Abstract
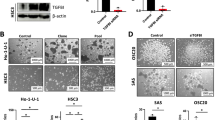
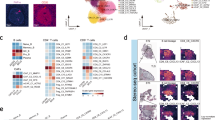
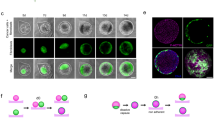
Caspases mediate apoptosis and have also been implicated in stem-cell biology. How caspases are linked to stem-cell biology is not known. Here, we show that the apoptotic blebs of cancer cells fuse together to form novel structures called ‘blebbishields’. Blebbishields form spheres by fusion. Both blebbishield formation and sphere formation involve active caspases and N-linked glycosylation. Sphere formation is enhanced by acidic pH and is counteracted by inhibitors of proton pump, caspases, and cholesterol. The blebbishields from VEGFR2High cells are capable of enhanced sphere formation. Blebbishields express transiently downregulated stem-cell markers and the sphere-forming blebbishield-derived cells are tumorigenic. Our study demonstrates that the cancer stem cells can survive after apoptosis by blebbishield formation and subsequent sphere formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- p70S6K:
-
70-kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase
- VEGF-A:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor-A
- VEGFR2:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2
- GSK-3β:
-
glycogen synthase kinase-3β
- BSE-2:
-
blebbishield serial ejection-2
- CSCs:
-
cancer stem cells
- TSC-2:
-
tuberous sclerosis complex-2
- NEAA:
-
non-essential amino acids
- 4EBP1:
-
4E binding protein-1
- PARP:
-
poly-ADP ribose polymerase
- BE medium:
-
blebbishield ejection medium
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
- PPI:
-
proton pump inhibitor
- ABCB1:
-
ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member-1
- CD44:
-
cluster of differentiation 44
- CK-20:
-
cytokeratin 20
References
Knoepfler PS . Why myc? An unexpected ingredient in the stem cell cocktail. Cell Stem Cell 2008; 2: 18–21.
Li F, He Z, Shen J, Huang Q, Li W, Liu X et al. Apoptotic caspases regulate induction of iPSCs from human fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 2010; 7: 508–520.
Kim J, Woo AJ, Chu J, Snow JW, Fujiwara Y, Kim CG et al. A Myc network accounts for similarities between embryonic stem and cancer cell transcription programs. Cell 2010; 143: 313–324.
Klonisch T, Wiechec E, Hombach-Klonisch S, Ande SR, Wesselborg S, Schulze-Osthoff K et al. Cancer stem cell markers in common cancers—therapeutic implications. Trends Mol Med 2008; 14: 450–460.
Golebiewska A, Brons NH, Bjerkvig R, Niclou SP . Critical appraisal of the side population assay in stem cell and cancer stem cell research. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 8: 136–147.
Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S . Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 275–284.
Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol G, Vecchi M, Ronzoni S et al. Biological and molecular heterogeneity of breast cancers correlates with their cancer stem cell content. Cell 2010; 140: 62–73.
Maugeri-Sacca M, Vigneri P, De Maria R . Cancer stem cells and chemosensitivity. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 4942–4947.
Cho RW, Clarke MF . Recent advances in cancer stem cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2008; 18: 48–53.
Nunez R, Sancho-Martinez SM, Novoa JM, Lopez-Hernandez FJ . Apoptotic volume decrease as a geometric determinant for cell dismantling into apoptotic bodies. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 1665–1671.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ . Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 755–768.
Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES, Hynes RO . Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 2000; 406: 532–535.
Gleason CE, Ning Y, Cominski TP, Gupta R, Kaestner KH, Pintar JE et al. Role of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) in organismal and pancreatic beta-cell growth. Mol Endocrinol 2010; 24: 178–192.
Zhang HH, Lipovsky AI, Dibble CC, Sahin M, Manning BD . S6K1 regulates GSK3 under conditions of mTOR-dependent feedback inhibition of Akt. Mol Cell 2006; 24: 185–197.
Armstrong JL, Bonavaud SM, Toole BJ, Yeaman SJ . Regulation of glycogen synthesis by amino acids in cultured human muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 952–956.
Dhar R, Persaud SD, Mireles JR, Basu A . Proteolytic cleavage of p70 ribosomal S6 kinase by caspase-3 during DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Biochemistry 2009; 48: 1474–1480.
Constantinou C, Elia A, Clemens MJ . Activation of p53 stimulates proteasome-dependent truncation of eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1). Biol Cell 2008; 100: 279–289.
Sato N, Meijer L, Skaltsounis L, Greengard P, Brivanlou AH . Maintenance of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells through activation of Wnt signaling by a pharmacological GSK-3-specific inhibitor. Nat Med 2004; 10: 55–63.
Laurenti E, Varnum-Finney B, Wilson A, Ferrero I, Blanco-Bose WE, Ehninger A et al. Hematopoietic stem cell function and survival depend on c-Myc and N-Myc activity. Cell Stem Cell 2008; 3: 611–624.
Yamamoto T, Yoneda K, Ueta E, Doi S, Osaki T . Enhanced apoptosis of squamous cell carcinoma cells by interleukin-2-activated cytotoxic lymphocytes combined with radiation and anticancer drugs. Eur J Cancer 2000; 36: 2007–2017.
Andrade F, Roy S, Nicholson D, Thornberry N, Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L . Granzyme B directly and efficiently cleaves several downstream caspase substrates: implications for CTL-induced apoptosis. Immunity 1998; 8: 451–460.
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K, Salvesen GS, Reed JC . Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J 1999; 18: 5242–5251.
Prescher JA, Bertozzi CR . Chemical technologies for probing glycans. Cell 2006; 126: 851–854.
