Abstract
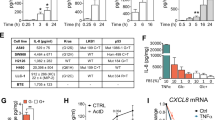
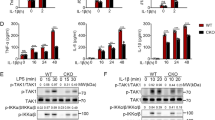
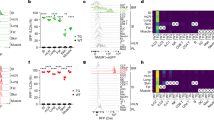
The family of death domain (DD)-containing proteins are involved in many cellular processes, including apoptosis, inflammation and development. One of these molecules, the adapter protein MyD88, is a key factor in innate and adaptive immunity that integrates signals from the Toll-like receptor/interleukin (IL)-1 receptor (TLR/IL-1R) superfamily by providing an activation platform for IL-1R-associated kinases (IRAKs). Here we show that the DD-containing protein Unc5CL (also known as ZUD) is involved in a novel MyD88-independent mode of IRAK signaling that culminates in the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Unc5CL required IRAK1, IRAK4 and TNF receptor-associated factor 6 but not MyD88 for its ability to activate these pathways. Interestingly, the protein is constitutively autoproteolytically processed, and is anchored by its N-terminus specifically to the apical face of mucosal epithelial cells. Transcriptional profiling identified mainly chemokines, including IL-8, CXCL1 and CCL20 as Unc5CL target genes. Its prominent expression in mucosal tissues, as well as its ability to induce a pro-inflammatory program in cells, suggests that Unc5CL is a factor in epithelial inflammation and immunity as well as a candidate gene involved in mucosal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- DD:
-
death domain
- EDA:
-
ectodysplasin-A
- EDAR:
-
ectodysplasin-A receptor
- IBD:
-
inflammatory bowel disease
- IκB:
-
inhibitor of kappa B
- IKKβ:
-
IκB kinase beta
- IL-1R:
-
interleukin (IL)-1 receptor
- IRAK:
-
IL-1R-associated kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MyD88:
-
myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- Nup98:
-
nuclear pore complex protein 98
- PIDD:
-
p53-induced protein with a DD
- PLA2G4C:
-
phospholipase A2 group IVC
- TIR:
-
Toll–IL-1R domain
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- TM:
-
transmembrane
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- TNFAIP3:
-
TNF alpha-induced protein 3
- TNF-RI:
-
tumor necrosis factor receptor type I
- TNFRSF9:
-
TNF receptor superfamily member 9
- TRAF6:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor 6
- Unc5CL:
-
Unc5C-like protein
- UPA, domain found in Unc5:
-
PIDD and Ankyrins
- ZU5:
-
domain found in ZO-1 and Unc5
References
O’Neill LA . The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: 10 years of progress. Immunol Rev 2008; 226: 10–18.
Kawai T, Akira S . The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 373–384.
Kawai T, Akira S . TLR signaling. Semin Immunol 2007; 19: 24–32.
Muzio M, Ni J, Feng P, Dixit VM . IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 1997; 278: 1612–1615.
Wesche H, Henzel WJ, Shillinglaw W, Li S, Cao Z . MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 1997; 7: 837–847.
Burns K, Martinon F, Esslinger C, Pahl H, Schneider P, Bodmer JL et al. MyD88, an adapter protein involved in interleukin-1 signaling. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 12203–12209.
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Kopp E, Stadlen A, Chen C, Ghosh S et al. MyD88 is an adaptor protein in the hToll/IL-1 receptor family signaling pathways. Mol Cell 1998; 2: 253–258.
Motshwene PG, Moncrieffe MC, Grossmann JG, Kao C, Ayaluru M, Sandercock AM et al. An oligomeric signaling platform formed by the Toll-like receptor signal transducers MyD88 and IRAK-4. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 25404–25411.
Lin SC, Lo YC, Wu H . Helical assembly in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature 2010; 465: 885–890.
Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV . TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 1996; 383: 443–446.
Dinarello CA . Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 519–550.
Chen K, Huang J, Gong W, Iribarren P, Dunlop NM, Wang JM . Toll-like receptors in inflammation, infection and cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 2007; 7: 1271–1285.
Picard C, von Bernuth H, Ghandil P, Chrabieh M, Levy O, Arkwright PD et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with IRAK-4 and MyD88 deficiency. Medicine (Baltimore) 2010; 89: 403–425.
Park HH, Lo YC, Lin SC, Wang L, Yang JK, Wu H . The death domain superfamily in intracellular signaling of apoptosis and inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol 2007; 25: 561–586.
Reed JC, Doctor KS, Godzik A . The domains of apoptosis: a genomics perspective. Sci STKE 2004; 2004: re9.
