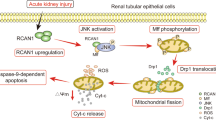
Abstract
Ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) causes inflammation and cell injury as a result of activating innate immune signaling. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has a key role in mediating kidney damages during IRI, but the downstream signaling pathway(s) stimulating apoptosis remains debated. In this study we show that TLR4 mediates MyD88-dependent activation of TNF receptor-associated factor 2, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1), and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAP kinases in ischemic-reperfused kidneys and posthypoxic renal tubule epithelial cells (RTECs). Hypoxia stimulated the expression of the endoplasmic-resident gp96, which co-immunoprecipitated TLR4, whereas silencing gp96 mRNA expression impaired hypoxia-induced apoptosis in TLR4-expressing RTECs. NAD(P)H oxidase 4 (NOX4) was shown to interact with TLR4 and to be required in lipopolysaccharide-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). IRI stimulated the expression of a 28-kDa NOX4 spliced isoform abundantly expressed in wild-type RTECs, which co-immunoprecipitated with TLR4, but not with gp96 in TLR4-deficient RTECs. Silencing NOX4 mRNA expression impaired hypoxia-induced activation of ASK1 and both JNK and p38, leading to the inhibition of ROS production and apoptosis in posthypoxic TLR4-expressing RTECs. These findings show that, concomitantly to the activation of p38, the gp96/TLR4 interaction is required for activation of ASK1/JNK signaling in posthypoxic mouse RTECs, and that the 28-kDa NOX4 has a key role in TLR4-mediated apoptosis during renal IRI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ASK1:
-
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- DAMP:
-
damage-associated molecular pattern
- DPI:
-
diphenyleneiodonium chloride
- HMGB1:
-
high-mobility group box 1
- Hsps:
-
heat shock proteins
- JNK:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MyD88:
-
myeloid differentiation factor-88
- NOX:
-
NAD(P)H oxidase
- PP5:
-
protein phosphatase 5
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RTEC:
-
renal tubule epithelial cell
- siRNA:
-
small-interfering RNA
- TRAF:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor
- UPR:
-
unfolded protein response
References
Bonventre JV, Weinberg JM . Recent advances in the pathophysiology of ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003; 14: 2199–2210.
Perico N, Cattaneo D, Sayegh MH, Remuzzi G . Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation. Lancet 2004; 364: 1814–1827.
Gribar SC, Richardson WM, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ . No longer an innocent bystander: epithelial toll-like receptor signaling in the development of mucosal inflammation. Mol Med 2008; 14: 645–659.
Tsung A, Klune JR, Zhang X, Jeyabalan G, Cao Z, Peng X et al. HMGB1 release induced by liver ischemia involves Toll-like receptor 4 dependent reactive oxygen species production and calcium-mediated signaling. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 2913–2923.
Oyama J, Blais Jr C, Liu X, Pu M, Kobzik L, Kelly RA et al. Reduced myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in toll-like receptor 4-deficient mice. Circulation 2004; 109: 784–789.
Barsness KA, Arcaroli J, Harken AH, Abraham E, Banerjee A, Reznikov L et al. Hemorrhage-induced acute lung injury is TLR-4 dependent. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004; 287: R592–R599.
Leemans JC, Stokman G, Claessen N, Rouschop KM, Teske GJ, Kirschning CJ et al. Renal-associated TLR2 mediates ischemia/reperfusion injury in the kidney. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2894–2903.
Shigeoka AA, Holscher TD, King AJ, Hall FW, Kiosses WB, Tobias PS et al. TLR2 is constitutively expressed within the kidney and participates in ischemic renal injury through both MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways. J Immunol 2007; 178: 6252–6258.
Wu H, Chen G, Wyburn KR, Yin J, Bertolino P, Eris JM et al. TLR4 activation mediates kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 2847–2859.
Wolfs TG, Buurman WA, van Schadewijk A, de Vries B, Daemen MA, Hiemstra PS et al. In vivo expression of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 by renal epithelial cells: IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha mediated up-regulation during inflammation. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1286–1293.
Kim BS, Lim SW, Li C, Kim JS, Sun BK, Ahn KO et al. Ischemia-reperfusion injury activates innate immunity in rat kidneys. Transplantation 2005; 79: 1370–1377.
Yang Y, Liu B, Dai J, Srivastava PK, Zammit DJ, Lefrançois L et al. Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages. Immunity 2007; 26: 215–226.
Mkaddem SB, Werts C, Goujon JM, Bens M, Pedruzzi E, Ogier-Denis E et al. Heat shock protein gp96 interacts with protein phosphatase 5 and controls toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2)-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 in post-hypoxic kidney cells. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 12541–12549.
Hornef MW, Normark BH, Vandewalle A, Normark S . Intracellular recognition of lipopolysaccharide by toll-like receptor 4 in intestinal epithelial cells. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 1225–1235.
Nakano H, Nakajima A, Sakon-Komazawa S, Piao JH, Xue X, Okumura K . Reactive oxygen species mediate crosstalk between NF-kappaB and JNK. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 730–737.
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P, Saitoh M, Moriguchi T et al. Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science 1997; 275: 90–94.
Tobiume K, Matsuzawa A, Takahashi T, Nishitoh H, Morita K, Takeda K et al. ASK1 is required for sustained activations of JNK/p38 MAP kinases and apoptosis. EMBO Rep 2001; 2: 222–228.
Noguchi T, Takeda K, Matsuzawa A, Saegusa K, Nakano H, Gohda J et al. Recruitment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family proteins to apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 signalosome is essential for oxidative stress-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 37033–37040.
