Abstract
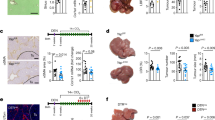
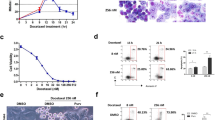
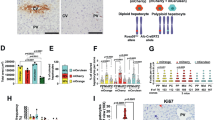
The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC) acts as a key regulator of mitosis, preventing asymmetric segregation of chromosomal material into daughter cells. The CPC is composed of three non-enzymatic components termed Survivin, the inner centromere protein (INCENP) and Borealin, and an enzymatic component, Aurora B kinase. Survivin is necessary for the appropriate separation of sister chromatids during mitosis and is involved in liver regeneration, but its role in regenerative processes is incompletely elucidated. Whether Survivin, which is classified as an inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) based on domain composition, also has a role in apoptosis is controversial. The present study examined the in vivo effects of Survivin ablation in the liver and during liver regeneration after 70% hepatectomy in a hepatocyte-specific knockout mouse model. The absence of Survivin caused a reduction in the number of hepatocytes in the liver, together with an increase in cell volume, macronucleation and polyploidy, but no changes in apoptosis. During liver regeneration, mitosis of hepatocytes was associated with mislocalization of the members of the CPC, which were no longer detectable at the centromere despite an unchanged protein amount. Furthermore, the loss of survivin in regenerating hepatocytes was associated with reduced levels of phosphorylated Histone H3 at serine 28 and abolished phosphorylation of CENP-A and Hec1 at serine 55, which is a consequence of decreased Aurora B kinase activity. These data indicate that Survivin expression determines hepatocyte number during liver development and liver regeneration. Lack of Survivin causes mislocalization of the CPC members in combination with reduced Aurora B activity, leading to impaired phosphorylation of its centromeric target proteins and inappropriate cytokinesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CPC:
-
chromosomal passenger complex
- INCENP:
-
inner centromere protein
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- CENP-A:
-
centromeric protein A
- Alb-surv−/−:
-
albumin-cre survivinflox/flox
- pHistone H3(S10):
-
phosphorylated Histone H3 at serine 10
- pHistone H3(S28):
-
phosphorylated Histone H3 at serine 28
- pHec-1(S55):
-
phosphorylated highly expressed in cancer protein 1 at serine 55
- pCENP-A(S7):
-
phosphorylated centromeric protein A at serine 7
- VRK-1:
-
vaccinia-related kinase 1
- ALAT:
-
serum alanine-aminotransferase
- ASAT:
-
serum aspartate-aminotransferase
References
Altieri DC . New wirings in the survivin networks. Oncogene 2008; 27: 6276–6284.
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC et al. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature 1998; 396: 580–584.
Baba HA, Wohlschlaeger J, Schmitz KJ, Nadalin S, Lang H, Benesch A et al. Survivin is upregulated during liver regeneration in rats and humans and is associated with hepatocyte proliferation. Liver Int 2009; 29: 585–592.
Deguchi M, Shiraki K, Inoue H, Okano H, Ito T, Yamanaka T et al. Expression of survivin during liver regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 297: 59–64.
Fukuda S, Mantel CR, Pelus LM . Survivin regulates hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation through p21WAF1/Cip1-dependent and -independent pathways. Blood 2004; 103: 120–127.
Ryan BM, O'Donovan N, Duffy MJ . Survivin: a new target for anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev 2009; 35: 553–562.
Xing Z, Conway EM, Kang C, Winoto A . Essential role of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, in T cell development, maturation, and homeostasis. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 69–80.
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST, Giles FJ . Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 5000–5005.
Liu D, Vader G, Vromans MJ, Lampson MA, Lens SM . Sensing chromosome bi-orientation by spatial separation of aurora B kinase from kinetochore substrates. Science 2009; 323: 1350–1353.
Vader G, Medema RH, Lens SM . The chromosomal passenger complex: guiding Aurora-B through mitosis. J Cell Biol 2006; 173: 833–837.
Guse A, Mishima M, Glotzer M . Phosphorylation of ZEN-4/MKLP1 by aurora B regulates completion of cytokinesis. Curr Biol 2005; 15: 778–786.
Sawicka A, Seiser C . Histone H3 phosphorylation – a versatile chromatin modification for different occasions. Biochimie 2012; 94: 2193–2201.
Zeitlin SG, Shelby RD, Sullivan KF . CENP-A is phosphorylated by Aurora B kinase and plays an unexpected role in completion of cytokinesis. J Cell Biol 2001; 155: 1147–1157.
Kelly RJ, Lopez-Chavez A, Citrin D, Janik JE, Morris JC . Impacting tumor cell-fate by targeting the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin. Mol Cancer 2011; 6: 35.
Kelly AE, Ghenoiu C, Xue JZ, Zierhut C, Kimura H, Funabiki H . Survivin reads phosphorylated histone H3 threonine 3 to activate the mitotic kinase Aurora B. Science 2010; 330: 235–239.
Wang F, Dai J, Daum JR, Niedzialkowska E, Banerjee B, Stukenberg PT et al. Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis. Science 2010; 330: 231–235.
Yamagishi Y, Honda T, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y . Two histone marks establish the inner centromere and chromosome bi-orientation. Science 2010; 330: 239–243.
