Abstract
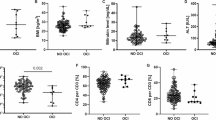
CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) are increased in patients with chronic hepatitis C, which may contribute to the sustained suppression of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific T-cell responses and viral persistence in HCV-infected individuals. We postulated that HCV core protein (HCVc) directly contributes to the expansion of Tregs in HCV-infected patients, and we provide evidence to support this hypothesis in the report. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and sera were collected from 87 treatment-naïve chronic HCV-infected patients, CD4+CD25+ Tregs were measured by flow cytometry, and HCV RNA and HCVc levels were detected using qPCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), respectively. CD4+, CD8+, CD4+CD25+ and CD4+CD25− T cells were purified from healthy donors and cultured with recombinant HCVc and Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands. Flow cytometry was used to analyze cell proliferation, and ELISA was performed to measure cytokine production. In the 87 chronic HCV-infected patients, HCVc showed a significant correlation with HCV RNA and CD4+CD25+ Tregs. Mechanistic studies showed that HCVc, together with anti-CD3 antibody, augmented CD4+CD25+ Treg proliferation, but inhibited CD4+CD25− T-cell proliferation and IFN-γ production, in a dose-dependent and Treg-dependent manner. Moreover, unlike the TLR3 ligand (poly I:C) and the TLR4 ligand (lipopolysaccharide, LPS), the TLR2 ligand (lipoteichoic acid, LTA) and HCVc both inhibited TCR-induced CD4+ T-cell proliferation and IFN-γ secretion in a Treg-dependent manner. These data indicate that HCVc, like other TLR2 ligands, triggers CD4+CD25+ Treg activation and expansion to inhibit host immune responses, which may play a critical role in viral persistence in HCV-infected patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Urbani S, Amadei B, Tola D, Massari M, Schivazappa S, Missale G et al. PD-1 expression in acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is associated with HCV-specific CD8 exhaustion. J Virol 2006; 80: 11398–11403.
Radziewicz H, Ibegbu CC, Fernandez ML, Workowski KA, Obideen K, Wehbi M et al. Liver-infiltrating lymphocytes in chronic human hepatitis C virus infection display an exhausted phenotype with high levels of PD-1 and low levels of CD127 expression. J Virol 2007; 81: 2545–2553.
Sekyere SO, Suneetha PV, Kraft A, Zhang S, Dietz J, Sarrazin C et al. A heterogeneous hierarchy of co-regulatory receptors regulates exhaustion of HCV-specific CD8 T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2014; in press. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.008.
Manigold T, Shin EC, Mizukoshi E, Mihalik K, Murthy KK, Rice CM et al. Foxp3+CD4+CD25+ T cells control virus-specific memory T cells in chimpanzees that recovered from hepatitis C. Blood 2006; 107: 4424–4432.
Rezaei N, Amirzargar AA, Shakiba Y, Mahmoudi M, Moradi B, Aghamohammadi A . Proinflammatory cytokine gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol 2009; 155: 21–27.
Tu Z, Pierce RH, Kurtis J, Kuroki Y, Crispe IN, Orloff MS . Hepatitis C virus core protein subverts the antiviral activities of human Kupffer cells. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 305–314.
Tu Z, Hamalainen-Laanaya HK, Nishitani C, Kuroki Y, Crispe IN, Orloff MS . HCV core and NS3 proteins manipulate human blood-derived dendritic cell development and promote Th 17 differentiation. Int Immunol 2012; 24: 97–106.
Rushbrook SM, Ward SM, Unitt E, Vowler SL, Lucas M, Klenerman P et al. Regulatory T cells suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2005; 79: 7852–7859.
Smyk-Pearson S, Golden-Mason L, Klarquist J, Burton JR Jr, Tester IA, Wang CC et al. Functional suppression by FoxP3+CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells during acute hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 2008; 197: 46–57.
Kittlesen DJ, Chianese-Bullock KA, Yao ZQ, Braciale TJ, Hahn YS . Interaction between complement receptor gC1qR and hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: 1239–1249.
