Abstract
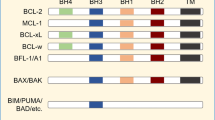
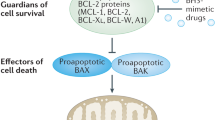
B-RAF is mutated to a constitutively active form in 8% of human cancers including 50% of melanomas. In clinical trials, the RAF inhibitor, PLX4032 (vemurafenib), caused partial or complete responses in 48–81% of mutant B-RAF harboring melanoma patients. However, the average duration of response was 6–7 months before tumor regrowth, indicating the acquisition of resistance to PLX4032. To understand the mechanisms of resistance, we developed mutant B-RAF melanoma cells that displayed resistance to RAF inhibition through continuous culture with PLX4720 (the tool compound for PLX4032). Resistance was associated with a partial reactivation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) signaling, recovery of G1/S cell-cycle events, and suppression of the pro-apoptotic B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) homology domain 3 (BH3)-only proteins, Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death-extra large (Bim-EL) and Bcl-2 modifying factor (Bmf). Preventing ERK1/2 reactivation with MEK (mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase) inhibitors blocked G1-S cell-cycle progression but failed to induce apoptosis or upregulate Bim-EL and Bmf. Treatment with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, led to de-repression of Bim-EL and enhanced cell death in the presence of PLX4720 or AZD6244 in resistant cells. These data indicate that acquired resistance to PLX4032/4720 likely involves ERK1/2 pathway reactivation as well as ERK1/2-independent silencing of BH3-only proteins. Furthermore, combined treatment of HDAC inhibitors and MEK inhibitors may contribute to overcoming PLX4032 resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ERK1/2:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
- BH3:
-
Bcl-2 homology domain 3
- Bim-EL:
-
Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death-extra large
- Bmf:
-
Bcl-2 modifying factor
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- SAHA:
-
suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid
- MEK:
-
mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase
- HER2:
-
human epidermal receptor 2
- BCR-ABL:
-
Breakpoint cluster region-v-abl abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1
- EGFR:
-
epidermal growth factor receptor
- PTEN:
-
phosphatase and tensin homolog
- PDGFRβ:
-
platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta
- IGF1R:
-
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- MAP3K:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- siRNA:
-
small interfering ribonucleic acid
- FAK:
-
focal adhesion kinase
- Rb:
-
retinoblastoma 1
- EdU:
-
5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2
- Bcl-xl:
-
B-cell lymphoma-extra large
- Mcl-1:
-
myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1
- Bad:
-
Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter
- qRT-PCR:
-
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- eGFP:
-
enhanced green fluorescence protein
- RTK:
-
receptor tyrosine kinase
- FoxO1:
-
forkhead box O1
- FoxO3a:
-
forkhead box O3a
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
References
Sharma SV, Settleman J . Oncogene addiction: setting the stage for molecularly targeted cancer therapy. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 3214–3231.
Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J, Baughman S, Benz C, Dantis L et al. Phase II study of weekly intravenous recombinant humanized anti-p185HER2 monoclonal antibody in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 737–744.
Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from ‘never smokers’ and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 13306–13311.
Druker BJ, Guilhot Fo,, O'Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2408–2417.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002; 417: 949–954.
Hingorani SR, Jacobetz MA, Robertson GP, Herlyn M, Tuveson DA . Suppression of BRAF(V599E) in human melanoma abrogates transformation. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 5198–5202.
Collisson EA, De A, Suzuki H, Gambhir SS, Kolodney MS . Treatment of metastatic melanoma with an orally available inhibitor of the Ras-Raf-MAPK cascade. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 5669–5673.
Sumimoto H, Miyagishi M, Miyoshi H, Yamagata S, Shimizu A, Taira K et al. Inhibition of growth and invasive ability of melanoma by inactivation of mutated BRAF with lentivirus-mediated RNA interference. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6031–6039.
Karasarides M, Chiloeches A, Hayward R, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Scanlon I, Friedlos F et al. B-RAF is a therapeutic target in melanoma. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6292–6298.
Bhatt KV, Spofford LS, Aram G, McMullen M, Pumiglia K, Aplin AE . Adhesion control of cyclin D1 and p27Kip1 levels is deregulated in melanoma cells through BRAF-MEK-ERK signaling. Oncogene 2005; 12: 3459–3471.
Boisvert-Adamo K, Aplin AE . B-RAF and PI-3 kinase signaling protect melanoma cells from anoikis. Oncogene 2006; 25: 4848–4856.
