Abstract
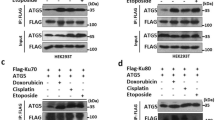
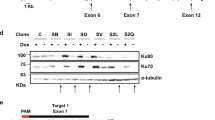
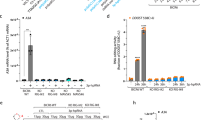
Apaf1 is a key regulator of the mitochondrial intrinsic pathway of apoptosis, as it activates executioner caspases by forming the apoptotic machinery apoptosome. Its genetic regulation and its post-translational modification are crucial under the various conditions where apoptosis occurs. Here we describe Ku70/86, a mediator of non-homologous end-joining pathway of DNA repair, as a novel regulator of Apaf1 transcription. Through analysing different Apaf1 promoter mutants, we identified an element repressing the Apaf1 promoter. We demonstrated that Ku70/86 is a nuclear factor able to bind this repressing element and downregulating Apaf1 transcription. We also found that Ku70/86 interaction with Apaf1 promoter is dynamically modulated upon DNA damage. The effect of this binding is a downregulation of Apaf1 expression immediately following the damage to DNA; conversely, we observed Apaf1 upregulation and apoptosis activation when Ku70/86 unleashes the Apaf1-repressing element. Therefore, besides regulating DNA repair, our results suggest that Ku70/86 binds to the Apaf1 promoter and represses its activity. This may help to inhibit the apoptosome pathway of cell death and contribute to regulate cell survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Apaf1:
-
apoptotic protease activating factor
- Bac:
-
bacterial artificial chromosome
- ChIP:
-
chromatin immunoprecipitation
- CMV:
-
Cytomegalovirus
- DNA-PKcs:
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit
- DSB:
-
double-strand break
- EMSA:
-
electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- ERBB2:
-
erythrocyte blastosis virus B2
- ETNA:
-
Embryonic Telencephalic Naïve Apaf1 cells
- G6pdx:
-
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase X-linked
- HDAC:
-
histone deacetylase
- NHEJ:
-
non-homologous end-joining
- 8-OHdG:
-
8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine
- Pol II:
-
RNA polymerase II
- STS:
-
staurosporine
- TSP:
-
transcription start point
References
Kim HE, Du F, Fang M, Wang X . Formation of apoptosome is initiated by cytochrome c-induced dATP hydrolysis and subsequent nucleotide exchange on Apaf-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 17545–17550.
Acehan D, Jiang X, Morgan DG, Heuser JE, Wang X, Akey CW . Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol Cell 2002; 9: 423–432.
Reubold TF, Wohlgemuth S, Eschenburg S . A new model for the transition of APAF-1 from inactive monomer to caspase-activating apoptosome. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 32717–32724.
Bao Q, Shi Y . Apoptosome: a platform for the activation of initiator caspases. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 56–65.
Boatright KM, Salvesen GS . Mechanisms of caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2003; 15: 725–731.
Fortin A, Cregan SP, MacLaurin JG, Kushwaha N, Hickman ES, Thompson CS et al. APAF1 is a key transcriptional target for p53 in the regulation of neuronal cell death. J Cell Biol 2001; 155: 207–216.
Kannan K, Kaminski N, Rechavi G, Jakob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Givol D . DNA microarray analysis of genes involved in p53 mediated apoptosis: activation of Apaf-1. Oncogene 2001; 20: 3449–3455.
Moroni MC, Hickman ES, Lazzerini Denchi E, Caprara G, Colli E, Cecconi F et al. Apaf-1 is a transcriptional target for E2F and p53. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 552–558.
Rozenfeld-Granot G, Krishnamurthy J, Kannan K, Toren A, Amariglio N, Givol D et al. A positive feedback mechanism in the transcriptional activation of Apaf-1 by p53 and the coactivator Zac-1. Oncogene 2002; 21: 1469–1476.
Furukawa Y, Nishimura N, Satoh M, Endo H, Iwase S, Yamada H et al. Apaf-1 is a mediator of E2F-1-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 39760–39768.
Furukawa Y, Sutheesophon K, Wada T, Nishimura M, Saito Y, Ishii H . Methylation silencing of the Apaf-1 gene in acute leukemia. Mol Cancer Res 2005; 3: 325–334.
Peltenburg LT, de Bruin EC, Meersma D, Smit NP, Schrier PI, Medema JP . Expression and function of the apoptosis effector Apaf-1 in melanoma. Cell Death Differ 2005; 12: 678–679.
Soengas MS, Capodieci P, Polsky D, Mora J, Esteller M, Opitz-Araya X et al. Inactivation of the apoptosis effector Apaf-1 in malignant melanoma. Nature 2001; 409: 207–211.
Teodoridis JM, Hall J, Marsh S, Kannall HD, Smyth C, Curto J et al. CpG island methylation of DNA damage response genes in advanced ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 8961–8967.
Wallace DM, Cotter TG . Histone deacetylase activity in conjunction with E2F-1 and p53 regulates Apaf-1 expression in 661W cells and the retina. J Neurosci Res 2009; 87: 887–905.
Wright KM, Smith MI, Farrag L, Deshmukh M . Chromatin modification of Apaf-1 restricts the apoptotic pathway in mature neurons. J Cell Biol 2007; 179: 825–832.
Johnson CE, Huang YY, Parrish AB, Smith MI, Vaughn AE, Zhang Q et al. Differential Apaf-1 levels allow cytochrome c to induce apoptosis in brain tumors but not in normal neural tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 20820–20825.
Lieber MR, Ma Y, Pannicke U, Schwarz K . Mechanism and regulation of human non-homologous DNA end-joining. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003; 4: 712–720.
