Abstract
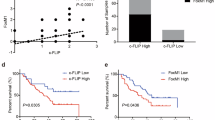
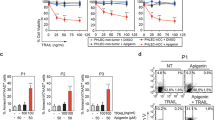
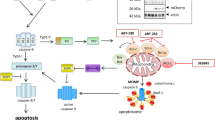
We found that procaspase 8 was overexpressed in non-small-cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) compared with matched normal tissues. The caspase 8 inhibitor FLICE-inhibitory protein (FLIP) was also overexpressed in the majority of NSCLCs. Silencing FLIP induced caspase 8 activation and apoptosis in NSCLC cell lines, but not in normal lung cell lines. Apoptosis induced by FLIP silencing was mediated by the TRAIL death receptors DR4 and DR5, but was not dependent on ligation of the receptors by TRAIL. Furthermore, the apoptosis induced by FLIP silencing was dependent on the overexpression of procaspase 8 in NSCLC cells. Moreover, in NSCLC cells, but not in normal cells, FLIP silencing induced co-localization of DR5 and ceramide, and disruption of this co-localization abrogated apoptosis. FLIP silencing supra-additively increased TRAIL-induced apoptosis of NSCLC cells; however, normal lung cells were resistant to TRAIL, even when FLIP was silenced. Importantly, FLIP silencing sensitized NSCLC cells but not normal cells to chemotherapy in vitro, and silencing FLIP in vivo retarded NSCLC xenograft growth and enhanced the anti-tumour effects of cisplatin. Collectively, our results suggest that due to frequent procaspase 8 overexpression, NSCLCs may be particularly sensitive to FLIP-targeted therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated death domain
- FLICE:
-
inactive procaspase 8
- DISC:
-
death-inducing signaling complex
- FLIP:
-
FLICE-inhibitory protein
- FLIPL:
-
long splice forms
- FLIPS:
-
short splice forms
- NSCLC:
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
References
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM . Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 1998; 281: 1305–1308.
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM . FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 1995; 81: 505–512.
Bodmer JL, Holler N, Reynard S, Vinciguerra P, Schneider P, Juo P et al. TRAIL receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 241–243.
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V et al. Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature 1997; 388: 190–195.
Micheau O, Thome M, Schneider P, Holler N, Tschopp J, Nicholson DW et al. The long form of FLIP is an activator of caspase-8 at the Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 45162–45171.
Zhou XD, Yu JP, Liu J, Luo HS, Chen HX, Yu HG . Overexpression of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (FLIP) in gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond) 2004; 106: 397–405.
Ryu BK, Lee MG, Chi SG, Kim YW, Park JH . Increased expression of cFLIP(L) in colonic adenocarcinoma. J Pathol 2001; 194: 15–19.
Remmelink M, Mijatovic T, Gustin A, Mathieu A, Rombaut K, Kiss R et al. Identification by means of cDNA microarray analyses of gene expression modifications in squamous non-small cell lung cancers as compared to normal bronchial epithelial tissue. Int J Oncol 2005; 26: 247–258.
Frese S, Brunner T, Gugger M, Uduehi A, Schmid RA . Enhancement of Apo2L/TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand)-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by chemotherapeutic agents without correlation to the expression level of cellular protease caspase-8 inhibitory protein. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002; 123: 168–174.
Maione P, Gridelli C, Troiani T, Ciardiello F . Combining targeted therapies and drugs with multiple targets in the treatment of NSCLC. Oncologist 2006; 11: 274–284.
Cooper WA, Kohonen-Corish MR, Zhuang L, McCaughan B, Kennedy C, Screaton G et al. Role and prognostic significance of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand death receptor DR5 in nonsmall-cell lung cancer and precursor lesions. Cancer 2008; 113: 135–142.
Hopkins-Donaldson S, Ziegler A, Kurtz S, Bigosch C, Kandioler D, Ludwig C et al. Silencing of death receptor and caspase-8 expression in small cell lung carcinoma cell lines and tumors by DNA methylation. Cell Death Differ 2003; 10: 356–364.
Shivapurkar N, Toyooka S, Eby MT, Huang CX, Sathyanarayana UG, Cunningham HT et al. Differential inactivation of caspase-8 in lung cancers. Cancer Biol Ther 2002; 1: 65–69.
Dumitru CA, Gulbins E . TRAIL activates acid sphingomyelinase via a redox mechanism and releases ceramide to trigger apoptosis. Oncogene 2006; 25: 5612–5625.