Matsuzawa A, Saegusa K, Noguchi T, Sadamitsu C, Nishitoh H, Nagai S et al. ROS-dependent activation of the TRAF6-ASK1-p38 pathway is selectively required for TLR4-mediated innate immunity. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 587–592.
Bedard K, Krause KH . The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 245–313.
Lambeth JD . NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol 2004; 4: 181–189.
Geiszt M, Kopp JB, Varnai P, Leto TL . Identification of renox, an NAD(P)H oxidase in kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 8010–8014.
Shiose A, Kuroda J, Tsuruya K, Hirai M, Hirakata H, Naito S et al. A novel superoxide-producing NAD(P)H oxidase in kidney. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 1417–1423.
Park HS, Jung HY, Park EY, Kim J, Lee WJ, Bae YS . Cutting edge: direct interaction of TLR4 with NAD(P)H oxidase 4 isozyme is essential for lipopolysaccharide-induced production of reactive oxygen species and activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol 2004; 173: 3589–3593.
Cory S, Adams JM . The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 647–656.
Pedruzzi E, Guichard C, Ollivier V, Driss F, Fay M, Prunet C et al. NAD(P)H oxidase Nox-4 mediates 7-ketocholesterol-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 10703–10717.
Randow F, Seed B . Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone gp96 is required for innate immunity but not cell viability. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 891–896.
Lacave R, Bens M, Cartier N, Vallet V, Robine S, Pringault E et al. Functional properties of proximal tubule cell lines derived from transgenic mice harboring L-pyruvate kinase-SV40 (T) antigen hybrid gene. J Cell Sci 1993; 104: 705–712.
Chamulitrat W, Schmidt R, Tomakidi P, Stremmel W, Chunglok W, Kawahara T et al. Association of gp91phox homolog Nox1 with anchorage-independent growth and MAP kinase-activation of transformed human keratinocytes. Oncogene 2003; 22: 6045–6053.
Goyal P, Weissmann N, Rose F, Grimminger F, Schäfers HJ, Seeger W et al. Identification of novel Nox4 splice variants with impact on ROS levels in A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 329: 32–39.
Serrander L, Cartier L, Bedard K, Banfi B, Lardy B, Plastre O et al. NOX4 activity is determined by mRNA levels and reveals a unique pattern of ROS generation. Biochem J 2007; 406: 105–114.
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Reed JC . Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2656–2664.
Yang Y, Li Z . Roles of heat shock protein gp96 in the ER quality control: redundant or unique function? Mol Cells 2005; 20: 173–182.
Kamata H, Hirata H . Redox regulation of cellular signalling. Cell Signal 1999; 11: 1–14.
Martyn KD, Frederick LM, von Loehneysen K, Dinauer MC, Knaus UG . Functional analysis of Nox4 reveals unique characteristics compared to other NADPH oxidases. Cell Signal 2006; 18: 69–82.
Wang Y, Ji HX, Zheng JN, Pei DS, Hu SQ, Qiu SL . Protective effect of selenite on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting ASK1-MKK3-p38 signal pathway. Redox Rep 2009; 14: 243–250.
Park KM, Kim JI, Ahn Y, Bonventre AJ, Bonventre JV . Testosterone is responsible for enhanced susceptibility of males to ischemic renal injury. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 52282–52292.
Pantano C, Anathy V, Ranjan P, Heintz NH, Janssen-Heininger YM . Nonphagocytic oxidase 1 causes death in lung epithelial cells via a TNF-RI-JNK signaling axis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007; 36: 473–479.
Gavazzi G, Banfi B, Deffert C, Fiette L, Schappi M, Herrmann F et al. Decreased blood pressure in NOX1-deficient mice. FEBS Lett 2006; 580: 497–504.
Chassin C, Goujon JM, Darche S, du Merle L, Bens M, Cluzeaud F et al. Renal collecting duct epithelial cells react to pyelonephritis-associated Escherichia coli by activating distinct TLR4-dependent and -independent inflammatory pathways. J Immunol 2006; 177: 4773–4784.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Akira for the use of Tlr4−/− and MyD88−/− mice. We also thank KH Krause for stimulating discussions, and for providing us with the NOX1−/− mice. We thank MW Hornef (Institut of Medical Microbiology and Hygiene, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany) for the gift of the TLR4 antibody. We also thank M Fay and G Pinon (INSERM U773, Paris, France), and B Fernandez and N Quellard (Service d’Anatomie et Cytologie Pathologiques, Hopital Universitaire de Poitiers, France) for their expert technical assistance. This work was funded by INSERM and in part by an Agence Nationale de la Recherche grant (ANR-08-MIEN-030, to AV). SBM was supported by a PhD student grant from the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer, AV was in receipt of an Interface INSERM-AP-HP fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by H Ichijo
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Mkaddem, S., Pedruzzi, E., Werts, C. et al. Heat shock protein gp96 and NAD(P)H oxidase 4 play key roles in Toll-like receptor 4-activated apoptosis during renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Differ 17, 1474–1485 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.26
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.26
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Single Cell Genomics Identifies Unique Cardioprotective Phenotype of Stem Cells derived from Epicardial Adipose Tissue under Ischemia
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2022)
-
Downregulation of XBP1 protects kidney against ischemia-reperfusion injury via suppressing HRD1-mediated NRF2 ubiquitylation
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
MicroRNA-532-3p Regulates Pro-Inflammatory Human THP-1 Macrophages by Targeting ASK1/p38 MAPK Pathway
Inflammation (2021)
-
6-O-angeloylplenolin exerts neuroprotection against lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2020)
-
Cyanidin attenuates Aβ25-35-induced neuroinflammation by suppressing NF-κB activity downstream of TLR4/NOX4 in human neuroblastoma cells
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)