Abstract
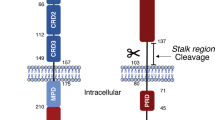
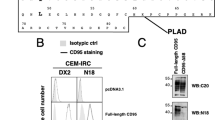
CD95 is a dual-function receptor that exerts pro- or antiapoptotic effects depending on the cellular context, the state of activation, the signal threshold and the mode of ligation. In this study, we report that CD95 engagement modulates TCR/CD3-driven signaling pathways in resting T lymphocytes in a dose-dependent manner. While high doses of immobilized CD95 agonists silence T cells, lower concentrations augment activation and proliferation. We analyzed the co-stimulatory capacity of CD95 in detail in resting human CD4+ T cells, and demonstrate that low-dose ligand-induced co-internalization of CD95 and TCR/CD3 complexes enables non-apoptotic caspase activation, the prolonged activation of MAP kinases, the upregulation of antiapoptotic proteins associated with apoptosis resistance, and the activation of transcription factors and cell-cycle regulators for the induction of proliferation and cytokine production. We propose that the levels of CD95L on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), neighboring T cells or epithelial cells regulate inhibitory or co-stimulatory CD95 signaling, which in turn is crucial for fine-tuning of primary T-cell activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- abs:
-
absorbance
- AMC:
-
7-amino-4-methylcoumarin
- APC:
-
antigen-presenting cell
- Bcl-XL:
-
B-cell lymphoma-extra large
- BrdU:
-
bromodeoxyuridine
- CD95L:
-
CD95 ligand
- CDK:
-
cyclin-dependent kinase
- cFLIP:
-
cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein
- cFLIPS/R:
-
cFLIPshort/Raji
- cFLIPL:
-
cFLIPlong
- CFSE:
-
carboxy-fluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester
- CTLA-4:
-
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4
- CytD:
-
cytochalasin D
- DC:
-
dendritic cell
- DISC:
-
death-inducing signaling complex
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- IFNγ:
-
interferon γ
- IκB:
-
inhibitor of NF-κB
- IL-2Rα/β:
-
interleukin-2 receptor α/β chain
- LatA:
-
latrunculin A
- LZ-CD95L:
-
leucin zipper CD95L
- mAb:
-
monoclonal antibody
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MFI:
-
mean fluorescence intensity
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor ‘kappa-light-chain-enhancer’ of activated B-cells
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PBMCs:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PCNA:
-
proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PD:
-
ERK1/2 inhibitor PD 98059
- PHA:
-
phytohemagglutinin
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- PLCγ:
-
phospholipase Cγ
- PMA:
-
phorbol myristate acetate
- Rb:
-
retinoblastoma
- rIL-2:
-
recombinant IL-2
- TC:
-
tissue culture
- TCR:
-
T cell receptor
- TdR:
-
thymidine
- Th1:
-
T helper 1
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- TNFR:
-
TNF receptor
- TRAF:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor
References
Frauwirth KA, Thompson CB . Activation and inhibition of lymphocytes by costimulation. J Clin Invest 2002; 109: 295–299.
Strasser A, Jost PJ, Nagata S . The many roles of FAS receptor signaling in the immune system. Immunity 2009; 30: 180–192.
Alderson MR, Armitage RJ, Maraskovsky E, Tough TW, Roux E, Schooley K et al. Fas transduces activation signals in normal human T lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1993; 178: 2231–2235.
Kennedy NJ, Kataoka T, Tschopp J, Budd RC . Caspase activation is required for T cell proliferation. J Exp Med 1999; 190: 1891–1896.
Alam A, Cohen LY, Aouad S, Sekaly RP . Early activation of caspases during T lymphocyte stimulation results in selective substrate cleavage in nonapoptotic cells. J Exp Med 1999; 190: 1879–1890.
Maksimow M, Soderstrom TS, Jalkanen S, Eriksson JE, Hanninen A . Fas costimulation of naive CD4T cells is controlled by NF-kappaB signaling and caspase activity. J Leukoc Biol 2006; 79: 369–377.
Kataoka T, Tschopp J . N-terminal fragment of c-FLIP(L) processed by caspase 8 specifically interacts with TRAF2 and induces activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 2627–2636.
Golks A, Brenner D, Krammer PH, Lavrik IN . The c-FLIP-NH2 terminus (p22-FLIP) induces NF-kappaB activation. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1295–1305.
Krammer PH, Arnold R, Lavrik IN . Life and death in peripheral T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 532–542.
Paulsen M, Ussat S, Jakob M, Scherer G, Lepenies I, Schütze S et al. Interaction with XIAP prevents full caspase-3/-7 activation in proliferating human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 2008; 38: 1979–1987.
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K, Scheurich P . Non-apoptotic Fas signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2003; 14: 53–66.
Strauss G, Lindquist JA, Arhel N, Felder E, Karl S, Haas TL et al. CD95 co-stimulation blocks activation of naive T cells by inhibiting T cell receptor signaling. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 1379–1393.
Crotzer VL, Mabardy AS, Weiss A, Brodsky FM . T cell receptor engagement leads to phosphorylation of clathrin heavy chain during receptor internalization. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 981–991.
Schütze S, Tchikov V, Schneider-Brachert W . Regulation of TNFR1 and CD95 signalling by receptor compartmentalization. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 655–662.
Falk M, Ussat S, Reiling N, Wesch D, Kabelitz D, Adam-Klages S . Caspase inhibition blocks human T cell proliferation by suppressing appropriate regulation of IL-2, CD25, and cell cycle-associated proteins. J Immunol 2004; 173: 5077–5085.
