Abstract
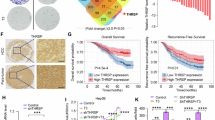
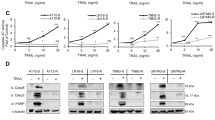
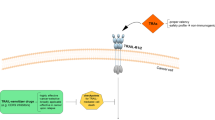
Although accumulating evidence has confirmed the important roles of thyroid hormone (T3) and its receptors (TRs) in tumor progression, the specific functions of TRs in carcinogenesis remain unclear. In the present study, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) was directly upregulated by T3 in TR-overexpressing hepatoma cell lines. TRAIL is an apoptotic inducer, but it can nonetheless trigger non-apoptotic signals favoring tumorigenesis in apoptosis-resistant cancer cells. We found that TR-overexpressing hepatoma cells treated with T3 were apoptosis resistant, even when TRAIL was upregulated. This apoptotic resistance may be attributable to simultaneous upregulation of Bcl-xL by T3, because (1) knockdown of T3-induced Bcl-xL expression suppressed T3-mediated protection against apoptosis, and (2) overexpression of Bcl-xL further protected hepatoma cells from TRAIL-induced apoptotic death, consequently leading to TRAIL-promoted metastasis of hepatoma cells. Moreover, T3-enhanced metastasis in vivo was repressed by the treatment of TRAIL-blocking antibody. Notably, TRAIL was highly expressed in a subset of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients, and this high-level expression was significantly correlated with that of TRs in these HCC tissues. Together, our findings provide evidence for the existence of a novel mechanistic link between increased TR and TRAIL levels in HCC. Thus, TRs induce TRAIL expression, and TRAIL thus synthesized acts in concert with simultaneously synthesized Bcl-xL to promote metastasis, but not apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- T3:
-
thyroid hormone
- TRs:
-
thyroid hormone receptors
- TRE:
-
thyroid response element
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- ActD:
-
actinomycin D
- CHX:
-
cycloheximide
- (r)-TRAIL:
-
recombinant TRAIL
- Ad-TRAIL:
-
Adenovirus expressing TRAIL
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- cFLIP:
-
cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloproteinase
- SCID:
-
severe combined immunodeficiency
- H&E:
-
hematoxylin and eosin
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemical staining
- ChIP:
-
chromatin immunoprecipitation
References
Huang YH, Tsai MM, Lin KH . Thyroid hormone dependent regulation of target genes and their physiological significance. Chang Gung Med J 2008; 31: 325–334.
Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Garcia V, Bonilla F, Munoz A . Thyroid hormone receptors/THR genes in human cancer. Cancer Lett 2003; 192: 121–132.
Barlow C, Meister B, Lardelli M, Lendahl U, Vennstrom B . Thyroid abnormalities and hepatocellular carcinoma in mice transgenic for v-erbA. Embo J 1994; 13: 4241–4250.
Sap J, Munoz A, Damm K, Goldberg Y, Ghysdael J, Leutz A et al. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature 1986; 324: 635–640.
Lin KH, Shieh HY, Chen SL, Hsu HC . Expression of mutant thyroid hormone nuclear receptors in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Carcinog 1999; 26: 53–61.
Chan IH, Privalsky ML . Thyroid hormone receptors mutated in liver cancer function as distorted antimorphs. Oncogene 2006; 25: 3576–3588.
Chan IH, Privalsky ML . Thyroid hormone receptor mutants implicated in human hepatocellular carcinoma display an altered target gene repertoire. Oncogene 2009; 28: 4162–4174.
Davis FB, Tang HY, Shih A, Keating T, Lansing L, Hercbergs A et al. Acting via a cell surface receptor, thyroid hormone is a growth factor for glioma cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7270–7275.
Plateroti M, Kress E, Mori JI, Samarut J . Thyroid hormone receptor alpha1 directly controls transcription of the beta-catenin gene in intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 3204–3214.
Wu SM, Huang YH, Yeh CT, Tsai MM, Liao CH, Cheng WL et al. Cathepsin H regulated by the thyroid hormone receptors associate with tumor invasion in human hepatoma cells. Oncogene 2011; 30: 2057–2069.
Kress E, Skah S, Sirakov M, Nadjar J, Gadot N, Scoazec JY et al. Cooperation between the thyroid hormone receptor TRα1 and the WNT pathway in the induction of intestinal tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 1863–1874 e1.
Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Baba M, Okuda S, Taniguchi H . Enhancement by thyroxine of experimental carcinogenesis induced in rat colon by azoxymethane. Int J Cancer 1992; 50: 974–976.
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 1995; 3: 673–682.
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A . Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 12687–12690.
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ, Smyth MJ . The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 782–798.
Trauzold A, Siegmund D, Schniewind B, Sipos B, Egberts J, Zorenkov D et al. TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2006; 25: 7434–7439.
Ehrenschwender M, Siegmund D, Wicovsky A, Kracht M, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Spindler V et al. Mutant PIK3CA licenses TRAIL and CD95L to induce non-apoptotic caspase-8-mediated ROCK activation. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 1435–1447.
