Abstract
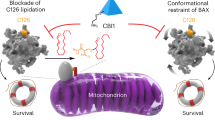
The proapoptotic Bcl-2 protein Bax can commit a cell to apoptosis by translocation from the cytosol to the mitochondria and permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Prosurvival Bcl-2 family members, such as Bcl-xL, control Bax activity. Bcl-xL recognizes Bax after a conformational change in the N-terminal segment of Bax on the mitochondria and retrotranslocates it back into the cytoplasm, stabilizing the inactive form of Bax. Here we show that Bax retrotranslocation depends on the C-terminal helix of Bcl-xL. Deletion or substitution of this segment reduces Bax retrotranslocation and correlates with the accumulation of GFP-tagged or endogenous Bax on the mitochondria of non-apoptotic cells. Unexpectedly, the substitution of the Bcl-xL membrane anchor by the corresponding Bax segment reverses the Bax retrotranslocation activity of Bcl-xL, but not that of Bcl-xL shuttling. Bax retrotranslocation depends on interaction to the Bcl-xL membrane anchor and interaction between the Bax BH3 domain and the Bcl-xL hydrophobic cleft. Interference with either interaction increases mitochondrial levels of endogenous Bax. In healthy cells, mitochondrial Bax does not permeabilize the outer mitochondrial membrane, but increases cell death after apoptosis induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- OMM:
-
outer mitochondrial membrane
- cyt c:
-
cytochrome c
- FLIP:
-
fluorescence loss in photobleaching
- STS:
-
staurosporine
- Mfn2:
-
mitofusin 2
References
Green DR, Kroemer G . The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 2004; 305: 626–629.
Martinou J-C, Youle RJ . Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 2011; 21: 92–101.
Adams JM, Cory S . Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis: mechanism and therapeutic potential. Curr Opin Immunol 2007; 19: 488–496.
Llambi F, Moldoveanu T, Tait SW, Bouchier-Hayes L, Temirov J, McCormick LL et al. A unified model of mammalian BCL-2 protein family interactions at the mitochondria. Mol Cell 2011; 44: 517–531.
Hsu YT, Wolter KG, Youle RJ . Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 3668–3672.
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ et al. Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1997; 139: 1281–1292.
Hsu YT, Youle RJ . Bax in murine thymus is a soluble monomeric protein that displays differential detergent-induced conformations. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 10777–10783.
Annis MG, Soucie EL, Dlugosz PJ, Cruz-Aguado JA, Penn LZ, Leber B et al. Bax forms multispanning monomers that oligomerize to permeabilize membranes during apoptosis. EMBO J 2005; 24: 2096–2103.
Edlich F, Banerjee S, Suzuki M, Cleland MM, Arnoult D, Wang C et al. Bcl-x(L) retrotranslocates Bax from the mitochondria into the cytosol. Cell 2011; 145: 104–116.
Eskes R, Antonsson B, Osen-Sand A, Montessuit S, Richter C, Sadoul R et al. Bax-induced cytochrome C release from mitochondria is independent of the permeability transition pore but highly dependent on Mg2+ ions. J Cell Biol 1998; 143: 217–224.
Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ . Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J 1998; 17: 3878–3885.
Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Nichols A, Eskes R, Montessuit S, Lauper S et al. Bid-induced conformational change of Bax is responsible for mitochondrial cytochrome c release during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1999; 144: 891–901.
Fletcher JI, Meusburger S, Hawkins CJ, Riglar DT, Lee EF, Fairlie WD et al. Apoptosis is triggered when prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins cannot restrain Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 18081–18087.
Valentijn AJ, Metcalfe AD, Kott J, Streuli CH, Gilmore AP . Spatial and temporal changes in Bax subcellular localization during anoikis. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 599–612.
Owens TW, Valentijn AJ, Upton JP, Keeble J, Zhang L, Lindsay J et al. Apoptosis commitment and activation of mitochondrial Bax during anoikis is regulated by p38MAPK. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 1551–1562.
Karbowski M, Norris KL, Cleland MM, Jeong S-Y, Youle RJ . Role of Bax and Bak in mitochondrial morphogenesis. Nature 2006; 443: 658–662.
Sheridan C, Delivani P, Cullen SP, Martin SJ . Bax- or Bak-induced mitochondrial fission can be uncoupled from cytochrome C release. Mol Cell 2008; 31: 570–585.
Berman SB, Chen YB, Qi B, McCaffery JM, Rucker EB, Goebbels S et al. Bcl-x L increases mitochondrial fission, fusion, and biomass in neurons. J Cell Biol 2009; 184: 707–719.
Meeusen S, McCaffery JM, Nunnari J . Mitochondrial fusion intermediates revealed in vitro. Science 2004; 305: 1747–1752.
Hoppins S, Edlich F, Cleland MM, Banerjee S, McCaffery JM, Youle RJ et al. The soluble form of Bax regulates mitochondrial fusion via MFN2 homotypic complexes. Mol Cell 2011; 41: 150–160.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 389–399.
Jeong S-Y, Gaume B, Lee YJ, Hsu YT, Ryu SW, Yoon SH et al. Bcl-x(L) sequesters its C-terminal membrane anchor in soluble, cytosolic homodimers. EMBO J 2004; 23: 2146–2155.
Goping IS, Gross A, Lavoie JN, Nguyen M, Jemmerson R, Roth K et al. Regulated targeting of BAX to mitochondria. J Cell Biol 1998; 143: 207–215.
Gavathiotis E, Reyna DE, Davis ML, Bird GH, Walensky LD . BH3-triggered structural reorganization drives the activation of proapoptotic BAX. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 481–492.
Sedlak TW, Oltvai ZN, Yang E, Wang K, Boise LH, Thompson CB et al. Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimerizations with Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1995; 92: 7834–7838.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ et al. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 2001; 292: 727–730.
Soucie EL, Annis MG, Sedivy J, Filmus J, Leber B, Andrews DW et al. Myc potentiates apoptosis by stimulating Bax activity at the mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 4725–4736.
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA et al. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 351–365.
Mason KD, Carpinelli MR, Fletcher JI, Collinge JE, Hilton AA, Ellis S et al. Programmed anuclear cell death delimits platelet life span. Cell 2007; 128: 1173–1186.
Wang C, Youle RJ . Predominant requirement of Bax for apoptosis in HCT116 cells is determined by Mcl-1’s inhibitory effect on Bak. Oncogene 2011; 31: 3177–3189.
Acknowledgements
We thank S Liebscher for superb technical assistance. This work is supported by the Emmy Noether program of the German Research Council (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) and the NINDS intramural programs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by C Borner
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todt, F., Cakir, Z., Reichenbach, F. et al. The C-terminal helix of Bcl-xL mediates Bax retrotranslocation from the mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 20, 333–342 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.131
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BAX activation in mouse retinal ganglion cells occurs in two temporally and mechanistically distinct steps
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Visualization of BOK pores independent of BAX and BAK reveals a similar mechanism with differing regulation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Acetic acid triggers cytochrome c release in yeast heterologously expressing human Bax
Apoptosis (2022)
-
BH3-only proteins are dispensable for apoptosis induced by pharmacological inhibition of both MCL-1 and BCL-XL
Cell Death & Differentiation (2019)
-
BFL1 modulates apoptosis at the membrane level through a bifunctional and multimodal mechanism showing key differences with BCLXL
Cell Death & Differentiation (2019)