Abstract
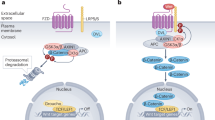
Merlin, encoded by the NF2 gene, is a tumor suppressor that acts by inhibiting mitogenic signaling and is mutated in Neurofibromatosis type II (NF2) disease, although its molecular mechanism is not fully understood. Here, we observed that Merlin inhibited Wnt/β-catenin signaling by blocking phosphorylation of LRP6, which is necessary for Wnt signal transduction, whereas mutated Merlin in NF2 patients did not. Treatment with Wnt3a enhanced phosphorylation of Ser518 in Merlin via activation of PAK1 in a PIP2-dependent manner. Phosphorylated Merlin dissociated from LRP6, allowing for phosphorylation of LRP6. Tissues from NF2 patients exhibited higher levels of β-catenin, and proliferation of RT4-D6P2T rat schwannoma cells was significantly reduced by treatment with chemical inhibitors of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Taken together, our findings suggest that sustained activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling due to abrogation of Merlin-mediated inhibition of LRP6 phosphorylation may be a cause of NF2 disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- APC:
-
adenomatous polyposis coli
- PIP2:
-
phosphatidylinositol 4,5 bisphosphate
- NF2:
-
Neurofibromatosis type II
- ERM:
-
Ezrin, Radixin, and Moesin
- WT:
-
wild-type
- SA:
-
S518A
- SD:
-
S518D
- Wnt3a-CM:
-
Wnt3a-conditioned media
- PAK:
-
p21 activated kinase
- dnPAK1:
-
dominant-negative form of PAK1
- DMZ:
-
dorsal marginal zone
- VMZ:
-
ventral marginal zone
- PFA:
-
paraformaldehyde
- ODC:
-
Ornithine decarboxylase 1
- Ct:
-
Control
- W.E:
-
whole embryo
- Nf2 MO:
-
Nf2 morpholino
- A.C.:
-
animal cap
References
Clevers H, Nusse R . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012; 149: 1192–1205.
Kim W, Kim M, Jho EH . Wnt/beta-catenin signalling: from plasma membrane to nucleus. Biochem J 2013; 450: 9–21.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 2009; 17: 9–26.
Guo X, Wang XF . Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res 2009; 19: 71–88.
Hu T, Li C . Convergence between Wnt-beta-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol Cancer 2010; 9: 236.
Collu GM, Hidalgo-Sastre A, Brennan K . Wnt-Notch signalling crosstalk in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 2014; 71: 3553–3567.
Baron R, Kneissel M . WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med 2013; 19: 179–192.
Anastas JN, Moon RT . WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: 11–26.
Pan W, Choi SC, Wang H, Qin Y, Volpicelli-Daley L, Swan L et al. Wnt3a-mediated formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 2008; 321: 1350–1353.
Kim W, Kim SY, Kim T, Kim M, Bae DJ, Choi HI et al. ADP-ribosylation factors 1 and 6 regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling via control of LRP6 phosphorylation. Oncogene 2012; 32: 3390–3396.
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY, Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP et al. Wnt signaling through inhibition of beta-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell 2012; 149: 1245–1256.
Tamai K, Zeng X, Liu C, Zhang X, Harada Y, Chang Z et al. A mechanism for Wnt coreceptor activation. Mol Cell 2004; 13: 149–156.
Hadfield KD, Smith MJ, Urquhart JE, Wallace AJ, Bowers NL, King AT et al. Rates of loss of heterozygosity and mitotic recombination in NF2 schwannomas, sporadic vestibular schwannomas and schwannomatosis schwannomas. Oncogene 2010; 29: 6216–6221.
Bretscher A, Chambers D, Nguyen R, Reczek D . ERM-Merlin and EBP50 protein families in plasma membrane organization and function. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2000; 16: 113–143.
Li W, Cooper J, Zhou L, Yang C, Erdjument-Bromage H, Zagzag D et al. Merlin/NF2 loss-driven tumorigenesis linked to CRL4(DCAF1)-mediated inhibition of the hippo pathway kinases Lats1 and 2 in the nucleus. Cancer Cell 2014; 26: 48–60.
Li W, You L, Cooper J, Schiavon G, Pepe-Caprio A, Zhou L et al. Merlin/NF2 suppresses tumorigenesis by inhibiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4(DCAF1) in the nucleus. Cell 2010; 140: 477–490.
Maitra S, Kulikauskas RM, Gavilan H, Fehon RG . The tumor suppressors Merlin and Expanded function cooperatively to modulate receptor endocytosis and signaling. Curr Biol 2006; 16: 702–709.
Pan D . The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell 2010; 19: 491–505.
Harvey KF, Zhang X, Thomas DM . The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13: 246–257.
Bosco EE, Nakai Y, Hennigan RF, Ratner N, Zheng Y . NF2-deficient cells depend on the Rac1-canonical Wnt signaling pathway to promote the loss of contact inhibition of proliferation. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2540–2549.
Zhou L, Ercolano E, Ammoun S, Schmid MC, Barczyk MA, Hanemann CO . Merlin-deficient human tumors show loss of contact inhibition and activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling linked to the PDGFR/Src and Rac/PAK pathways. Neoplasia 2011; 13: 1101–1112.
McClatchey AI, Fehon RG . Merlin and the ERM proteins—regulators of receptor distribution and signaling at the cell cortex. Trends Cell Biol 2009; 19: 198–206.
Surace EI, Haipek CA, Gutmann DH . Effect of merlin phosphorylation on neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) gene function. Oncogene 2004; 23: 580–587.