Stoop JN, van der Molen RG, Baan CC, van der Laan LJ, Kuipers EJ, Kusters JG et al. Regulatory T cells contribute to the impaired immune response in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2005; 41: 771–778.
Dolganiuc A, Oak S, Kodys K . Hepatitis C core and non-structural 3 proteins trigger Toll-like receptor 2-mediated path-ways and inflammatory activation. Gastroenterology 2004; 127: 1513–1524.
Cabrera R, Tu Z, Xu Y, Firpi RJ, Rosen HR, Liu C et al. An immunomodulatory role for CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T lymphocytes in hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2004; 40: 1062–1071.
Boettler T, Spangenberg HC, Neumann-Haefelin C . T cells with a CD4+CD25+ regulatory phenotype suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8þT cells during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2005; 79: 7860–7867.
Ebinuma H, Nakamoto N, Li Y, Price DA, Gostick E, Levine BL et al. Identification and in vitro expansion of functional antigen-specific CD25FoxP3 regulatory T cells in hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2008; 82: 5043–5053.
Gale M Jr, Foy EM . Evasion of intracellular host defence by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005; 436: 939–945.
Saito T, Owen DM, Jiang F, Marcotrigiano J, Gale M . Innate immunity induced by composition-dependent RIG-I recognition of hepatitis C virus RNA. Nature 2008; 454: 523–527.
Machida K, Cheng KT, Sung VM, Levine AM, Foung S, Lai MM . Hepatitis c virus induces Toll-like receptor 4 expression, leading to enhanced production of beta interferon and interleukin-6. J Virol 2006; 80: 866–874.
Dolganiuc A, Chang S, Kodys K, Mandrekar P, Bakis G, Cormier M et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein-induced, monocyte-mediated mechanisms of reduced IFN-alpha and plasmacytoid dendritic cell loss in chronic HCV infection. J Immunol 2006; 177: 6758–6768.
Fernandez-Ponce C, Dominguez-Villar M, Aguado E, Garcia-Cozar F . CD4+ primary T cells expressing HCV-core protein upregulate Foxp3 and IL-10, suppressing CD4 and CD8 T cells. PLoS One 2014; 9: e85191.
Doumba PP, Serti E, Boutsikou M, Konstadoulakis MM, Georgopoulou U, Koskinas J . Phenotypic and functional alterations of primary human PBMCs induced by HCV non-enveloped capsid-like particles uptake. Cell Mol Life Sci 2013; 70: 3463–3474.
Sundstrom S, Ota S, Dimberg LY, Masucci MG, Bergqvist A . Hepatitis C virus core protein induces an anergic state characterized by decreased interleukin-2 production and perturbation of mitogen-activated protein kinase responses. J Virol 2005; 79: 2230–2239.
Kittlesen DJ, Chianese-Bullock KA, Yao ZQ, Braciale TJ, Hahn YS . Interaction between complement receptor gC1qR and hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits T-lymphocyte proliferation. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: 1239–1249.
Cummings KL, Rosen HR, Hahn YS . Frequency of gC1qR+CD4+ T cells increases during acute hepatitis C virus infection and remains elevated in patients with chronic infection. Clin Immunol 2009; 132: 401–411.
Dominguez-Villar M, Fernandez-Ponce C, Munoz-Suano A, Gomez E, Rodríguez-Iglesias M, Garcia-Cozar F . Up-regulation of FOXP3 and induction of suppressive function in CD4-Jurkat T-cells expressing hepatitis C virus core protein. Clin Sci 2012; 123: 15–27.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81373143, to ZT) and by NIH (AI095097, to LS). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website. (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, N., Chi, X., Li, T. et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein triggers expansion and activation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in chronic hepatitis C patients. Cell Mol Immunol 12, 743–749 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.119
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.119
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
HCV immune evasion and regulatory T cell activation: cause or consequence?
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
HCV core protein inhibits polarization and activity of both M1 and M2 macrophages through the TLR2 signaling pathway
Scientific Reports (2016)