Downs JA, Jackson SP . A means to a DNA end: the many roles of Ku. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 367–378.
Mimori T, Akizuki M, Yamagata H, Inada S, Yoshida S, Homma M . Characterization of a high molecular weight acidic nuclear protein recognized by autoantibodies in sera from patients with polymyositis-scleroderma overlap. J Clin Invest 1981; 68: 611–620.
Amsel AD, Rathaus M, Kronman N, Cohen HY . Regulation of the proapoptotic factor Bax by Ku70-dependent deubiquitylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 5117–5122.
Mo X, Dynan WS . Subnuclear localization of Ku protein: functional association with RNA polymerase II elongation sites. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 8088–8099.
Sucharov CC, Helmke SM, Langer SJ, Perryman MB, Bristow M, Leinwand L . The Ku protein complex interacts with YY1, is up-regulated in human heart failure, and represses alpha myosin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 8705–8715.
Nolens G, Pignon JC, Koopmansch B, Elmoualij B, Zorzi W, De Pauw E et al. Ku proteins interact with activator protein-2 transcription factors and contribute to ERBB2 overexpression in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res 2009; 11: R83.
Errami A, Smider V, Rathmell WK, He DM, Hendrickson EA, Zdzienicka MZ et al. Ku86 defines the genetic defect and restores X-ray resistance and V(D)J recombination to complementation group 5 hamster cell mutants. Mol Cell Biol 1996; 16: 1519–1526.
Gu Y, Jin S, Gao Y, Weaver DT, Alt FW . Ku70-deficient embryonic stem cells have increased ionizing radiosensitivity, defective DNA end-binding activity, and inability to support V(D)J recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 8076–8081.
Singleton BK, Priestley A, Steingrimsdottir H, Gell D, Blunt T, Jackson SP et al. Molecular and biochemical characterization of xrs mutants defective in Ku80. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17: 1264–1273.
Bonner WM, Redon CE, Dickey JS, Nakamura AJ, Sedelnikova OA, Solier S et al. GammaH2AX and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 957–967.
Lan L, Nakajima S, Oohata Y, Takao M, Okano S, Masutani M et al. In situ analysis of repair processes for oxidative DNA damage in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 13738–13743.
Margaritis T, Holstege FC . Poised RNA polymerase II gives pause for thought. Cell 2008; 133: 581–584.
Saunders A, Core LJ, Lis JT . Breaking barriers to transcription elongation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 557–567.
Cozzolino M, Ferraro E, Ferri A, Rigamonti D, Quondamatteo F, Ding H et al. Apoptosome inactivation rescues proneural and neural cells from neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ 2004; 11: 1179–1191.
Hediger F, Neumann FR, Van Houwe G, Dubrana K, Gasser SM . Live imaging of telomeres: yKu and Sir proteins define redundant telomere-anchoring pathways in yeast. Curr Biol 2002; 12: 2076–2089.
Cecconi F, Alvarez-Bolado G, Meyer BI, Roth KA, Gruss P . Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed cell death in mammalian development. Cell 1998; 94: 727–737.
Gu Y, Sekiguchi J, Gao Y, Dikkes P, Frank K, Ferguson D et al. Defective embryonic neurogenesis in Ku-deficient but not DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 2668–2673.
Kruse JP, Gu W . Modes of p53 regulation. Cell 2009; 137: 609–622.
Gullo C, Au M, Feng G, Teoh G . The biology of Ku and its potential oncogenic role in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006; 1765: 223–234.
Li GC, Ouyang H, Li X, Nagasawa H, Little JB, Chen DJ et al. Ku70: a candidate tumor suppressor gene for murine T cell lymphoma. Mol Cell 1998; 2: 1–8.
Pucci S, Mazzarelli P, Rabitti C, Giai M, Gallucci M, Flammia G et al. Tumor specific modulation of KU70/80 DNA binding activity in breast and bladder human tumor biopsies. Oncogene 2001; 20: 739–747.
Tong WM, Cortes U, Hande MP, Ohgaki H, Cavalli LR, Lansdorp PM et al. Synergistic role of Ku80 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in suppressing chromosomal aberrations and liver cancer formation. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 6990–6996.
Klein A, Miera O, Bauer O, Golfier S, Schriever F . Chemosensitivity of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and correlated expression of proteins regulating apoptosis, cell cycle and DNA repair. Leukemia 2000; 14: 40–46.
Lim JW, Kim H, Kim KH . Expression of Ku70 and Ku80 mediated by NF-kappa B and cyclooxygenase-2 is related to proliferation of human gastric cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 46093–46100.
Schafer ZT, Kornbluth S . The apoptosome: physiological, developmental, and pathological modes of regulation. Dev Cell 2006; 10: 549–561.
Acknowledgements
F Cecconi is supported by grants from the Telethon Foundation, AIRC, the Italian Ministry of Health and the Italian Ministry of University and Research. D De Zio is supported by a fellowship from the Telethon Foundation. The authors thank M Acuna Villa and MW Bennett for editorial and secretarial work, F Florenzano and G Filomeni for research assistance, and A Nobili for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by JP Medema
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Zio, D., Bordi, M., Tino, E. et al. The DNA repair complex Ku70/86 modulates Apaf1 expression upon DNA damage. Cell Death Differ 18, 516–527 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.125
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.125
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
mTOR hyperactivation in Down Syndrome underlies deficits in autophagy induction, autophagosome formation, and mitophagy
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Bax deficiency extends the survival of Ku70 knockout mice that develop lung and heart diseases
Cell Death & Disease (2015)