Abstract
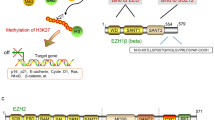
Deregulation of the pRB/E2F pathway, which occurs frequently in human malignancy, is often associated with inappropriate proliferation and/or apoptosis. While the role of E2F1 in apoptosis induction has been well-established, it remains unclear how this pro-apoptotic activity is regulated in cancer. Here we describe EZH2, an oncogenic polycomb histone methyltransferase and an E2F1 target, as an important regulator of E2F1-dependent apoptosis. We show that E2F1 induces EZH2 expression, which in turn antagonizes the induction of E2F1 pro-apoptotic target Bim expression. RNAi-mediated gene depletion of EZH2 enhances E2F1-dependent Bim expression, thereby promoting the pro-apoptotic activity of E2F1. Hence, the concomitant induction of EZH2 and Bim by E2F1 constitutes a fail-safe mechanism to allow tumor cells with aberrant E2F1 activity to evade apoptosis. These findings reveal a novel mechanism by which the apoptotic activity of E2F1 is restrained in human cancer and also provide the first evidence that EZH2 directly regulates apoptotic process in cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- APAF1:
-
apoptosis protease-activating factor 1
- ARF:
-
alternative reading frame
- BH3:
-
BCL-2 homology 3
- EZH2:
-
enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- HDAC:
-
histone deacetylase
- MDM2:
-
human homolog of mouse double minute 2
- MCL-1:
-
myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein 1
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinoditol-3-kinase
- PRC2:
-
polycomb repressive complex 2
References
Iaquinta PJ, Lees JA . Life and death decisions by the E2F transcription factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2007; 19: 649–657.
Polager S, Ginsberg D . E2F—at the crossroads of life and death. Trends Cell Biol 2008; 18: 528–535.
Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL et al. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 1998; 395: 124–125.
Irwin M, Marin MC, Phillips AC, Seelan RS, Smith DI, Liu W et al. Role for the p53 homologue p73 in E2F-1-induced apoptosis. Nature 2000; 407: 645–648.
Stiewe T, Putzer BM . Role of the p53-homologue p73 in E2F1-induced apoptosis. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 464–469.
Moroni MC, Hickman ES, Lazzerini Denchi E, Caprara G, Colli E, Cecconi F et al. Apaf-1 is a transcriptional target for E2F and p53. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 552–558.
Hershko T, Ginsberg D . Up-regulation of Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3)-only proteins by E2F1 mediates apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 8627–8634.
Zhao Y, Tan J, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Liu ET, Yu Q . Inhibitors of histone deacetylases target the Rb-E2F1 pathway for apoptosis induction through activation of proapoptotic protein Bim. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 16090–16095.
Hallstrom TC, Mori S, Nevins JR . An E2F1-Dependent Gene Expression Program that Determines the Balance between Proliferation and Cell Death. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 11–22.
Hallstrom TC, Nevins JR . Specificity in the activation and control of transcription factor E2F-dependent apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 10848–10853.
Loughran O, La Thangue NB . Apoptotic and growth-promoting activity of E2F modulated by MDM2. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 2186–2197.
Kitagawa M, Aonuma M, Lee SH, Fukutake S, McCormick F . E2F-1 transcriptional activity is a critical determinant of Mdm2 antagonist-induced apoptosis in human tumor cell lines. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5303–5314.
Laurie NA, Donovan SL, Shih CS, Zhang J, Mills N, Fuller C et al. Inactivation of the p53 pathway in retinoblastoma. Nature 2006; 444: 61–66.
Johnson L, Shen A, Boyle L, Kunich J, Pandey K, Lemmon M et al. Selectively replicating adenoviruses targeting deregulated E2F activity are potent, systemic antitumor agents. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 325–337.
Baylin SB, Ohm JE . Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer—a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 107–116.
Esteller M . Epigenetics provides a new generation of oncogenes and tumour-suppressor genes. Br J Cancer 2006; 94: 179–183.
Gazin C, Wajapeyee N, Gobeil S, Virbasius CM, Green MR . An elaborate pathway required for Ras-mediated epigenetic silencing. Nature 2007; 449: 1073–1077.
Cowling VH, D'Cruz CM, Chodosh LA, Cole MD . c-Myc transforms human mammary epithelial cells through repression of the Wnt inhibitors DKK1 and SFRP1. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 5135–5146.
Cao R, Zhang Y . The functions of E(Z)/EZH2-mediated methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2004; 14: 155–164.
Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M, Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG et al. The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in progression of prostate cancer. Nature 2002; 419: 624–629.
Cao Q, Yu J, Dhanasekaran SM, Kim JH, Mani RS, Tomlins SA et al. Repression of E-cadherin by the polycomb group protein EZH2 in cancer. Oncogene 2008; 27: 7274–7284.