Sharma A, Trivedi NR, Zimmerman MA, Tuveson DA, Smith CD, Robertson GP . Mutant V599E B-Raf regulates growth and vascular development of malignant melanoma tumors. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 2412–2421.
Dankort D, Curley DP, Cartlidge RA, Nelson B, Karnezis AN, Damsky WE et al. Braf(V600E) cooperates with Pten loss to induce metastatic melanoma. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 544–552.
Dhomen N, Reis-Filho JS, da Rocha Dias S, Hayward R, Savage K, Delmas V et al. Oncogenic Braf induces melanocyte senescence and melanoma in mice. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 294–303.
Eisen T, Ahmad T, Flaherty KT, Gore M, Kaye S, Marais R et al. Sorafenib in advanced melanoma: a Phase II randomised discontinuation trial analysis. Br J Cancer 2006; 95: 581–586.
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 809–819.
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS et al. Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 707–714.
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J et al. Improved survival with Vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2507–2516.
Smalley KSM, Sondak VK . Melanoma – an unlikely poster child for personalized cancer therapy. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 876–878.
Pao W, Miller VA, Politi KA, Riely GJ, Somwar R, Zakowski MF et al. Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med 2005; 2: e73.
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K, Hsu N, Paquette R, Rao PN et al. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001; 293: 876–880.
Nazarian R, Shi H, Wang Q, Kong X, Koya RC, Lee H et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010; 468: 973–977.
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 683–695.
Johannessen CM, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Thomas SR, Wardwell L, Johnson LA et al. COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature 2010; 468: 968–972.
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M, Kong X, Ng C, Moriceau G et al. RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature 2011; 480: 387–390.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007; 316: 1039–1043.
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J, Ibrahim PN, Cho H et al. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature 2010; 467: 596–599.
Herlyn M . Human melanoma: development and progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 1990; 9: 101–112.
Sondergaard JN, Nazarian R, Wang Q, Guo D, Hsueh T, Mok S et al. Differential sensitivity of melanoma cell lines with BRAFV600E mutation to the specific Raf inhibitor PLX4032. J Transl Med 2010; 8: 39.
Tsai J, Lee JT, Wang W, Zhang J, Cho H, Mamo S et al. Discovery of a selective inhibitor of oncogenic B-Raf kinase with potent antimelanoma activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 3041–3046.
Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Ye Q, Viale A, Sander C, Solit DB et al. V600EBRAF is associated with disabled feedback inhibition of RAF-MEK signaling and elevated transcriptional output of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 4519–4524.
Joseph EW, Pratilas CA, Poulikakos PI, Tadi M, Wang W, Taylor BS et al. The RAF inhibitor PLX4032 inhibits ERK signaling and tumor cell proliferation in a V600E BRAF-selective manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14903–14908.
Brummer T, Naegele H, Reth M, Misawa Y . Identification of novel ERK-mediated feedback phosphorylation sites at the C-terminus of B-Raf. Oncogene 2003; 22: 8823–8834.
Ritt DA, Monson DM, Specht SI, Morrison DK . Impact of feedback phosphorylation and Raf heterodimerization on normal and mutant B-Raf signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 806–819.
Paraiso KHT, Fedorenko IV, Cantini LP, Munko AC, Hall M, Sondak VK et al. Recovery of phospho-ERK activity allows melanoma cells to escape from BRAF inhibitor therapy. Br J Cancer 2010; 102: 1724–1730.
Emery CM, Vijayendran KG, Zipser MC, Sawyer AM, Niu L, Kim JJ et al. MEK1 mutations confer resistance to MEK and B-RAF inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 20411–20416.
Wagle N, Emery C, Berger MF, Davis MJ, Sawyer A, Pochanard P et al. Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by tumor genomic profiling. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 3085–3096.
Geng Y, Yu Q, Sicinska E, Das M, Bronson RT, Sicinski P . Deletion of the p27Kip1 gene restores normal development in cyclin D1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 194–199.
Hoeflich KP, Herter S, Tien J, Wong L, Berry L, Chan J et al. Antitumor efficacy of the novel RAF inhibitor GDC-0879 is predicted by BRAFV600E mutational status and sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway suppression. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 3042–3051.
Shao Y, Aplin A . Akt3-mediated resistance to apoptosis in B-RAF targeted melanoma cells. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 6670–6681.
