with apoptosis and neuronal death. Pharmacol Ther 2002; 93: 217–224.
Zhang AS, West Jr AP, Wyman AE, Bjorkman PJ, Enns CA . Interaction of hemojuvelin with neogenin results in iron accumulation in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 33885–33894.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Research Grant from the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (05-12) and Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (S) from JSPS. We thank Tetsuichiro Saito and Yuko Muroyama for technical guidance for in ovo electroporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by L Greene
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, Y., Taniguchi, J., Uchikawa, M. et al. Neogenin regulates neuronal survival through DAP kinase. Cell Death Differ 15, 1593–1608 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.92
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.92
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Death-associated protein kinase 1 phosphorylates NDRG2 and induces neuronal cell death
Cell Death & Differentiation (2017)
-
Role of DAPK in neuronal cell death
Apoptosis (2014)
-
DAPK activates MARK1/2 to regulate microtubule assembly, neuronal differentiation, and tau toxicity
Cell Death & Differentiation (2011)
-
Dependence receptors: a new paradigm in cell signaling and cancer therapy
Oncogene (2010)