Abstract
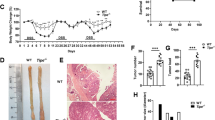
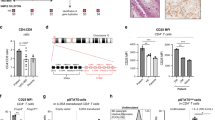
miR-148a has been shown to regulate inflammation, immunity and the growth of certain tumors, but its roles in colitis and colorectal tumorigenesis remain largely undetermined. Here we found miR-148a-deficient mice to be more susceptible to colitis and colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Both were associated with increased nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling. Bone marrow- and non-bone marrow-derived miR-148a contributed to colitis and colitis-associated tumorigenesis. miR-148a loss of heterozygosity exacerbated Apcmin/+ colon and small intestinal spontaneous tumor development. Restoring miR-148a expression prevented both spontaneous and carcinogen-induced colon tumor development. miR-148a was downregulated in human inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer patient tissues. This correlated with a high degree of miR-148a promoter methylation mediated by a complex comprised of P65 and DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha (DNMT3A). miR-148a directly targets several well-accepted upstream regulators of NF-κB and STAT3 signaling, including GP130, IKKα, IKKβ, IL1R1 and TNFR2, which leads to decreased NF-κB and STAT3 activation in macrophages and colon tissues. Our findings reveal that miR-148a is an indirect tumor suppressor that modulates colitis and colitis-associated tumorigenesis by suppressing the expression of signaling by NF-κB and STAT3 and their pro-inflammatory consequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Haggar FA, Boushey RP . Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 2009; 22: 191–197.
Terzic J, Grivennikov S, Karin E, Karin M . Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 2101–2114.
Allen IC, Wilson JE, Schneider M, Lich JD, Roberts RA, Arthur JC et al. NLRP12 suppresses colon inflammation and tumorigenesis through the negative regulation of noncanonical NF-κB signaling. Immunity 2012; 36: 742–754.
Bollrath J, Phesse TJ, von Burstin VA, Putoczki T, Bennecke M, Bateman T et al. gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 91–102.
Cooks T, Pateras IS, Tarcic O, Solomon H, Schetter AJ, Wilder S et al. Mutant p53 prolongs NF-κB activation and promotes chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 2013; 23: 634–646.
Zaki MH, Vogel P, Malireddi RK, Body-Malapel M, Anand PK, Bertin J et al. The NOD-like receptor NLRP12 attenuates colon inflammation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 649–660.
Boulard O, Kirchberger S, Royston DJ, Maloy KJ, Powrie FM . Identification of a genetic locus controlling bacteria-driven colitis and associated cancer through effects on innate inflammation. J Exp Med 2012; 209: 1309–1324.
Chiba T, Marusawa H, Ushijima T . Inflammation-associated cancer development in digestive organs: mechanisms and roles for genetic and epigenetic modulation. Gastroenterology 2012; 143: 550–563.
Bhattacharya N, Yuan R, Prestwood TR, Penny HL, DiMaio MA, Reticker-Flynn NE et al. Normalizing microbiota-induced retinoic acid deficiency stimulates protective CD8(+) T cell-mediated immunity in colorectal cancer. Immunity 2016; 45: 641–655.
Kalla R, Ventham NT, Kennedy NA, Quintana JF, Nimmo ER, Buck AH et al. MicroRNAs: new players in IBD. Gut 2015; 64: 504–517.
Koukos G, Polytarchou C, Kaplan JL, Morley-Fletcher A, Gras-Miralles B, Kokkotou E et al. MicroRNA-124 regulates STAT3 expression and is down-regulated in colon tissues of pediatric patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2013; 145: 842–852.
Liu X, Zhan Z, Xu L, Ma F, Li D, Guo Z et al. MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIα. J Immunol 2010; 185: 7244–7251.
Patel V, Carrion K, Hollands A, Hinton A, Gallegos T, Dyo J et al. The stretch responsive microRNA miR-148a-3p is a novel repressor of IKBKB, NF-κB signaling, and inflammatory gene expression in human aortic valve cells. FASEB J 2015; 29: 1859–1868.
Gonzalez-Martin A, Adams BD, Lai M, Shepherd J, Salvador-Bernaldez M, Salvador JM et al. The microRNA miR-148a functions as a critical regulator of B cell tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 2016; 17: 433–440.
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero S, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Blanco D et al. A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 13556–13561.
Kesselring R, Glaesner J, Hiergeist A, Naschberger E, Neumann H, Brunner SM et al. IRAK-M expression in tumor cells supports colorectal cancer progression through reduction of antimicrobial defense and stabilization of STAT3. Cancer Cell 2016; 29: 684–696.
Koblansky AA, Truax AD, Liu R, Montgomery SA, Ding S, Wilson JE et al. The innate immune receptor NLRX1 functions as a tumor suppressor by reducing colon tumorigenesis and key tumor-promoting signals. Cell Rep 2016; 14: 2562–2575.
Hu S, Peng L, Kwak YT, Tekippe EM, Pasare C, Malter JS et al. The DNA sensor AIM2 maintains intestinal homeostasis via regulation of epithelial antimicrobial host defense. Cell Rep 2015; 13: 1922–1936.
Chen R, Li M, Zhang Y, Zhou Q, Shu HB . The E3 ubiquitin ligase MARCH8 negatively regulates IL-1β-induced NF-κB activation by targeting the IL1RAP coreceptor for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 14128–14133.
Dondelinger Y, Jouan-Lanhouet S, Divert T, Theatre E, Bertin J, Gough PJ et al. NF-kappaB-independent role of IKKα/IKKβ in preventing ripk1 kinase-dependent apoptotic and necroptotic cell death during TNF signaling. Mol Cell 2015; 60: 63–76.