Ishimura N, Isomoto H, Bronk SF, Gores GJ . Trail induces cell migration and invasion in apoptosis-resistant cholangiocarcinoma cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006; 290: G129–G136.
Hoogwater FJ, Nijkamp MW, Smakman N, Steller EJ, Emmink BL, Westendorp BF et al. Oncogenic K-Ras turns death receptors into metastasis-promoting receptors in human and mouse colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 2357–2367.
Fingas CD, Blechacz BRA, Smoot RL, Guicciardi ME, Mott J, Bronk SF et al. A smac mimetic reduces TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced invasion and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Hepatology 2010; 52: 550–561.
Spierings DC, de Vries EG, Timens W, Groen HJ, Boezen HM, de Jong S . Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL death receptors in stage III non-small cell lung cancer tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 3397–3405.
Ozawa F, Friess H, Kleeff J, Xu ZW, Zimmermann A, Sheikh MS et al. Effects and expression of TRAIL and its apoptosis-promoting receptors in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 2001; 163: 71–81.
Zender L, Hutker S, Mundt B, Waltemathe M, Klein C, Trautwein C et al. NFkappaB-mediated upregulation of bcl-xl restrains TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in murine viral hepatitis. Hepatology 2005; 41: 280–288.
Muhlethaler-Mottet A, Bourloud KB, Auderset K, Joseph JM, Gross N . Drug-mediated sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in caspase-8-complemented neuroblastoma cells proceeds via activation of intrinsic and extrinsic pathways and caspase-dependent cleavage of XIAP, Bcl-xL and RIP. Oncogene 2004; 23: 5415–5425.
Malhi H, Gores GJ . TRAIL resistance results in cancer progression: a TRAIL to perdition? Oncogene 2006; 25: 7333–7335.
Guigon CJ, Cheng SY . Novel oncogenic actions of TRbeta mutants in tumorigenesis. IUBMB Life 2009; 61: 528–536.
Martinez-Iglesias O, Garcia-Silva S, Tenbaum SP, Regadera J, Larcher F, Paramio JM et al. Thyroid hormone receptor beta1 acts as a potent suppressor of tumor invasiveness and metastasis. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 501–509.
Hall LC, Salazar EP, Kane SR, Liu N . Effects of thyroid hormones on human breast cancer cell proliferation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2008; 109: 57–66.
Rae MT, Gubbay O, Kostogiannou A, Price D, Critchley HO, Hillier SG . Thyroid hormone signaling in human ovarian surface epithelial cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92: 322–327.
Hetschko H, Voss V, Horn S, Seifert V, Prehn JH, Kogel D . Pharmacological inhibition of Bcl-2 family members reactivates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 2008; 86: 265–272.
Secchiero P . TRAIL promotes the survival and proliferation of primary human vascular endothelial cells by activating the Akt and ERK pathways. Circulation 2003; 107: 2250–2256.
Wei W, Wang D, Shi J, Xiang Y, Zhang Y, Liu S et al. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces chemotactic migration of monocytes via a death receptor 4-mediated RhoGTPase pathway. Mol Immunol 2010; 47: 2475–2484.
Grimm M, Kim M, Rosenwald A, von Rahden B, Tsaur I, Meier E et al. Tumour-mediated TRAIL-receptor expression indicates effective apoptotic depletion of infiltrating CD8+ immune cells in clinical colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 2010; 46: 2314–2323.
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese P, Squarcina P et al. Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 1796–1804.
Zhou DH, Trauzold A, Roder C, Pan G, Zheng C, Kalthoff H . The potential molecular mechanism of overexpression of uPA, IL-8, MMP-7 and MMP-9 induced by TRAIL in pancreatic cancer cell. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2008; 7: 201–209.
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z . How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2001; 17: 463–516.
Kim JH, Choi C, Benveniste EN, Kwon D . TRAIL induces MMP-9 expression via ERK activation in human astrocytoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 377: 195–199.
Liao CJ, Wu TI, Huang YH, Chang TC, Wang CS, Tsai MM et al. Glucose-regulated protein 58 modulates cell invasiveness and serves as a prognostic marker for cervical cancer. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: 2255–2263.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Chang-Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan (CMRPD 34013, NMRP 140511) and National Science Council of the Republic of China (NSC 94–2320-B-182–052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by JP Medema
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, HC., Chen, SL., Liao, CJ. et al. Thyroid hormone receptors promote metastasis of human hepatoma cells via regulation of TRAIL. Cell Death Differ 19, 1802–1814 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.58
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.58
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular functions and clinical impact of thyroid hormone-triggered autophagy in liver-related diseases
Journal of Biomedical Science (2019)
-
Thyroid hormone protects hepatocytes from HBx-induced carcinogenesis by enhancing mitochondrial turnover
Oncogene (2017)
-
Chemotherapy resistance and metastasis-promoting effects of thyroid hormone in hepatocarcinoma cells are mediated by suppression of FoxO1 and Bim pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2016)
-
Recurrence of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma During Full TSH Suppression: Is the Tumor Now Thyroid Hormone Dependent?
Hormones and Cancer (2015)
-
Restoring TRAIL Mediated Signaling in Ovarian Cancer Cells
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2014)