Abstract
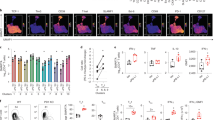
Helper T cells are crucial for maintaining proper immune responses. Yet, they have an undefined relationship with one of the most potent immune stimulatory cytokines, granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). By depleting major cytokines during the differentiation of CD4+ T cells in vitro, we derived cells that were found to produce large amounts of GM-CSF, but little of the cytokines produced by other helper T subsets. By their secretion of GM-CSF, this novel subset of helper T cells (which we have termed ThGM cells) promoted the production of cytokines by other T-cell subtypes, including type 1 helper T cell (Th1), type 2 helper T cell (Th2), type 1 cytotoxic T cell (Tc1), type 2 cytotoxic T cell (Tc2), and naive T cells, as evidenced by the fact that antibody neutralization of GM-CSF abolished this effect. ThGM cells were found to be highly prone to activation-induced cell death (AICD). Inhibitors of TRAIL or granzymes could not block AICD in ThGM cells, whereas inhibition of FasL/Fas interaction partially rescued ThGM cells from AICD. Thus, ThGM cells are a novel subpopulation of T helper cells that produce abundant GM-CSF, exhibit exquisite susceptibility to apoptosis, and therefore play a pivotal role in the regulation of the early stages of immune responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- IFN-γ:
-
interferon-γ
- GM-CSF:
-
granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor
- AICD:
-
activation-induced cell death
- Th1:
-
type 1 helper T cell
- Th2:
-
type 2 helper T cell
- ThGM:
-
GM-CSF-secreting helper T cell
- Tc1:
-
type 1 cytotoxic T cell
- Tc2:
-
type 2 cytotoxic T cell
References
Romagnani S . Regulation of the T cell response. Clin Exp Allergy 2006; 36: 1357–1366.
Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A . Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature 1996; 383: 787–793.
Chitnis T, Salama AD, Grusby MJ, Sayegh MH, Khoury SJ . Defining Th1 and Th2 immune responses in a reciprocal cytokine environment in vivo. J Immunol 2004; 172: 4260–4265.
Del Prete G . Human Th1 and Th2 lymphocytes: their role in the pathophysiology of atopy. Allergy 1992; 47: 450–455.
Feili-Hariri M, Falkner DH, Morel PA . Polarization of naive T cells into Th1 or Th2 by distinct cytokine-driven murine dendritic cell populations: implications for immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 2005; 78: 656–664.
O'Garra A, Arai N . The molecular basis of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cell differentiation. Trends Cell Biol 2000; 10: 542–550.
Adikari SB, Pettersson A, Soderstrom M, Huang YM, Link H . Interleukin-10-modulated immature dendritic cells control the proinflammatory environment in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Immunol 2004; 59: 600–606.
Kaplan MH, Chang HC, Cooper S, Lee Y, Broxmeyer HE . Distinct requirements for Stat4 and Stat6 in hematopoietic progenitor cell responses to growth factors and chemokines. J Hematother Stem Cell Res 2003; 12: 401–408.
Voisine C, Hubert FX, Trinite B, Heslan M, Josien R . Two phenotypically distinct subsets of spleen dendritic cells in rats exhibit different cytokine production and T cell stimulatory activity. J Immunol 2002; 169: 2284–2291.
Rose S, Guevara P, Farach S, Adkins B . The key regulators of adult T helper cell responses, STAT6 and T-bet, are established in early life in mice. Eur J Immunol 2006; 36: 1241–1253.
Luo Y, Yamada H, Chen X, Ryan AA, Evanoff DP, Triccas JA et al. Recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) expressing mouse IL-18 augments Th1 immunity and macrophage cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol 2004; 137: 24–34.
Constant SL, Bottomly K . Induction of Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cell responses: the alternative approaches. Annu Rev Immunol 1997; 15: 297–322.
Jean WC, Spellman SR, Wallenfriedman MA, Flores CT, Kurtz BP, Hall WA et al. Effects of combined granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin-2, and interleukin-12 based immunotherapy against intracranial glioma in the rat. J Neurooncol 2004; 66: 39–49.