VanBrocklin MW, Verhaegen M, Soengas MS, Holmen SL . Mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition induces translocation of Bmf to promote apoptosis in melanoma. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 1985–1994.
Ley R, Balmanno K, Hadfield K, Weston C, Cook SJ . Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway promotes phosphorylation and proteasome-dependent degradation of the BH3-only protein, Bim. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 18811–18816; Order.
Richter-Larrea JA, Robles EF, Fresquet V, Beltran E, Rullan AJ, Agirre X et al. Reversion of epigenetically mediated BIM silencing overcomes chemoresistance in Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2010; 116: 2531–2542.
Zhang Y, Adachi M, Zhao X, Kawamura R, Imai K . Histone deacetylase inhibitors FK228, N-(2-aminophenyl)-4-[N-(pyridin-3-yl-methoxycarbonyl)amino- methyl]benzamide and m-carboxycinnamic acid bis-hydroxamide augment radiation-induced cell death in gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 2004; 110: 301–308.
Zhang Y, Adachi M, Kawamura R, Imai K . Bmf is a possible mediator in histone deacetylase inhibitors FK228 and CBHA-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 129–140.
Montagut C, Sharma SV, Shioda T, McDermott U, Ulman M, Ulkus LE et al. Elevated CRAF as a potential mechanism of acquired resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 4853–4861.
Poulikakos PI, Zhang C, Bollag G, Shokat KM, Rosen N . RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 2010; 464: 427–430.
Hanafusa H, Torii S, Yasunaga T, Sprouty1 Nishida E . and Sprouty2 provide a control mechanism for the Ras/MAPK signalling pathway. Nat Cell Biol 2002; 4: 850–858.
Boisvert-Adamo K, Aplin AE . Mutant B-RAF mediates resistance to anoikis via Bad and Bim. Oncogene 2008; 27: 3301–3312.
Gilley J, Coffer PJ, Ham J . FOXO transcription factors directly activate bim gene expression and promote apoptosis in sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 613–622.
Esteller M . Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1148–1159.
Wang J, Hoshino T, Redner RL, Kajigaya S, ETO Liu JM . fusion partner in t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia, represses transcription by interaction with the human N-CoR/mSin3/HDAC1 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 10860–10865.
Lin RJ, Sternsdorf T, Tini M, Evans RM . Transcriptional regulation in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene 2001; 20: 7204–7215.
Sharma S, Lee D, Li B, Quinlan M, Takahashi F, Maheswaran S et al. A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 2010; 141: 69–80.
Xargay-Torrent S, Lopez-Guerra M, Saborit-Villarroya I, Rosich L, Campo E, Roue G et al. Vorinostat-induced apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma is mediated by acetylation of proapoptotic BH3-only gene promoters. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 3956–3968.
Yamaguchi K, Mandai M, Oura T, Matsumura N, Hamanishi J, Baba T et al. Identification of an ovarian clear cell carcinoma gene signature that reflects inherent disease biology and the carcinogenic processes. Oncogene 2010; 29: 1741–1752.
Pfaffl MW . A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: e45.
Acknowledgements
We thank Melanie Mayberry for the sequencing of WM793-Res cells, Dr Gideon Bollag (Plexxikon, Berkeley, CA) for providing PLX4720, Dr Meenhard Herlyn (Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, PA) for WM793 cell line and Dr Antoni Ribas (UCLA, CA) for M238 cell line. This work was supported by NIH grants R01-GM067893 and R01-CA125103 (AE Aplin) and an Outrun the Sun fellowship (Y Shao). The Kimmel Cancer Center is supported by National Cancer Institute Support Grant 1P30CA56036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by C Borner
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., Aplin, A. BH3-only protein silencing contributes to acquired resistance to PLX4720 in human melanoma. Cell Death Differ 19, 2029–2039 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.94
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.94
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Destabilization of NOXA mRNA as a common resistance mechanism to targeted therapies
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Inhibition of MEK suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth through independent MYC and BIM regulation
Cellular Oncology (2019)
-
Restraining FOXO3-dependent transcriptional BMF activation underpins tumour growth and metastasis of E-cadherin-negative breast cancer
Cell Death & Differentiation (2016)
-
Tumor heterogeneity and plasticity as elusive drivers for resistance to MAPK pathway inhibition in melanoma
Oncogene (2015)
-
Alternative Treatments For Melanoma: Targeting BCL-2 Family Members to De-Bulk and Kill Cancer Stem Cells
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2015)