Abstract
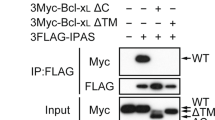
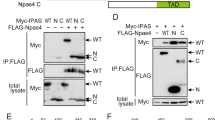
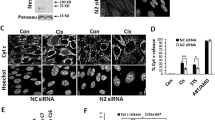
Inhibitory PAS (Per/Arnt/Sim) domain protein (IPAS) is a dominant negative transcription factor that represses hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) activity. In this study, we show that IPAS also functions as a pro-apoptotic protein through binding to pro-survival Bcl-2 family members. In a previous paper, we reported that NF-κB-dependent IPAS induction by cobalt chloride repressed the hypoxic response in PC12 cells. We found that prolonged incubation under the same conditions caused apoptosis in PC12 cells. Repression of IPAS induction protected cells from apoptosis. Furthermore, knockdown of IPAS recovered cell viability. EGFP-IPAS protein was localized in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm, with a large fraction associated with mitochondria. Mitochondrial IPAS induced mitochondria depolarization and caspase-3 activation. Immunoprecipitation assays revealed that IPAS is associated with Bcl-xL, Bcl-w and Mcl-1. The association of IPAS with Bcl-xL was also observed in living cells by the FLIM-based FRET analysis, indicating direct binding between the two proteins. IPAS contributed to dysfunction of Bcl-xL by inhibiting the interaction of Bcl-xL with Bax. These results demonstrate that IPAS functions as a dual function protein involved in transcription repression and apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- bHLH:
-
basic helix-loop-helix
- CHO:
-
Chinese hamster ovary
- CoCl2:
-
cobalt chloride
- FLIM:
-
fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy
- FRET:
-
fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- HEK:
-
human embryonic kidney
- HIF-1:
-
hypoxia-inducible factor 1
- HLF:
-
HIF-1α-like factor
- HRE:
-
hypoxia-response element
- IPAS:
-
inhibitory PAS domain protein
- Mcl-1V:
-
Mcl-1 variant
- PAS:
-
Per/Arnt/Sim
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
References
Hirota K, Semenza GL . Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 by prolyl and asparaginyl hydroxylases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 338: 610–616.
Kaelin Jr WG . The von Hippel-Lindau protein, HIF hydroxylation, and oxygen sensing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 338: 627–638.
Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ . Signalling hypoxia by HIF hydroxylases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 338: 617–626.
Makino Y, Cao R, Svensson K, Bertilsson G, Asman M, Tanaka H et al. Inhibitory PAS domain protein is a negative regulator of hypoxia-inducible gene expression. Nature 2001; 414: 550–554.
Makino Y, Uenishi R, Okamoto K, Isoe T, Hosono O, Tanaka H et al. Transcriptional up-regulation of inhibitory PAS domain protein gene expression by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1): a negative feedback regulatory circuit in HIF-1-mediated signaling in hypoxic cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14073–14082.
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M et al. Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 1998; 394: 485–490.
Bruick RK . Expression of the gene encoding the proapoptotic Nip3 protein is induced by hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 9082–9087.
Kim JY, Ahn HJ, Ryu JH, Suk K, Park JH . BH3-only protein Noxa is a mediator of hypoxic cell death induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 113–124.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Piret JP, Minet E, Cosse JP, Ninane N, Debacq C, Raes M et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent overexpression of myeloid cell factor-1 protects hypoxic cells against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 9336–9344.
Chen N, Chen X, Huang R, Zeng H, Gong J, Meng W et al. BCL-xL is a target gene regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 10004–10012.
Xu W, Chi L, Row BW, Xu R, Ke Y, Xu B et al. Increased oxidative stress is associated with chronic intermittent hypoxia-mediated brain cortical neuronal cell apoptosis in a mouse model of sleep apnea. Neuroscience 2004; 126: 313–323.
Fujimura M, Tominaga T, Chan PH . Neuroprotective effect of an antioxidant in ischemic brain injury: involvement of neuronal apoptosis. Neurocrit Care 2005; 2: 59–66.
Lipton P . Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 1999; 79: 1431–1568.
Scherz-Shouval R, Elazar Z . ROS, mitochondria and the regulation of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol 2007; 17: 422–427.
