Abstract
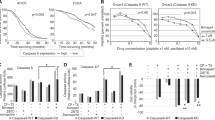
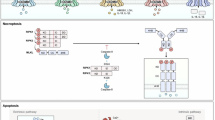
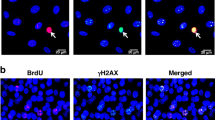
Mitotic death is a major form of cell death in cancer cells that have been treated with chemotherapeutic drugs. However, the mechanisms underlying this form of cell death is poorly understood. Here, we report that the loss of chromosome integrity is an important determinant of mitotic death. During prolonged mitotic arrest, caspase-3 is activated and it cleaves Cap-H, a subunit of condensin I. The depletion of Cap-H results in the loss of condensin I complex at the chromosomes, thus affecting the integrity of the chromosomes. Consequently, DNA fragmentation by caspase-activated DNase is facilitated, thus driving the cell towards mitotic death. By expressing a caspase-resistant form of Cap-H, mitotic death is abrogated and the cells are able to reenter interphase after a long mitotic delay. Taken together, we provide new insights into the molecular events that occur during mitotic death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CAD:
-
caspase-activated DNase
- EGFP:
-
enhanced green fluorescent protein
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- ICAD:
-
inhibitor of CAD
- SEM:
-
scanning electron microscopy
- SMC:
-
structural maintenance of chromosome
References
Lowe SW, Lin AW . Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2000; 21: 485–495.
Brown JM, Attardi LD . The role of apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 231–237.
Makin G, Hickman JA . Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy. Cell Tissue Res 2000; 301: 143–152.
Portugal J, Bataller M, Mansilla S . Cell death pathways in response to antitumor therapy. Tumori 2009; 95: 409–421.
Roninson IB, Broude EV, Chang BD . If not apoptosis, then what? Treatment-induced senescence and mitotic catastrophe in tumor cells. Drug Resist Updat 2001; 4: 303–313.
Mansilla S, Bataller M, Portugal J . Mitotic catastrophe as a consequence of chemotherapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2006; 6: 589–602.
Okada H, Mak TW . Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 592–603.
Schmidt M, Bastians H . Mitotic drug targets and the development of novel anti-mitotic anticancer drugs. Drug Resist Updat 2007; 10: 162–181.
Sudakin V, Yen TJ . Targeting mitosis for anti-cancer therapy. BioDrugs 2007; 21: 225–233.
Jackson JR, Patrick DR, Dar MM, Huang PS . Targeted anti-mitotic therapies: can we improve on tubulin agents? Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 107–117.
Weaver BA, Cleveland DW . Decoding the links between mitosis, cancer, and chemotherapy: the mitotic checkpoint, adaptation, and cell death. Cancer Cell 2005; 8: 7–12.
Castedo M, Perfettini JL, Roumier T, Andreau K, Medema R, Kroemer G . Cell death by mitotic catastrophe: a molecular definition. Oncogene 2004; 23: 2825–2837.
Gascoigne KE, Taylor SS . Cancer cells display profound intra- and interline variation following prolonged exposure to antimitotic drugs. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 111–122.
Gascoigne KE, Taylor SS . How do anti-mitotic drugs kill cancer cells? J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 2579–2585.
Holland AJ, Cleveland DW . Beyond genetics: surprising determinants of cell fate in antitumor drugs. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 103–105.
Nunez G, Benedict MA, Hu Y, Inohara N . Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 1998; 17: 3237–3245.
Mansilla S, Priebe W, Portugal J . Mitotic catastrophe results in cell death by caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms. Cell Cycle 2006; 5: 53–60.
Niikura Y, Dixit A, Scott R, Perkins G, Kitagawa K . BUB1 mediation of caspase-independent mitotic death determines cell fate. J Cell Biol 2007; 178: 283–296.
Kitagawa K, Niikura Y . Caspase-independent mitotic death (CIMD). Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 1001–1005.
Stevens JB, Liu G, Bremer SW, Ye KJ, Xu W, Xu J et al. Mitotic cell death by chromosome fragmentation. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 7686–7694.