Berclaz PY, Shibata Y, Whitsett JA, Trapnell BC . GM-CSF, via PU.1, regulates alveolar macrophage Fcgamma R-mediated phagocytosis and the IL-18/IFN-gamma -mediated molecular connection between innate and adaptive immunity in the lung. Blood 2002; 100: 4193–4200.
Barouch DH, Santra S, Tenner-Racz K, Racz P, Kuroda MJ, Schmitz JE et al. Potent CD4+ T cell responses elicited by a bicistronic HIV-1 DNA vaccine expressing gp120 and GM-CSF. J Immunol 2002; 168: 562–568.
Chen GH, Olszewski MA, McDonald RA, Wells JC, Paine R 3rd, Huffnagle GB et al. Role of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in host defense against pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection during murine allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis. Am J Pathol 2007; 170: 1028–1040.
Kriegel MA, Tretter T, Blank N, Schiller M, Gabler C, Winkler S et al. Interleukin-4 supports interleukin-12-induced proliferation and interferon-gamma secretion in human activated lymphoblasts and T helper type 1 cells. Immunology 2006; 119: 43–53.
Guimond M, Fry TJ, Mackall CL . Cytokine signals in T-cell homeostasis. J Immunother 2005; 28: 289–294.
Ritz SA, Cundall MJ, Gajewska BU, Alvarez D, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Coyle AJ et al. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-driven respiratory mucosal sensitization induces Th2 differentiation and function independently of interleukin-4. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002; 27: 428–435.
Ureta G, Osorio F, Morales J, Rosemblatt M, Bono MR, Fierro JA . Generation of dendritic cells with regulatory properties. Transplant Proc 2007; 39: 633–637.
L'Huillier A, Ren G, Shi Y, Zhang J . A two-hit model of autoimmunity: lymphopenia and unresponsiveness to TGF-beta signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 369–370.
Della Bella S, Nicola S, Riva A, Biasin M, Clerici M, Villa ML . Functional repertoire of dendritic cells generated in granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor and interferon-alpha. J Leukoc Biol 2004; 75: 106–116.
O'Keeffe M, Hochrein H, Vremec D, Pooley J, Evans R, Woulfe S et al. Effects of administration of progenipoietin 1, Flt-3 ligand, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and pegylated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on dendritic cell subsets in mice. Blood 2002; 99: 2122–2130.
Lu H, Xing Z, Brunham RC . GM-CSF transgene-based adjuvant allows the establishment of protective mucosal immunity following vaccination with inactivated Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol 2002; 169: 6324–6331.
Gonzalez-Juarrero M, Hattle JM, Izzo A, Junqueira-Kipnis AP, Shim TS, Trapnell BC et al. Disruption of granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor production in the lungs severely affects the ability of mice to control Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Leukoc Biol 2005; 77: 914–922.
Stampfli MR, Wiley RE, Neigh GS, Gajewska BU, Lei XF, Snider DP et al. GM-CSF transgene expression in the airway allows aerosolized ovalbumin to induce allergic sensitization in mice. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1704–1714.
Sin JI, Kim JJ, Ugen KE, Ciccarelli RB, Higgins TJ, Weiner DB . Enhancement of protective humoral (Th2) and cell-mediated (Th1) immune responses against herpes simplex virus-2 through co-delivery of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor expression cassettes. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 3530–3540.
Atzeni F, Schena M, Ongari AM, Carrabba M, Bonara P, Minonzio F et al. Induction of CD69 activation molecule on human neutrophils by GM-CSF, IFN-gamma, and IFN-alpha. Cell Immunol 2002; 220: 20–29.
Tanaka S, Aso H, Miyazawa K, Nagai Y, Watanabe K, Ohwada S et al. Differential cytokine gene expression in CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell subsets of calves. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2007; 118: 84–91.
Otto M, Barfield RC, Iyengar R, Gatewood J, Muller I, Holladay MS et al. Human gammadelta T cells from G-CSF-mobilized donors retain strong tumoricidal activity and produce immunomodulatory cytokines after clinical-scale isolation. J Immunother 2005; 28: 73–78.