Wang R, Wei Z, Jin H, Wu H, Yu C, Wen W et al. Autoinhibition of UNC5b revealed by the cytoplasmic domain structure of the receptor. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 692–703.
Zhang J, Xu LG, Han KJ, Shu HB . Identification of a ZU5 and death domain-containing inhibitor of NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 17819–17825.
Cole C, Barber JD, Barton GJ . The Jpred 3 secondary structure prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36 (Web Server issue): W197–W201.
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007; 23: 2947–2948.
Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL . Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 2001; 305: 567–580.
Tinel A, Janssens S, Lippens S, Cuenin S, Logette E, Jaccard B et al. Autoproteolysis of PIDD marks the bifurcation between pro-death caspase-2 and pro-survival NF-kappaB pathway. EMBO J 2007; 26: 197–208.
Rosenblum JS, Blobel G . Autoproteolysis in nucleoporin biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 11370–11375.
Bordier C . Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem 1981; 256: 1604–1607.
Spiess M . Heads or tails--what determines the orientation of proteins in the membrane. FEBS Lett 1995; 369: 76–79.
Beltzer JP, Fiedler K, Fuhrer C, Geffen I, Handschin C, Wessels HP et al. Charged residues are major determinants of the transmembrane orientation of a signal-anchor sequence. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 973–978.
Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6062–6067.
Meunier V, Bourrie M, Berger Y, Fabre G . The human intestinal epithelial cell line Caco-2; pharmacological and pharmacokinetic applications. Cell Biol Toxicol 1995; 11: 187–194.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 2195–2224.
Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M . Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 693–733.
Ting AT, Pimentel-Muinos FX, Seed B . RIP mediates tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 activation of NF-kappaB but not Fas/APO-1-initiated apoptosis. EMBO J 1996; 15: 6189–6196.
Laurikkala J, Pispa J, Jung HS, Nieminen P, Mikkola M, Wang X et al. Regulation of hair follicle development by the TNF signal ectodysplasin and its receptor Edar. Development 2002; 129: 2541–2553.
Bossen C, Ingold K, Tardivel A, Bodmer JL, Gaide O, Hertig S et al. Interactions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF receptor family members in the mouse and human. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 13964–13971.
Yamin TT, Miller DK . The interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase is degraded by proteasomes following its phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 21540–21547.
Gribar SC, Richardson WM, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ . No longer an innocent bystander: epithelial toll-like receptor signaling in the development of mucosal inflammation. Mol Med 2008; 14: 645–659.
Viola A, Luster AD . Chemokines and their receptors: drug targets in immunity and inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2008; 48: 171–197.
Fontoura BM, Blobel G, Matunis MJ . A conserved biogenesis pathway for nucleoporins: proteolytic processing of a 186-kilodalton precursor generates Nup98 and the novel nucleoporin, Nup96. J Cell Biol 1999; 144: 1097–1112.
Janssens S, Tinel A, Lippens S, Tschopp J . PIDD mediates NF-kappaB activation in response to DNA damage. Cell 2005; 123: 1079–1092.
Kaser A, Zeissig S, Blumberg RS . Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol 2010; 28: 573–621.
Gaide O, Schneider P . Permanent correction of an inherited ectodermal dysplasia with recombinant EDA. Nat Med 2003; 9: 614–618.
Burns K, Janssens S, Brissoni B, Olivos N, Beyaert R, Tschopp J . Inhibition of interleukin 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit IRAK-4. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 263–268.
Acknowledgements
We thank C Thomas for critically reading the manuscript and A Tardivel, S Hertig, G Guarda and TK Vogt for their technical help. This work was supported by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation, NCCR Molecular Oncology, the EU-FP6 framework program RTN-ApopTrain, the Institute for Arthritis Research and Fondation Louis-Jeantet.
Author Contributions
LXH and JT designed research; LXH, MR, DCR, FS, KS, MQ, OG and PS performed the experiments; LXH, KS and OG analyzed the data; LXH and JT wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinz, L., Rebsamen, M., Rossi, D. et al. The death domain-containing protein Unc5CL is a novel MyD88-independent activator of the pro-inflammatory IRAK signaling cascade. Cell Death Differ 19, 722–731 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.147
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: SP1-induced lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 expression promotes chemoresistance of breast cancer by epigenetic regulation of MyD88
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018)
-
MicroRNA367 negatively regulates the inflammatory response of microglia by targeting IRAK4 in intracerebral hemorrhage
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015)
-
Toll-like receptor-associated sequence variants and prostate cancer risk among men of African descent
Genes & Immunity (2013)
-
P53-induced protein with a death domain (PIDD): master of puppets?
Oncogene (2012)