Sher I, Hanemann CO, Karplus PA, Bretscher A . The tumor suppressor merlin controls growth in its open state, and phosphorylation converts it to a less-active more-closed state. Dev Cell 2012; 22: 703–705.
Ahronowitz I, Xin W, Kiely R, Sims K, MacCollin M, Nunes FP . Mutational spectrum of the NF2 gene: a meta-analysis of 12 years of research and diagnostic laboratory findings. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 1–12.
Gutmann DH, Hirbe AC, Haipek CA . Functional analysis of neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) missense mutations. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 1519–1529.
Lallemand D, Curto M, Saotome I, Giovannini M, McClatchey AI . NF2 deficiency promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis by destabilizing adherens junctions. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 1090–1100.
Okada T, You L, Giancotti FG . Shedding light on Merlin's wizardry. Trends Cell Biol 2007; 17: 222–229.
Abramowicz A, Gos M . Neurofibromin in neurofibromatosis type 1 - mutations in NF1gene as a cause of disease. Dev Period Med 2014; 18: 297–306.
Yu FX, Guan KL . The Hippo pathway: regulators and regulations. Genes Dev 2013; 27: 355–371.
Rong R, Surace EI, Haipek CA, Gutmann DH, Ye K . Serine 518 phosphorylation modulates merlin intramolecular association and binding to critical effectors important for NF2 growth suppression. Oncogene 2004; 23: 8447–8454.
Chen B, Dodge ME, Tang W, Lu J, Ma Z, Fan CW et al. Small molecule-mediated disruption of Wnt-dependent signaling in tissue regeneration and cancer. Nat Chem Biol 2009; 5: 100–107.
Emami KH, Nguyen C, Ma H, Kim DH, Jeong KW, Eguchi M et al. A small molecule inhibitor of beta-catenin/CREB-binding protein transcription [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 12682–12687.
Lee H, Hwang SJ, Kim HR, Shin CH, Choi KH, Joung JG et al. Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) controls the invasiveness of glioblastoma through YAP-dependent expression of CYR61/CCN1 and miR-296-3p. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1859: 599–611.
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A, Stegmeier F, Michaud GA et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature 2009; 461: 614–620.
Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H, Habas R et al. A dual-kinase mechanism for Wnt co-receptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature 2005; 438: 873–877.
Regimbald-Dumas Y, He X . Wnt signalling: What The X@# is WTX? EMBO J 2011; 30: 1415–1417.
Shaw RJ, Paez JG, Curto M, Yaktine A, Pruitt WM, Saotome I et al. The Nf2 tumor suppressor, merlin, functions in Rac-dependent signaling. Dev Cell 2001; 1: 63–72.
Wu X, Tu X, Joeng KS, Hilton MJ, Williams DA, Long F . Rac1 activation controls nuclear localization of beta-catenin during canonical Wnt signaling. Cell 2008; 133: 340–353.
Zhu G, Wang Y, Huang B, Liang J, Ding Y, Xu et al. A Rac1/PAK1 cascade controls beta-catenin activation in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 2012; 31: 1001–1012.
Strochlic TI, Viaud J, Rennefahrt UE, Anastassiadis T, Peterson JR . Phosphoinositides are essential coactivators for p21-activated kinase 1. Mol Cell 2010; 40: 493–500.
Gabev E, Kasianowicz J, Abbott T, McLaughlin S . Binding of neomycin to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). Biochim Biophys Acta 1989; 979: 105–112.
Pilot F, Philippe JM, Lemmers C, Lecuit T . Spatial control of actin organization at adherens junctions by a synaptotagmin-like protein Btsz. Nature 2006; 442: 580–584.
Heasman J . Patterning the early Xenopus embryo. Development 2006; 133: 1205–1217.
Tanneberger K, Pfister AS, Brauburger K, Schneikert J, Hadjihannas MV, Kriz V et al. Amer1/WTX couples Wnt-induced formation of PtdIns(4,5)P2 to LRP6 phosphorylation. EMBO J 2011; 30: 1433–1443.
Lallemand D, Manent J, Couvelard A, Watilliaux A, Siena M, Chareyre F et al. Merlin regulates transmembrane receptor accumulation and signaling at the plasma membrane in primary mouse Schwann cells and in human schwannomas. Oncogene 2009; 28: 854–865.
Yeo D, He H, Patel O, Lowy AM, Baldwin GS, Nikfarjam M . FRAX597, a PAK1 inhibitor, synergistically reduces pancreatic cancer growth when combined with gemcitabine. BMC Cancer 2016; 16: 24.
Beauchamp RL, James MF, DeSouza PA, Wagh V, Zhao WN, Jordan JT et al. A high-throughput kinome screen reveals serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 as a therapeutic target for NF2-deficient meningiomas. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 16981–16997.
Chen C . Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol 1987; 7: 2745–2752.
Smith JC, Slack JM . Dorsalization and neural induction: properties of the organizer in Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1983; 78: 299–317.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NRF grants funded by the MSIP (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning; NRF-2011-0019353) and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (1420060) to E-HJ. JK was supported by NRF- 2013R1A1A2008541.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by JP Medema
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Kim, S., Lee, SH. et al. Merlin inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling by blocking LRP6 phosphorylation. Cell Death Differ 23, 1638–1647 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.54
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.54
This article is cited by
-
CCN3/NOV promotes metastasis and tumor progression via GPNMB-induced EGFR activation in triple-negative breast cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Celastrol suppresses the growth of vestibular schwannoma in mice by promoting the degradation of β-catenin
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2022)
-
Merlin regulates signaling events at the nexus of development and cancer
Cell Communication and Signaling (2020)