Li Q, Yan J, Mao AP, Li C, Ran Y, Shu HB et al. Tripartite motif 8 (TRIM8) modulates TNFα- and IL-1β-triggered NF-κB activation by targeting TAK1 for K63-linked polyubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 19341–19346.
Liao J, Karnik R, Gu H, Ziller MJ, Clement K, Tsankov AM et al. Targeted disruption of DNMT1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet 2015; 47: 469–478.
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM, Li ZW, Egan LJ et al. IKKβ links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 2004; 118: 285–296.
Hamilton KE, Simmons JG, Ding S, Van Landeghem L, Lund PK . Cytokine induction of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 is mediated by STAT3 in colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 2011; 9: 1718–1731.
Koliaraki V, Pasparakis M, Kollias G . IKKβ in intestinal mesenchymal cells promotes initiation of colitis-associated cancer. J Exp Med 2015; 212: 2235–2251.
Stoffels B, Hupa KJ, Snoek SA, van Bree S, Stein K, Schwandt T et al. Postoperative ileus involves interleukin-1 receptor signaling in enteric glia. Gastroenterology 2014; 146: 176–187.
Xiao H, Yin W, Khan MA, Gulen MF, Zhou H, Sham HP et al. Loss of single immunoglobulin interlukin-1 receptor-related molecule leads to enhanced colonic polyposis in Apc(min) mice. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 574–585.
McKenna LB, Schug J, Vourekas A, McKenna JB, Bramswig NC, Friedman JR et al. MicroRNAs control intestinal epithelial differentiation, architecture, and barrier function. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 1654–1664 1664.e1651.
Shi C, Yang Y, Xia Y, Okugawa Y, Yang J, Liang Y et al. Novel evidence for an oncogenic role of microRNA-21 in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut 2016; 65: 1470–1481.
Neudecker V, Haneklaus M, Jensen O, Khailova L, Masterson JC, Tye H et al. Myeloid-derived miR-223 regulates intestinal inflammation via repression of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Exp Med 2017; 214: 1737–1752.
Wang H, Chao K, Ng SC, Bai AH, Yu Q, Yu J et al. Pro-inflammatory miR-223 mediates the cross-talk between the IL23 pathway and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Biol 2016; 17: 58.
He C, Yu T, Shi Y, Ma C, Yang W, Fang L et al. MicroRNA 301A promotes intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated cancer development by inhibiting BTG1. Gastroenterology 2017; 152: 1434–1448.
Li M, Zhang S, Qiu Y, He Y, Chen B, Mao R et al. Upregulation of miR-665 promotes apoptosis and colitis in inflammatory bowel disease by repressing the endoplasmic reticulum stress components XBP1 and ORMDL3. Cell Death Dis 2017; 8: e2699.
Vereecke L, Sze M, Mc Guire C, Rogiers B, Chu Y, Schmidt-Supprian M et al. Enterocyte-specific A20 deficiency sensitizes to tumor necrosis factor-induced toxicity and experimental colitis. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 1513–1523.
Fang L, Lu W, Choi HH, Yeung SC, Tung JY, Hsiao CD et al. ERK2-dependent phosphorylation of CSN6 is critical in colorectal cancer development. Cancer Cell 2015; 28: 183–197.
Elinav E, Strowig T, Kau AL, Henao-Mejia J, Thaiss CA, Booth CJ et al. NLRP6 inflammasome regulates colonic microbial ecology and risk for colitis. Cell 2011; 145: 745–757.
Chivukula RR, Shi G, Acharya A, Mills EW, Zeitels LR, Anandam JL et al. An essential mesenchymal function for miR-143/145 in intestinal epithelial regeneration. Cell 2014; 157: 1104–1116.
Valeri N, Braconi C, Gasparini P, Murgia C, Lampis A, Paulus-Hock V et al. MicroRNA-135b promotes cancer progression by acting as a downstream effector of oncogenic pathways in colon cancer. Cancer Cell 2014; 25: 469–483.
Lamas B, Richard ML, Leducq V, Pham HP . CARD9 impacts colitis by altering gut microbiota metabolism of tryptophan into aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. Nat Med 2016; 22: 598–605.
Han H, Li W, Shen H, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Li Y . microRNA-129-5p, a c-Myc negative target, affects hepatocellular carcinoma progression by blocking the Warburg effect. J Mol Cell Biol 2016; 8: 600–610.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772609, 81472549, 31521091) and National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC1302300, 2014CB910600). We thank Professor Hongbing Shu (Wuhan University, Wuhan, China) for providing reagents and the Model Animal Research Center of Nanjing University for miR-148a KO mice.
Author contributions
YZ, LG, YL and YL designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. YZ, LG and YL performed most of the experiments. BZ and EP provided the reagents. JZ, FZ and QZ provided the human colon samples. YL and EP wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by R De Mari
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Cell Death and Differentiation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Gu, L., Li, Y. et al. miR-148a inhibits colitis and colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. Cell Death Differ 24, 2199–2209 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.151
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.151
This article is cited by
-
Impact of mare milk-derived small extracellular vesicles on proliferation, phagocytosis, and migration in RAW264.7 macrophage
Scientific Reports (2026)
-
The influence of blood levels of circRNAs and microRNAs on the development of ulcerative colitis
Molecular Biology Reports (2026)
-
Targeting Dicer reprograms tumor-associated macrophages to promote anti-tumoral immunity in colorectal cancer liver metastasis
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2025)
-
MicroRNA in intestinal tight junction regulation
npj Gut and Liver (2025)
-
The role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of colorectal cancer and colitis-associated cancer
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2025)