Abstract
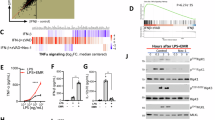
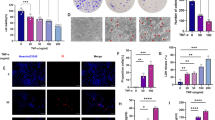
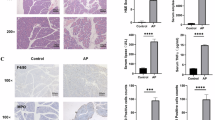
It is intriguing that some pan-caspase inhibitors such as zVAD-fmk (zVAD) are capable of inducing necrotic cell death in a selected group of cells. As earlier reports from our laboratory have ruled out the original notion that zVAD-induced necrosis in mouse fibrosarcoma L929 cells was autophagic cell death, the main objective of this study was thus to determine the underlying mechanism of this form of cell death. In this study, we provided clear evidence that zVAD-induced necroptosis in L929 cells and such cell death is dependent on autocrine production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) at the transcriptional level. More importantly, we identified that activating protein-1 (AP-1), but not nuclear factor κ-B, is the transcription factor controlling zVAD-induced TNFα transcription. Moreover, zVAD is able to activate AP-1 through activation of two upstream mitogen-activated kinases (MAPKs), c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Finally, we found that protein kinase C is the important upstream signaling molecule in mediating zVAD-induced activation of MAPKs and AP-1, and subsequent autocrine production of TNFα and cell death. Data from this study reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying zVAD-induced necroptosis, an important form of programmed necrotic cell death with increasing understanding of its biological significance in health and diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- FADD:
-
fas-associated death domain
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- RIP1:
-
receptor-interacting protein 1
- RIP3:
-
receptor-interacting protein-3
- AP-1:
-
activating protein-1
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- IKK:
-
I-κB kinase
- TNFR1:
-
TNF receptor-1
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor κ-B
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- PARP-1:
-
poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1
- TPA:
-
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
References
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH et al. Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 3–11.
White E . Autophagic cell death unraveled: pharmacological inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy enables necrosis. Autophagy 2008; 4: 399–401.
Levine B, Yuan J . Autophagy in cell death: an innocent convict? J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 2679–2688.
Zong WX, Thompson CB . Necrotic death as a cell fate. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 1–15.
Degterev A, Yuan J . Expansion and evolution of cell death programmes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 378–390.
Micheau O, Tschopp J . Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 2003; 114: 181–190.
Vercammen D, Vandenabeele P, Beyaert R, Declercq W, Fiers W . Tumour necrosis factor-induced necrosis versus anti-Fas-induced apoptosis in L929 cells. Cytokine 1997; 9: 801–808.
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L et al. Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 2009; 137: 1100–1111.
Holler N, Zaru R, Micheau O, Thome M, Attinger A, Valitutti S et al. Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat Immunol 2000; 1: 489–495.
Lin Y, Choksi S, Shen HM, Yang QF, Hur GM, Kim YS et al. Tumor necrosis factor-induced nonapoptotic cell death requires receptor-interacting protein-mediated cellular reactive oxygen species accumulation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 10822–10828.
Festjens N, Vanden Berghe T, Cornelis S, Vandenabeele P . RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell′s decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 400–410.
Kim YS, Morgan MJ, Choksi S, Liu ZG . TNF-induced activation of the Nox1 NADPH oxidase and its role in the induction of necrotic cell death. Mol Cell 2007; 26: 675–687.
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M et al. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009; 137: 1112–1123.
Zhang DW, Shao J, Lin J, Zhang N, Lu BJ, Lin SC et al. RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science 2009; 325: 332–336.
Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe T, Festjens N . Caspase inhibitors promote alternative cell death pathways. Sci STKE 2006; 2006: pe44.
Vercammen D, Beyaert R, Denecker G, Goossens V, Van Loo G, Declercq W et al. Inhibition of caspases increases the sensitivity of L929 cells to necrosis mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 1477–1485.
Lin Y, Devin A, Rodriguez Y, Liu ZG . Cleavage of the death domain kinase RIP by caspase-8 prompts TNF-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 2514–2526.
Van Noorden CJ . The history of Z-VAD-FMK, a tool for understanding the significance of caspase inhibition. Acta Histochem 2001; 103: 241–251.
Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S et al. Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 2004; 304: 1500–1502.
Wu YT, Tan HL, Huang Q, Kim YS, Pan N, Ong WY et al. Autophagy plays a protective role during zVAD-induced necrotic cell death. Autophagy 2008; 4: 457–466.