Delmas D, Rebe C, Micheau O, Athias A, Gambert P, Grazide S et al. Redistribution of CD95, DR4 and DR5 in rafts accounts for the synergistic toxicity of resveratrol and death receptor ligands in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 8979–8986.
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J . Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 1998; 94: 491–501.
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ et al. Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J 1998; 17: 1675–1687.
Wilson TR, McLaughlin KM, McEwan M, Sakai H, Rogers KM, Redmond KM et al. c-FLIP: a key regulator of colorectal cancer cell death. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 5754–5762.
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 1999; 104: 155–162.
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ, Smyth MJ . The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 782–798.
Schimmer AD, Thomas MP, Hurren R, Gronda M, Pellecchia M, Pond GR et al. Identification of small molecules that sensitize resistant tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor-family death receptors. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 2367–2375.
Abedini MR, Qiu Q, Yan X, Tsang BK . Possible role of FLICE-like inhibitory protein (FLIP) in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6997–7004.
Kamarajan P, Sun NK, Chao CC . Up-regulation of FLIP in cisplatin-selected HeLa cells causes cross-resistance to CD95/Fas death signalling. Biochem J 2003; 376: 253–260.
Longley DB, Wilson TR, McEwan M, Allen WL, McDermott U, Galligan L et al. c-FLIP inhibits chemotherapy-induced colorectal cancer cell death. Oncogene 2006; 25: 838–848.
Grassme H, Cremesti A, Kolesnick R, Gulbins E . Ceramide-mediated clustering is required for CD95-DISC formation. Oncogene 2003; 22: 5457–5470.
Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Huang A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D et al. A novel receptor for Apo2L/TRAIL contains a truncated death domain. Curr Biol 1997; 7: 1003–1006.
Fulda S, Meyer E, Debatin KM . Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2 overexpression. Oncogene 2002; 21: 2283–2294.
Taniai M, Grambihler A, Higuchi H, Werneburg N, Bronk SF, Farrugia DJ et al. Mcl-1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 3517–3524.
Ndozangue-Touriguine O, Sebbagh M, Merino D, Micheau O, Bertoglio J, Breard J . A mitochondrial block and expression of XIAP lead to resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis during progression to metastasis of a colon carcinoma. Oncogene 2008; 27: 6012–6022.
Vogler M, Durr K, Jovanovic M, Debatin KM, Fulda S . Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by XIAP in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2007; 26: 248–257.
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J, Rue M, Comella JX, Matias-Guiu X . FLIP is frequently expressed in endometrial carcinoma and has a role in resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Lab Invest 2005; 85: 885–894.
Mathas S, Lietz A, Anagnostopoulos I, Hummel F, Wiesner B, Janz M et al. c-FLIP mediates resistance of Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells to death receptor-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 1041–1052.
Wagner KW, Punnoose EA, Januario T, Lawrence DA, Pitti RM, Lancaster K et al. Death-receptor O-glycosylation controls tumor-cell sensitivity to the proapoptotic ligand Apo2L/TRAIL. Nat Med 2007; 13: 1070–1077.
Eggert A, Grotzer MA, Zuzak TJ, Wiewrodt BR, Ho R, Ikegaki N et al. Resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells correlates with a loss of caspase-8 expression. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 1314–1319.
Sun T, Gao Y, Tan W, Ma S, Shi Y, Yao J et al. A six-nucleotide insertion-deletion polymorphism in the CASP8 promoter is associated with susceptibility to multiple cancers. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 605–613.
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M et al. The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-kappaB and Erk signaling pathways. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 640–648.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Cancer Research UK (TRW, KMM, CL-C, DAF, PGJ, DBL), the Medical Research Council (DBL), Department of Employment and Learning Northern Ireland (KMR, NC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by C Duckett
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website (http://www.nature.com/cdd)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, T., Redmond, K., McLaughlin, K. et al. Procaspase 8 overexpression in non-small-cell lung cancer promotes apoptosis induced by FLIP silencing. Cell Death Differ 16, 1352–1361 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.76
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.76
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pevonedistat (MLN4924): mechanism of cell death induction and therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2020)
-
Droxinostat sensitizes human colon cancer cells to apoptotic cell death via induction of oxidative stress
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2018)
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibition promotes lysosome-dependent degradation of c-FLIPL in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
IHC-based subcellular quantification provides new insights into prognostic relevance of FLIP and procaspase-8 in non-small-cell lung cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2017)
-
Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: live or let die
Nature Reviews Immunology (2015)