Veugelers K, Motyka B, Goping IS, Shostak I, Sawchuk T, Bleackley RC . Granule-mediated killing by granzyme B and perforin requires a mannose 6-phosphate receptor and is augmented by cell surface heparan sulfate. Mol Biol Cell 2006; 17: 623–633.
Chernomordik LV, Leikina E, Frolov V, Bronk P, Zimmerberg J . An early stage of membrane fusion mediated by the low pH conformation of influenza hemagglutinin depends upon membrane lipids. J Cell Biol 1997; 136: 81–93.
Parolini I, Federici C, Raggi C, Lugini L, Palleschi S, De Milito A et al. Microenvironmental pH is a key factor for exosome traffic in tumor cells. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 34211–34222.
Fais S, De Milito A, You H, Qin W . Targeting vacuolar H+-ATPases as a new strategy against cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10627–10630.
Hjelmeland AB, Wu Q, Heddleston JM, Choudhary GS, MacSwords J, Lathia JD et al. Acidic stress promotes a glioma stem cell phenotype. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 829–840.
Fais S . Proton pump inhibitor-induced tumour cell death by inhibition of a detoxification mechanism. J Intern Med 2010; 267: 515–525.
Raaijmakers MH, Scadden DT . Divided within: heterogeneity within adult stem cell pools. Cell 2008; 135: 1006–1008.
Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP, Sherman D, Liang XH, Meng G et al. VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism. Nature 2002; 417: 954–958.
Takahashi T, Shibuya M . The 230kDa mature form of KDR/Flk-1 (VEGF receptor-2) activates the PLC-gamma pathway and partially induces mitotic signals in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene 1997; 14: 2079–2089.
You WK, Kasman I, Hu-Lowe DD, McDonald DM . Ricinus communis agglutinin I leads to rapid down-regulation of VEGFR-2 and endothelial cell apoptosis in tumor blood vessels. Am J Pathol 2010; 176: 1927–1940.
Meyer RD, Srinivasan S, Singh AJ, Mahoney JE, Gharahassanlou KR, Rahimi N . PEST motif serine and tyrosine phosphorylation controls vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 stability and downregulation. Mol Cell Biol 2011; 31: 2010–2025.
Hamerlik P, Lathia JD, Rasmussen R, Wu Q, Bartkova J, Lee M et al. Autocrine VEGF-VEGFR2-Neuropilin-1 signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell viability and tumor growth. J Exp Med 2012; 209: 507–520.
Banerjee A, Lang JY, Hung MC, Sengupta K, Banerjee SK, Baksi K et al. Unfolded protein response is required in nu/nu mice microvasculature for treating breast tumor with tunicamycin. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 29127–29138.
Dougher AM, Wasserstrom H, Torley L, Shridaran L, Westdock P, Hileman RE et al. Identification of a heparin binding peptide on the extracellular domain of the KDR VEGF receptor. Growth Factors 1997; 14: 257–268.
Xu L, Fukumura D, Jain RK . Acidic extracellular pH induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in human glioblastoma cells via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway: mechanism of low pH-induced VEGF. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 11368–11374.
Taraboletti G, D'Ascenzo S, Giusti I, Marchetti D, Borsotti P, Millimaggi D et al. Bioavailability of VEGF in tumor-shed vesicles depends on vesicle burst induced by acidic pH. Neoplasia 2006; 8: 96–103.
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D . Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14863–14868.
Kamat AM, Karashima T, Davis DW, Lashinger L, Bar-Eli M, Millikan R et al. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib synergizes with gemcitabine to block the growth of human 253JB-V bladder tumors in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 2004; 3: 279–290.
Kamat AM, Tharakan ST, Sung B, Aggarwal BB . Curcumin potentiates the antitumor effects of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin against bladder cancer through the downregulation of NF-kappaB and upregulation of TRAIL receptors. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 8958–8966.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Dr. David J McConkey for generously providing microarray data, cell lines, and for intellectual and editorial help with the manuscript, and Drs Bharat B. Aggarwal, Gomez-Manzano Candelaria, Felipe Samaniego, Isaiah J Fidler, Sun-Jin Kim, Guillermo Garcia-Manero, Xiongbin Lu, Chun Li, Gordon B Mills, and Molina Jennifer for providing cell lines/reagents, Dr. Robert R Langley and Mr. Kenneth Dunner Jr. for helping with electron microscopy, Mr. Kunal Mandal and Ms. Karen Ramirez for helping in cell sorting, Dr. Aron Mobley, Dr. Neema Navai and Ms. I-Ling Lee for various helps, Ms. Deming Stephanie for editorial assistance with the manuscript. GJG was supported by MD Anderson Cancer Center and the Clayton Foundation for Research. This research was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health through MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Support Grant, CA016672.
Author contributions
GJG designed, performed all experiments (except microarray), interpreted and documented results, and wrote the manuscript. WC contributed to the microarray experiment. JBS, EKL, DLW, and GJG performed the orthotopic mice experiments. AMK provided expert guidance in the design of experiments and interpretation of data, writing the manuscript, and generating the RT4v6 cell line.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by R De Maria
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death & Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jinesh, G., Choi, W., Shah, J. et al. Blebbishields, the emergency program for cancer stem cells: sphere formation and tumorigenesis after apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 20, 382–395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.140
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Beyond Death: Unmasking the Intricacies of Apoptosis Escape
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2024)
-
Bladder cancer: therapeutic challenges and role of 3D cell culture systems in the screening of novel cancer therapeutics
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Targeting K-Ras and apoptosis-driven cellular transformation in cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Mutant p53s and chromosome 19 microRNA cluster overexpression regulate cancer testis antigen expression and cellular transformation in hepatocellular carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Requirement of transcription factor NME2 for the maintenance of the stemness of gastric cancer stem-like cells
Cell Death & Disease (2021)