Fujii S, Ito K, Ito Y, Ochiai A . Enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (EZH2) down-regulates RUNX3 by increasing histone H3 methylation. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 17324–17332.
Yang X, Karuturi RK, Sun F, Aau M, Yu K, Shao R et al. CDKN1C (p57) is a direct target of EZH2 and suppressed by multiple epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e5011.
Jiang X, Tan J, Li J, Kivimae S, Yang X, Zhuang L et al. DACT3 is an epigenetic regulator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer and is a therapeutic target of histone modifications. Cancer Cell 2008; 13: 529–541.
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota I, Tomlins SA et al. EZH2 is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 11606–11611.
Tan J, Yang X, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Chen W, Lee PL et al. Pharmacologic disruption of Polycomb-repressive complex 2-mediated gene repression selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 1050–1063.
Bracken AP, Pasini D, Capra M, Prosperini E, Colli E, Helin K . EZH2 is downstream of the pRB-E2F pathway, essential for proliferation and amplified in cancer. EMBO J 2003; 22: 5323–5335.
Nahle Z, Polakoff J, Davuluri RV, McCurrach ME, Jacobson MD, Narita M et al. Direct coupling of the cell cycle and cell death machinery by E2F. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: 859–864.
Bracken AP, Ciro M, Cocito A, Helin K . E2F target genes: unraveling the biology. Trends Biochem Sci 2004; 29: 409–417.
Putzer BM . E2F1 death pathways as targets for cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med 2007; 11: 239–251.
Burkhart DL, Sage J . Cellular mechanisms of tumour suppression by the retinoblastoma gene. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 671–682.
Kawabe S, Nishikawa T, Munshi A, Roth JA, Chada S, Meyn RE . Adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene expression radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells via TP53-independent mechanisms. Mol Ther 2002; 6: 637–644.
Zhao XD, Han X, Chew JL, Liu J, Chiu KP, Choo A et al. Whole-genome mapping of histone H3 Lys4 and 27 trimethylations reveals distinct genomic compartments in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1: 286–298.
Pan G, Tian S, Nie J, Yang C, Ruotti V, Wei H et al. Whole-genome analysis of histone H3 lysine 4 and lysine 27 methylation in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1: 299–312.
Vigo E, Muller H, Prosperini E, Hateboer G, Cartwright P, Moroni MC et al. CDC25A phosphatase is a target of E2F and is required for efficient E2F-induced S phase. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 6379–6395.
Kondo Y, Shen L, Cheng AS, Ahmed S, Boumber Y, Charo C et al. Gene silencing in cancer by histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation independent of promoter DNA methylation. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 741–750.
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P . Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 2000; 351 (Pt 1): 95–105.
Lynch 3rd JJ, Jarvis MF, Kowaluk EA . An adenosine kinase inhibitor attenuates tactile allodynia in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 1999; 364: 141–146.
Sander S, Bullinger L, Klapproth K, Fiedler K, Kestler HA, Barth TF et al. MYC stimulates EZH2 expression by repression of its negative regulator miR-26a. Blood 2008; 112: 4202–4212.
Egle A, Harris AW, Bouillet P, Cory S . Bim is a suppressor of Myc-induced mouse B cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6164–6169.
Villunger A, Michalak EM, Coultas L, Mullauer F, Bock G, Ausserlechner MJ et al. p53- and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only proteins puma and noxa. Science 2003; 302: 1036–1038.
Semizarov D, Kroeger P, Fesik S . siRNA-mediated gene silencing: a global genome view. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: 3836–3845.
Tan J, Zhuang L, Jiang X, Yang KK, Karuturi KM, Yu Q . Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 is a direct target of E2F1 and contributes to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis through positive feedback regulation of E2F1 apoptotic activity. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 10508–10515.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Kristian Helin (European Institute of Oncology, Milan) for the ER-E2F1 plasmids and Dr Claudio Brancolini for providing the IMR90/E1A cells. This work was supported by the Agency for Science, Technology and Research of Singapore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by J Silke
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zheng, S., Li, Z. et al. Polycomb protein EZH2 regulates E2F1-dependent apoptosis through epigenetically modulating Bim expression. Cell Death Differ 17, 801–810 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.162
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.162
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Depletion of enhancer zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) directs transcription factors associated with T cell differentiation through epigenetic regulation of Yin Yang 1(YY1) in combating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
lncRNA-AC079061.1/VIPR1 axis may suppress the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
EZH2: a novel target for cancer treatment
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2020)
-
MiR-137 inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of human glioblastoma cells by targeting EZH2
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2015)
-
Polycomb protein EZH2 suppresses apoptosis by silencing the proapoptotic miR-31
Cell Death & Disease (2014)