Wu YT, Tan HL, Huang Q, Ong CN, Shen HM . Activation of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway promotes necrotic cell death via suppression of autophagy. Autophagy 2009; 5: 824–834.
Chauvier D, Ankri S, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Casimir R, Jacotot E . Broad-spectrum caspase inhibitors: from myth to reality? Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 387–391.
Ray CA, Black RA, Kronheim SR, Greenstreet TA, Sleath PR, Salvesen GS et al. Viral inhibition of inflammation: cowpox virus encodes an inhibitor of the interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Cell 1992; 69: 597–604.
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch′en IL, Korkina O, Teng X et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol 2008; 4: 313–321.
Vercammen D, Vandenabeele P, Declercq W, Van de Craen M, Grooten J, Fiers W . Cytotoxicity in L929 murine fibrosarcoma cells after triggering of transfected human p75 tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor is mediated by endogenous murine TNF. Cytokine 1995; 7: 463–470.
Vince JE, Wong WW, Khan N, Feltham R, Chau D, Ahmed AU et al. IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007; 131: 682–693.
Petersen SL, Wang L, Yalcin-Chin A, Li L, Peyton M, Minna J et al. Autocrine TNFalpha signaling renders human cancer cells susceptible to Smac-mimetic-induced apoptosis. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 445–456.
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM, Fedorova AV, Kayagaki N, Garg P et al. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007; 131: 669–681.
Zalevsky J, Secher T, Ezhevsky SA, Janot L, Steed PM, O′Brien C et al. Dominant-negative inhibitors of soluble TNF attenuate experimental arthritis without suppressing innate immunity to infection. J Immunol 2007; 179: 1872–1883.
Hitomi J, Christofferson DE, Ng A, Yao J, Degterev A, Xavier RJ et al. Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway. Cell 2008; 135: 1311–1323.
Zhang S, Lin ZN, Yang CF, Shi X, Ong CN, Shen HM . Suppressed NF-kappaB and sustained JNK activation contribute to the sensitization effect of parthenolide to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004; 25: 2191–2199.
Das M, Sabio G, Jiang F, Rincon M, Flavell RA, Davis RJ . Induction of hepatitis by JNK-mediated expression of TNF-alpha. Cell 2009; 136: 249–260.
Devin A, Lin Y, Liu ZG . The role of the death-domain kinase RIP in tumour-necrosis-factor-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases. EMBO Rep 2003; 4: 623–627.
Eferl R, Wagner EF . AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 859–868.
Kresse M, Latta M, Kunstle G, Riehle HM, van Rooijen N, Hentze H et al. Kupffer cell-expressed membrane-bound TNF mediates melphalan hepatotoxicity via activation of both TNF receptors. J Immunol 2005; 175: 4076–4083.
Baud V, Karin M . Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol 2001; 11: 372–377.
Ding J, Huang Y, Ning B, Gong W, Li J, Wang H et al. TNF-alpha induction by nickel compounds is specific through ERKs/AP-1-dependent pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2009; 9: 81–90.
Mackay HJ, Twelves CJ . Targeting the protein kinase C family: are we there yet? Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7: 554–562.
Newton AC . Protein kinase C: structure, function, and regulation. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 28495–28498.
Moretti L, Kim KW, Jung DK, Willey CD, Lu B . Radiosensitization of solid tumors by Z-VAD, a pan-caspase inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 1270–1279.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Szymkowski for providing reagent. Y-T Wu is supported by an NUS research scholarship. This study is supported by grants from the NUS University Research Council (URC) and Singapore Biomedical Research Council (BMRC) to H-M Shen. This work is also supported in part by the Toxicology Program under the Life Science Institute, NUS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by P Vandenabeele
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, YT., Tan, HL., Huang, Q. et al. zVAD-induced necroptosis in L929 cells depends on autocrine production of TNFα mediated by the PKC–MAPKs–AP-1 pathway. Cell Death Differ 18, 26–37 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.72
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.72
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IKK-mediated TRAF6 and RIPK1 interaction stifles cell death complex assembly leading to the suppression of TNF-α-induced cell death
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Housing conditions affect enterocyte death mode and turnover rate in mouse small intestine
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
HSPA8 acts as an amyloidase to suppress necroptosis by inhibiting and reversing functional amyloid formation
Cell Research (2023)
-
Potential therapeutic efficiency of pan-ERBB inhibitors for canine glioma
Veterinary Research Communications (2023)
-
The regulation of necroptosis and perspectives for the development of new drugs preventing ischemic/reperfusion of cardiac injury
Apoptosis (2022)