Wang G, Hazra TK, Mitra S, Lee HM, Englander EW . Mitochondrial DNA damage and a hypoxic response are induced by CoCl2 in rat neuronal PC12 cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2000; 28: 2135–2140.
Jung JY, Kim WJ . Involvement of mitochondrial- and Fas-mediated dual mechanism in CoCl2-induced apoptosis of rat PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 2004; 371: 85–90.
Jung JY, Han CR, Jeong YJ, Kim HJ, Lim HS, Lee KH et al. Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in rat PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett 2007; 411: 222–227.
Jung JY, Roh KH, Jeong YJ, Kim SH, Lee EJ, Kim MS et al. Estradiol protects PC12 cells against CoCl2-induced apoptosis. Brain Res Bull 2008; 76: 579–585.
Araya J, Maruyama M, Inoue A, Fujita T, Kawahara J, Sassa K et al. Inhibition of proteasome activity is involved in cobalt-induced apoptosis of human alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002; 283: L849–L858.
Chachami G, Simos G, Hatziefthimiou A, Bonanou S, Molyvdas PA, Paraskeva E . Cobalt induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in airway smooth muscle cells by a reactive oxygen species- and PI3K-dependent mechanism. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2004; 31: 544–551.
Griguer CE, Oliva CR, Kelley EE, Giles GI, Lancaster Jr JR, Gillespie GY . Xanthine oxidase-dependent regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor in cancer cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 2257–2263.
Torii S, Kobayashi K, Takahashi M, Katahira K, Goryo K, Matsushita N et al. Magnesium deficiency causes loss of response to intermittent hypoxia in paraganglion cells. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 19077–19089.
Hu Y, Benedict MA, Wu D, Inohara N, Nunez G . Bcl-XL interacts with Apaf-1 and inhibits Apaf-1-dependent caspase-9 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 4386–4391.
Yuan J, Yankner BA . Apoptosis in the nervous system. Nature 2000; 407: 802–809.
Shen J, Cookson MR . Mitochondria and dopamine: new insights into recessive parkinsonism. Neuron 2004; 43: 301–304.
Yasumoto K, Kowata Y, Yoshida A, Torii S, Sogawa K . Role of the intracellular localization of HIF-prolyl hydroxylases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793: 792–797.
Tomokuni Y, Goryo K, Katsura A, Torii S, Yasumoto K, Kemnitz K et al. Loose interaction between glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate kinase revealed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer-fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy in living cells. Febs J 2010; 277: 1310–1318.
Carpentier E, Paris S, Kamen AA, Durocher Y . Limiting factors governing protein expression following polyethylenimine-mediated gene transfer in HEK293-EBNA1 cells. J Biotechnol 2007; 128: 268–280.
Ema M, Hirota K, Mimura J, Abe H, Yodoi J, Sogawa K et al. Molecular mechanisms of transcription activation by HLF and HIF1alpha in response to hypoxia: their stabilization and redox signal-induced interaction with CBP/p300. Embo J 1999; 18: 1905–1914.
Torii S, Kusakabe M, Yamamoto T, Maekawa M, Nishida E . Sef is a spatial regulator for Ras/MAP kinase signaling. Dev Cell 2004; 7: 33–44.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Y Makino for the gift of mouse IPAS cDNA. We also thank K Saka, N Tajikawa and A Suzuki for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by V De Laurenzi
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torii, S., Goto, Y., Ishizawa, T. et al. Pro-apoptotic activity of inhibitory PAS domain protein (IPAS), a negative regulator of HIF-1, through binding to pro-survival Bcl-2 family proteins. Cell Death Differ 18, 1711–1725 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.47
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.47
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cobalt chloride postconditioning as myoprotective therapy in cardiac ischemia–reperfusion
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2022)
-
Attenuation of inhibitory PAS domain protein-induced cell death by synthetic peptides derived from Mcl-1 transmenbrane domain
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Direct protein–protein interaction between Npas4 and IPAS mutually inhibits their critical roles in neuronal cell survival and death
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Inhibitory PAS domain protein is a substrate of PINK1 and Parkin and mediates cell death in a Parkinson’s disease model
Cell Death & Disease (2015)
-
Involvement of inhibitory PAS domain protein in neuronal cell death in Parkinson’s disease
Cell Death Discovery (2015)