Brito DA, Rieder CL . The ability to survive mitosis in the presence of microtubule poisons differs significantly between human nontransformed (RPE-1) and cancer (U2OS, HeLa) cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 2009; 66: 437–447.
Shi J, Orth JD, Mitchison T . Cell type variation in responses to antimitotic drugs that target microtubules and kinesin-5. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3269–3276.
Jordan MA, Kamath K . How do microtubule-targeted drugs work? An overview. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2007; 7: 730–742.
Jordan MA, Wilson L . Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 253–265.
Rieder CL, Maiato H . Stuck in division or passing through: what happens when cells cannot satisfy the spindle assembly checkpoint. Dev Cell 2004; 7: 637–651.
Ha GH, Kim HS, Lee CG, Park HY, Kim EJ, Shin HJ et al. Mitotic catastrophe is the predominant response to histone acetyltransferase depletion. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 483–497.
Dalton WB, Nandan MO, Moore RT, Yang VW . Human cancer cells commonly acquire DNA damage during mitotic arrest. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 11487–11492.
Quignon F, Rozier L, Lachages AM, Bieth A, Simili M, Debatisse M et al. Sustained mitotic block elicits DNA breaks: one-step alteration of ploidy and chromosome integrity in mammalian cells. Oncogene 2007; 26: 165–172.
Leslie M . Mitosis first, DNA repair later. J Cell Bio 2010; 190: 160.
Giunta S, Belotserkovskaya R, Jackson SP . DNA damage signaling in response to double-strand breaks during mitosis. J Cell Biol 190: 197–207.
Nagata S . Apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Exp Cell Res 2000; 256: 12–18.
Sakahira H, Enari M, Nagata S . Cleavage of CAD inhibitor in CAD activation and DNA degradation during apoptosis. Nature 1998; 391: 96–99.
Hudson DF, Vagnarelli P, Gassmann R, Earnshaw WC . Condensin is required for nonhistone protein assembly and structural integrity of vertebrate mitotic chromosomes. Dev Cell 2003; 5: 323–336.
Hirano T . Condensins: organizing and segregating the genome. Curr Biol 2005; 15: R265–R275.
Legagneux V, Cubizolles F, Watrin E . Multiple roles of condensins: a complex story. Biol Cell 2004; 96: 201–213.
Degterev A, Boyce M, Yuan J . A decade of caspases. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8543–8567.
Janicke RU . MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells do not express caspase-3. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009; 117: 219–221.
Vogel C, Hager C, Bastians H . Mechanisms of mitotic cell death induced by chemotherapy-mediated G2 checkpoint abrogation. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 339–345.
Toh WH, Nam SY, Sabapathy K . An essential role for p73 in regulating mitotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 2009; 17: 787–800.
Blank M, Lerenthal Y, Mittelman L, Shiloh Y . Condensin I recruitment and uneven chromatin condensation precede mitotic cell death in response to DNA damage. J Cell Biol 2006; 174: 195–206.
Acknowledgements
We thank Carl Zeiss Advanced Imaging Centre Singapore for technical assistance with scanning electron microscopy. This work was supported by Academic Research Council, Ministry of Education, Singapore (Academic Research Fund AcRF Tier 1, RG37/08) and A*STAR, Biomedical Research Council (BMRC grant 08/1/22/19/568).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Salvesen
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, SK., Wong, CH., Lee, YP. et al. Caspase-3-mediated degradation of condensin Cap-H regulates mitotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 18, 996–1004 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.165
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.165
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NCAPH is a prognostic biomarker and associated with immune infiltrates in lung adenocarcinoma
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Identification of NCAPH as a biomarker for prognosis of breast cancer
Molecular Biology Reports (2020)
-
Condensin controls mitotic chromosome stiffness and stability without forming a structurally contiguous scaffold
Chromosome Research (2018)
-
Mitosis-targeted anti-cancer therapies: where they stand
Cell Death & Disease (2012)