Uren AG, Wong L, Pakusch M, Fowler KJ, Burrows FJ, Vaux DL et al. Survivin and the inner centromere protein INCENP show similar cell-cycle localization and gene knockout phenotype. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 1319–1328.
Levkau B, Schafers M, Wohlschlaeger J, von Wnuck Lipinski K, Keul P, Hermann S et al. Survivin determines cardiac function by controlling total cardiomyocyte number. Circulation 2008; 117: 1583–1593.
Sandall S, Severin F, McLeod IX, Yates JR, Oegema K, Hyman A et al. A Bir1-Sli15 complex connects centromeres to microtubules and is required to sense kinetochore tension. Cell 2006; 127: 1179–1191.
Yue Z, Carvalho A, Xu Z, Yuan X, Cardinale S, Ribeiro S et al. Deconstructing Survivin: comprehensive genetic analysis of Survivin function by conditional knockout in a vertebrate cell line. J Cell Biol 2008; 183: 279–296.
Lens SM, Wolthuis RM, Klompmaker R, Kauw J, Agami R, Brummelkamp T et al. Survivin is required for a sustained spindle checkpoint arrest in response to lack of tension. Embo J 2003; 22: 2934–2947.
Jiang Y, de Bruin A, Caldas H, Fangusaro J, Hayes J, Conway EM et al. Essential role for survivin in early brain development. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 6962–6970.
Zwerts F, Lupu F, De Vriese A, Pollefeyt S, Moons L, Altura RA et al. Lack of endothelial cell survivin causes embryonic defects in angiogenesis, cardiogenesis, and neural tube closure. Blood 2007; 109: 4742–4752.
Goto H, Tomono Y, Ajiro K, Kosako H, Fujita M, Sakurai M et al. Identification of a novel phosphorylation site on histone H3 coupled with mitotic chromosome condensation. J Biol Chem 1999; 174: 25543–25549.
Goto H, Yasui Y, Nigg EA, Inagaki M . Aurora-B phosphorylates Histone H3 at serine28 with regard to the mitotic chromosome condensation. Genes Cells 2002; 7: 11–17.
Hendzel MJ, Wei Y, Mancini MA, Van Hooser A, Ranalli T, Brinkley BR et al. Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of histone H3 initiates primarily within pericentromeric heterochromatin during G2 and spreads in an ordered fashion coincident with mitotic chromosome condensation. Chromosoma 1997; 106: 348–360.
Loomis RJ, Naoe Y, Parker JB, Savic V, Bozovsky MR, Macfarlan T et al. Chromatin binding of SRp20 and ASF/SF2 and dissociation from mitotic chromosomes is modulated by histone H3 serine 10 phosphorylation. Mol Cell 2009; 33: 450–461.
Banerjee T, Chakravarti D . A peek into the complex realm of histone phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 2011; 31: 4858–4873.
Carmena M, Earnshaw WC . The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003; 4: 842–854.
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA . Aurora kinases link chromosome segregation and cell division to cancer susceptibility. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2004; 14: 29–36.
Carmena M, Ruchaud S, Earnshaw WC . Making the Auroras glow: regulation of Aurora A and B kinase function by interacting proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2009; 21: 796–805.
Kang TH, Park DY, Choi YH, Kim KJ, Yoon HS, Kim KT . Mitotic histone H3 phosphorylation by vaccinia-related kinase 1 in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 8533–8546.
DeLuca JG, Gall WE, Ciferri C, Cimini D, Musacchio A, Salmon ED . Kinetochore microtubule dynamics and attachment stability are regulated by Hec1. Cell 2006; 127: 969–982.
DeLuca KF, Lens SM, DeLuca JG . Temporal changes in Hec1 phosphorylation control kinetochore-microtubule attachment stability during mitosis. J Cell Sci 2011; 124: 622–634.
Regnier V, Vagnarelli P, Fukagawa T, Zerjal T, Burns E, Trouche D et al. CENP-A is required for accurate chromosome segregation and sustained kinetochore association of BubR1. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 3967–3981.
Becker M, Stolz A, Ertych N, Bastians H . Centromere localization of INCENP-Aurora B is sufficient to support spindle checkpoint function. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1360–1372.
Berezov A, Cai Z, Freudenberg JA, Zhang H, Cheng X, Thompson T et al. Disabling the mitotic spindle and tumor growth by targeting a cavity-induced allosteric site of survivin. Oncogene 2012; 31: 1938–1948.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Dr. Yanli Gu for performing the liver resections. Laura Malkus, Mareike Müller and Nicole Macha for their technical assistance. We also want to thank Ms Lucie Horn for her assistance in analyzing the DNA content in hepatocyte nuclei. This study was supported by the DFG (KFO 117, TP B5 (Ba 1730/10-1)).
Authors contributions
Study design: BL, HAB, AM. Data acquisition: SH, SB, DM, GPP, GK, KL, BS. Material support: EMC, AM. Manuscript drafting: SH, JW, EMC, HAB. Important intellectual content: AM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by J Silke
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hagemann, S., Wohlschlaeger, J., Bertram, S. et al. Loss of Survivin influences liver regeneration and is associated with impaired Aurora B function. Cell Death Differ 20, 834–844 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.20
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.20
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Survivin, a molecular target for therapeutic interventions in squamous cell carcinoma
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2017)
-
Hepatocyte polyploidization and its association with pathophysiological processes
Cell Death & Disease (2017)