Abstract
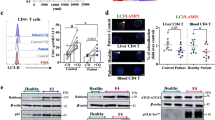
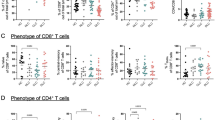
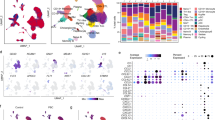
Increasing evidence indicates a role for regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the immune response and in autoimmune diseases, but the role of Tregs and cytokines in autoimmune hepatic diseases remains largely unclear and controversial, especially in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). This study was undertaken to investigate Tregs and different cytokines in the liver and peripheral blood of PBC patients. We found that these patients demonstrated a reduction of CD4+CD25+ T cells but elevated CD4+Foxp3+ T cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and CD4+ T cells. The percentage of CD4+CD25+ T cells in PBMCs was negatively correlated with elevated plasma interferon (IFN)-γ levels. A liver-specific analysis showed that the frequency of Foxp3+ Tregs, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and IFN-γ were increased in PBC patients. Our findings suggest that an imbalance between CD4+CD25+ Tregs and cytotoxic cytokines plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of PBC while the role of Foxp3 needs further investigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan MM, Gershwin ME . Primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1261–1273.
Prince M, Chetwynd A, Newman WL, Metcalf JV, James OF . Survival and symptom progression in a geographically based cohort of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: follow-up for up to 28 years. Gastroenterology 2002; 123: 1044–1051.
Jones DE . Pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2003; 39: 639–648.
Jones DE . Pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. Postgrad Med J 2008; 84: 23–33.
Denning TL, Wang YC, Patel SR, Williams IR, Pulendran B . Lamina propria macrophages and dendritic cells differentially induce regulatory and interleukin 17-producing T cell responses. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 1086–1094.
Kita H, Lian ZX, van de Water J, He XS, Matsumura S, Kaplan M et al. Identification of HLA-A2-restricted CD8+ cytotoxic T cell responses in primary biliary cirrhosis: T cell activation is augmented by immune complexes cross-presented by dendritic cells. J Exp Med 2002; 195: 113–123.
Kita H, Imawari M, Gershwin ME . Cellular immune response in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatol Res 2004; 28: 12–17.
Sakaguchi S . Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 345–352.
Sakaguchi S, Setoguchi R, Yagi H, Nomura T . Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2006; 305: 51–66.
Valencia X, Yarboro C, Illei G, Lipsky PE . Deficient CD4+CD25high T regulatory cell function in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2007; 178: 2579–2588.
Behrens F, Himsel A, Rehart S, Stanczyk J, Beutel B, Zimmermann SY et al. Imbalance in distribution of functional autologous regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2007; 66: 1151–1156.
Boissier MC, Assier E, Bitona J, Denys A, Falgarone G, Bessis N . Regulatory T cells (Treg) in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 2009; 76: 10–14.
Sakaguchi S . Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 2004; 22: 531–562.
Yamashiki M, Kosaka Y, Nishimura A, Watanabe S, Nomoto M, Ichida F . Analysis of serum cytokine levels in primary biliary cirrhosis patients and healthy adults. J Clin Lab Anal 1998; 12: 77–82.
Zachou K, Rigopoulou EI, Tsikrikoni A, Alexandrakis MG, Passam F, Kyriakou DS et al. Autoimmune hepatitis type 1 and primary biliary cirrhosis have distinct bone marrow cytokine production. J Autoimmun 2005; 25: 283–288.
Heathcote EJ . Management of primary biliary cirrhosis. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases practice guidelines. Hepatology 2000; 31: 1005–1013.
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M . Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol 1995; 155: 1151–1164.
Sakaguchi S, Powrie F . Emerging challenges in regulatory T cell function and biology. Science 2007; 317: 627–629.
Fontenot JD, Rudensky AY . A well adapted regulatory contrivance: regulatory T cell development and the forkhead family transcription factor Foxp3. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 331–337.
Jiang SP . Regulatory T cells: from bench to bedside. Int Immunopharmacol 2009; 9: 515–517.
Lan RY, Cheng C, Lian ZX, Tsuneyama K, Yang GX, Moritoki Y et al. Liver-targeted and peripheral blood alterations of regulatory T cells in primary biliary cirrhsis. Hepatology 2006; 43: 729–737.
Liu B, Shi XH, Zhang FC, Zhang W, Gao LX . Antimitochondrial antibodidy-negative primary biliary cirrhosis: a subset of primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver Int 2008; 28: 233–239.
Sakaki M, Hiroishi K, Baba T, Ito T, Hirayama Y, Saito K et al. Intrahepatic status of regulatory T cells in autoimmune liver diseases and chronic viral hepatitis. Hepatol Res 2008; 38: 354–361.
Sasaki M, Ikeda H, Sawada S, Sato Y, Nakanuma Y . Naturally-occurring regulatory T cells are increased in inflamed portal tracts with cholangiopathy in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Pathol 2007; 60: 1102–1107.
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S . Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 2003; 299: 1057–1061.
Wang J, Ioan-Facsinay A, van der Voort EI, Huizinga TW, Toes RE . Transient expression of FOXP3 in human activated nonregulatory CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 129–138.
Allan SE, Crome SQ, Crellin NK, Passerini L, Steiner TS, Bacchetta R et al. Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int Immunol 2007; 19: 345–354.
Ziegler S . FOXP3: not just for regulatory T cells anymore. Eur J Immunol 2007; 37: 21–23.
Bonelli M, von Dalwigk K, Savitskaya A, Smolen JS, Scheinecker C . Foxp3 expression in CD4+ T cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparative phenotypic analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 2008; 67: 664–671.
Han GM, O'Neil-Andersen NJ, Zurier RB, Lawrence DA . CD4+CD25high T cell numbers are enriched in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol 2008; 253: 92–101.
Yamashiki M, Kosaka Y, Nishimura A, Watanabe S, Nomoto M, Ichida F . Analysis of serum cytokine levels in primary biliary cirrhosis patients and healthy adults. J Clin Lab Anal 1998; 12: 77–82.
Shimoda S, Ishikawa F, Kamihira T, Komori A, Niiro H, Baba E et al. Autoreactive T-cell responses in primary biliary cirrhosis are proinflammatory whereas those of controls are regulatory. Gastroenterology 2006; 131: 606–618.
Camara NO, Sebille F, Lechler RI . Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory cells have marked and sustained effects on CD8+ T cell activation. Eur J Immunol 2003; 33: 3473–3483.
Tran DQ, Ramsey H, Shevach EM . Induction of FOXP3 expression in naive human CD4+ FOXP3 T cells by T-cell receptor stimulation is transforming growth factor-β dependent but does not confer a regulatory phenotype. Blood 2007; 110: 2983–2990.
Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK, Flavell RA . Transforming growth factor-β regulation of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 2006; 24: 99–146.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Jiangsu Province 135 Talent Foundation (RC2007004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Note: Supplementary information is available on the Cellular & Molecular Immunology website.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Zhang, H., Liang, J. et al. CD4+CD25+ but not CD4+Foxp3+ T cells as a regulatory subset in primary biliary cirrhosis. Cell Mol Immunol 7, 485–490 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.40
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hair dyes as a risk for autoimmunity: from systemic lupus erythematosus to primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmunity Highlights (2013)
-
Dense fine-mapping study identifies new susceptibility loci for primary biliary cirrhosis
Nature Genetics (2012)
-
Efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid combined with Tongdan Decoction (通胆汤) on immunological indices and histopathological changes in primary biliary cirrhosis patients
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2012)