Janssen O, Scheffler A, Kabelitz D . In vitro effects of mistletoe extracts and mistletoe lectins. Cytotoxicity towards tumor cells due to the induction of programmed cell death (apoptosis). Drug Research 1993; 43: 1221–1227.
Peter ME, Budd RC, Desbarats J, Hedrick SM, Hueber AO, Newell MK et al. The CD95 receptor: apoptosis revisited. Cell 2007; 129: 447–450.
Strauss G, Osen W, Knape I, Jacobsen EM, Muller SM, Debatin KM . Membrane-bound CD95 ligand expressed on human antigen-presenting cells prevents alloantigen-specific T cell response without impairment of viral and third-party T cell immunity. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 480–488.
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Riess D, Bentele M, Eils R, Krammer PH . Analysis of CD95 threshold signaling: triggering of CD95 (FAS/APO-1) at low concentrations primarily results in survival signaling. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 13664–13671.
Alcover A, Alarcon B . Internalization and intracellular fate of TCR-CD3 complexes. Crit Rev Immunol 2000; 20: 325–346.
Chakrabandhu K, Huault S, Garmy N, Fantini J, Stebe E, Mailfert S et al. The extracellular glycosphingolipid-binding motif of Fas defines its internalization route, mode and outcome of signals upon activation by ligand. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 1824–1837.
Rossin A, Kral R, Lounnas N, Chakrabandhu K, Mailfert S, Marguet D et al. Identification of a lysine-rich region of Fas as a raft nanodomains targeting signal necessary for Fas-mediated cell death. Exp Cell Res 2010; 316: 1513–1522.
Shinohara H, Yagita H, Ikawa Y, Oyaizu N . Fas drives cell cycle progression in glioma cells via extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 1766–1772.
Kataoka T, Budd RC, Holler N, Thome M, Martinon F, Irmler M et al. The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-kappaB and Erk signaling pathways. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 640–648.
Newton K, Strasser A . Caspases signal not only apoptosis but also antigen-induced activation in cells of the immune system. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 819–825.
Thome M, Tschopp J . TCR-induced NF-kappaB activation: a crucial role for Carma1, Bcl10 and MALT1. Trends Immunol 2003; 24: 419–424.
Zhang N, Hopkins K, He YW . c-FLIP protects mature T lymphocytes from TCR-mediated killing. J Immunol 2008; 181: 5368–5373.
Maksimow M, Santanen M, Jalkanen S, Hanninen A . Responding naive T cells differ in their sensitivity to Fas engagement: early death of many T cells is compensated by costimulation of surviving T cells. Blood 2003; 101: 4022–4028.
Cancedda C, LeMaoult J, Harris PE, Suciu-Foca N, Cortesini R . Specific T-cell deletion by transfected human monocytes expressing Fas ligand and antigen. Transplant Proc 2001; 33: 165–166.
Chen A, Zheng G, Tykocinski ML . Quantitative interplay between activating and pro-apoptotic signals dictates T cell responses. Cell Immunol 2003; 221: 128–137.
Hahne M, Renno T, Schroeter M, Irmler M, French L, Bornard T et al. Activated B cells express functional Fas ligand. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26: 721–724.
Suss G, Shortman K . A subclass of dendritic cells kills CD4T cells via Fas/Fas-ligand-induced apoptosis. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 1789–1796.
Badley AD, McElhinny JA, Leibson PJ, Lynch DH, Alderson MR, Paya CV . Upregulation of Fas ligand expression by human immunodeficiency virus in human macrophages mediates apoptosis of uninfected T lymphocytes. J Virol 1996; 70: 199–206.
Hoves S, Krause SW, Herfarth H, Halbritter D, Zhang HG, Mountz JD et al. Elimination of activated but not resting primary human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by Fas ligand (FasL/CD95L)-expressing Killer-dendritic cells. Immunobiology 2004; 208: 463–475.
Raftery MJ, Schwab M, Eibert SM, Samstag Y, Walczak H, Schonrich G . Targeting the function of mature dendritic cells by human cytomegalovirus: a multilayered viral defense strategy. Immunity 2001; 15: 997–1009.
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AM, Matzku S, Moller P, Falk W et al. Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 1989; 245: 301–305.
Paulsen M, Mathew B, Qian J, Lettau M, Kabelitz D, Janssen O . FasL cross-linking inhibits activation of human peripheral T cells. Int Immunol 2009; 21: 587–598.
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 1999; 5: 157–163.
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME . The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 1541–1548.
Scaffidi C, Medema JP, Krammer PH, Peter ME . FLICE is predominantly expressed as two functionally active isoforms, caspase-8/a and caspase-8/b. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 26953–26958.
Acknowledgements
This work forms part of the PhD thesis of M Paulsen. The project was sponsored by grants from the German Research Council (SFB 415, SFB 877) and the Medical Faculty of the Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by H-U Simon
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paulsen, M., Valentin, S., Mathew, B. et al. Modulation of CD4+ T-cell activation by CD95 co-stimulation. Cell Death Differ 18, 619–631 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.134
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.134
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The abscopal effect of anti-CD95 and radiotherapy in melanoma
Discover Oncology (2023)
-
Increased Expression of CD95 in CD4+ Effector Memory T Cells Promotes Th17 Response in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2022)
-
c-FLIP and CD95 signaling are essential for survival of renal cell carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2019)
-
Fas signaling-mediated TH9 cell differentiation favors bowel inflammation and antitumor functions
Nature Communications (2019)
-
A20 Curtails Primary but Augments Secondary CD8+ T Cell Responses in Intracellular Bacterial Infection
Scientific Reports (2016)