Street NE, Schumacher JH, Fong TA, Bass H, Fiorentino DF, Leverah JA et al. Heterogeneity of mouse helper T cells. Evidence from bulk cultures and limiting dilution cloning for precursors of Th1 and Th2 cells. J Immunol 1990; 144: 1629–1639.
Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL . Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol 1986; 136: 2348–2357.
Shi Y, Liu CH, Roberts AI, Das J, Xu G, Ren G et al. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and T-cell responses: what we do and don't know. Cell Res 2006; 16: 126–133.
Cooney LA, Towery K, Endres J, Fox DA . Sensitivity and resistance to regulation by IL-4 during Th17 maturation. J Immunol 2011; 187: 4440–4450.
Wohlfert EA, Grainger JR, Bouladoux N, Konkel JE, Oldenhove G, Ribeiro CH et al. GATA3 controls Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell fate during inflammation in mice. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 4503–4515.
Zhao J, Zhao J, Perlman S . Differential effects of IL-12 on Tregs and non-Treg T cells: roles of IFN-gamma, IL-2 and IL-2R. PloS One 2012; 7: e46241.
Cockerill PN, Osborne CS, Bert AG, Grotto RJ . Regulation of GM-CSF gene transcription by core-binding factor. Cell Growth Differ 1996; 7: 917–922.
Li X, Vradii D, Gutierrez S, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL et al. Subnuclear targeting of Runx1 is required for synergistic activation of the myeloid specific M-CSF receptor promoter by PU.1. J Cell Biochem 2005; 96: 795–809.
Devadas S, Das J, Liu C, Zhang L, Roberts AI, Pan Z et al. Granzyme B is critical for T cell receptor-induced cell death of type 2 helper T cells. Immunity 2006; 25: 237–247.
Li L, Qi X, Williams M, Shi Y, Keegan AD . Overexpression of insulin receptor substrate-1, but not insulin receptor substrate-2, protects a T cell hybridoma from activation-induced cell death. J Immunol 2002; 168: 6215–6223.
D'Adamio F, Zollo O, Moraca R, Ayroldi E, Bruscoli S, Bartoli A et al. A new dexamethasone-induced gene of the leucine zipper family protects T lymphocytes from TCR/CD3-activated cell death. Immunity 1997; 7: 803–812.
Saha B, Saini A, Germond R, Perrin PJ, Harlan DM, Davis TA . Susceptibility or resistance to Leishmania infection is dictated by the macrophages evolved under the influence of IL-3 or GM-CSF. Eur J Immunol 1999; 29: 2319–2329.
Pawelec G, Schaudt K, Rehbein A, Busch FW . Differential secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factors but not interferon-gamma from CD4+ compared to CD8+ human T cell clones. Eur J Immunol 1989; 19: 197–200.
Santoli D, Clark SC, Kreider BL, Maslin PA, Rovera G . Amplification of IL-2-driven T cell proliferation by recombinant human IL-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol 1988; 141: 519–526.
Shannon MF, Himes SR, Coles LS . GM-CSF and IL-2 share common control mechanisms in response to costimulatory signals in T cells. J Leukoc Biol 1995; 57: 767–773.
O'Garra A . Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immunity 1998; 8: 275–283.
Brunner T, de Weck AL, Dahinden CA . Platelet-activating factor induces mediator release by human basophils primed with IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, or IL-5. J Immunol 1991; 147: 237–242.
Wang R, Shi YF . A simplified protocol for apoptosis assay by DNA content analysis. Biotechniques 2002 (Suppl): 88–91.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by USPHS grants (AI43384, AI057596, DE014913, DE019932, and GM866889), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2010CB945600), and the National Science and Technology Project of China (2009ZX09503-024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by RA Knight
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Roberts, A., Liu, C. et al. A novel subset of helper T cells promotes immune responses by secreting GM-CSF. Cell Death Differ 20, 1731–1741 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.130
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.130
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Crosstalk between CD64+MHCII+ macrophages and CD4+ T cells drives joint pathology during chikungunya
EMBO Molecular Medicine (2024)
-
GM-CSF-based treatments in COVID-19: reconciling opposing therapeutic approaches
Nature Reviews Immunology (2020)
-
High levels of circulating GM-CSF+CD4+ T cells are predictive of poor outcomes in sepsis patients: a prospective cohort study
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2019)