Abstract
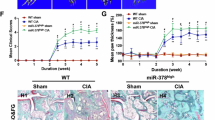
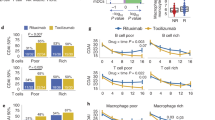
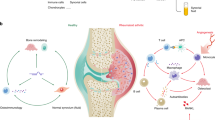
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by abnormal inflammation, angiogenesis, and cartilage destruction. Our previous study demonstrated an increased expression of thioredoxin domain containing 5 (TXNDC5) in the synovial tissues of RA, and its overexpression was implicated in RA pathology. Although TXNDC5 variation is linked to genetic susceptibility to RA, the regulation of its abnormal expression has not been well defined. Here, we show that TXNDC5 is directly targeted by microRNA (miR)-573, and TXNDC5, in turn, mediates the suppressive effect of miR-573 on the invasion of synovial fibroblasts of RA (RASFs). miR-573 overexpression suppressed the expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and cyclooxygenase 2 in RASFs, as well as the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta by activated THP-1 cells in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. Moreover, treatment with conditioned medium of RASFs transfected with miR-573 mimic inhibited the angiogenic ability of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Of note, epidermal growth factor receptor and Toll-like receptor 2 were validated as new direct targets of miR-573, and mediate the regulation of miR-573 on IL-6 production as well as the angiogenesis of HUVECs. In addition, exogenous miR-573 expression suppressed the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/activate protein kinase B in RASFs in response to LPS. Indeed, MAPK signaling was essential to ensure the function of miR-573. Taken together, our study points toward the protective roles of miR-573 in the pathological process of RA and suggests a potential target in the treatment of RA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meier FM, Frerix M, Hermann W, Muller-Ladner U . Current immunotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunotherapy 2013; 5: 955–974.
Chang X, Cui Y, Zong M, Zhao Y, Yan X, Chen Y et al. Identification of proteins with increased expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues. J Rheumatol 2009; 36: 872–880.
Chang X, Zhao Y, Yan X, Pan J, Fang K, Wang L . Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2011; 13: R124.
Horna-Terrón E, Pradilla-Dieste A, Sánchez-de-Diego C, Osada J . TXNDC5, a newly discovered disulfide isomerase with a key role in cell physiology and pathology. Int J Mol Sci 2014; 15: 23501–23518.
Wang L, Zheng Y, Xu H, Yan X, Chang X . Investigate pathogenic mechanism of TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 2013; 8: e53301.
Filkova M, Jungel A, Gay RE, Gay S . MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: potential role in diagnosis and therapy. BioDrugs 2012; 26: 131–141.
Hochberg MC, Chang RW, Dwosh I, Lindsey S, Pincus T, Wolfe F . The American College of Rheumatology 1991 revised criteria for the classification of global functional status in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1992; 35: 498–502.
Kong X, Zhang Y, Liu C, Guo W, Li X, Su X et al. Anti-angiogenic effect of triptolide in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting angiogenic cascade. PLoS One 2013; 8: e77513.
Wang L, Chang X, Yuan G, Zhao Y, Wang P . Expression of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 in ovarian tumors. Int J Biol Sci 2010; 6: 454–464.
Wang L, Zhang J, Yang X, Chang YW, Qi M, Zhou Z et al. SOX4 is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2013; 16: 301–307.
Boissier MC, Semerano L, Challal S, Saidenberg-Kermanac’h N, Falgarone G . Rheumatoid arthritis: from autoimmunity to synovitis and joint destruction. J Autoimmun 2012; 39: 222–228.
Choi HM, Oh da H, Bang JS, Yang HI, Yoo MC, Kim KS . Differential effect of IL-1beta and TNFalpha on the production of IL-6, IL-8 and PGE2 in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and THP-1 macrophages. Rheumatol Int 2010; 30: 1025–1033.
Yao X, Huang J, Zhong H, Shen N, Faggioni R, Fung M et al. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol Ther 2014; 141: 125–139.
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Pichot A, Ostermann E, Zuber G, Frisch B et al. MiR-20a regulates ASK1 expression and TLR4-dependent cytokine release in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 2013; 72: 1071–1079.
Chang X, Yamada R, Sawada T, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Yamamoto K . The inhibition of antithrombin by peptidylarginine deiminase 4 may contribute to pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005; 44: 293–298.
Malemud CJ . Intracellular signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Cell Immunol 2013; 4: 160.
Wittmann J, Jack HM . microRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: midget RNAs with a giant impact. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: i92–i96.
Wang HF, Chen H, Ma MW, Wang JA, Tang TT, Ni LS et al. miR-573 regulates melanoma progression by targeting the melanoma cell adhesion molecule. Oncol Rep 2013; 30: 520–526.
Siebuhr AS, Wang J, Karsdal M, Bay-Jensen AC, Jin Y, Zheng Q . Matrix metalloproteinase-dependent turnover of cartilage, synovial membrane, and connective tissue is elevated in rats with collagen induced arthritis. J Transl Med 2012; 10: 195.
Siebert S, Tsoukas A, Robertson J, McInnes I . Cytokines as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2015; 67: 280–309.
Xu L, Feng X, Tan W, Gu W, Guo D, Zhang M et al. IL-29 enhances Toll-like receptor-mediated IL-6 and IL-8 production by the synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 2013; 15: R170.
Xu Z, Xiao SB, Xu P, Xie Q, Cao L, Wang D et al. miR-365, a novel negative regulator of interleukin-6 gene expression, is cooperatively regulated by Sp1 and NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 21401–21412.
Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Filer A, Raza K, Kolling C et al. Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:373–381.
Youn J, Cho ML, Kim YJ, Yun HS, Park SH, Jin CZ et al. New cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor DFU regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Immunol Lett 2005; 96: 219–224.
He ZW, Qin YH, Wang ZW, Chen Y, Shen Q, Dai SM . HMGB1 acts in synergy with lipopolysaccharide in activating rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Mediators Inflamm 2013; 2013: 596716.
Lai NS, Yu HC, Chen HC, Yu CL, Huang HB, Lu MC . Aberrant expression of microRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis contributes to the immunopathogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol 2013; 173: 47–57.
Androulidaki A, Iliopoulos D, Arranz A, Doxaki C, Schworer S, Zacharioudaki V et al. The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity 2009; 31: 220–231.
Liu Y, Chen Q, Song Y, Lai L, Wang J, Yu H et al. MicroRNA-98 negatively regulates IL-10 production and endotoxin tolerance in macrophages after LPS stimulation. FEBS Lett 2011; 585: 1963–1968.
Tang CH, Hsu CJ, Yang WH, Fong YC . Lipoteichoic acid enhances IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts via TLR2 receptor, PKCdelta and c-Src dependent pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 2010; 9: 1648–1657.
Swanson CD, Akama-Garren EH, Stein EA, Petralia JD, Ruiz PJ, Edalati A et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 2012; 188: 3513–3521.
Killock D . Experimental arthritis: targeting EGFR to fight synovitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2012; 8: 247.
Chiu YC, Lin CY, Chen CP, Huang KC, Tong KM, Tzeng CY et al. Peptidoglycan enhances IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts via TLR2 receptor, focal adhesion kinase, Akt, and AP-1- dependent pathway. J Immunol 2009; 183: 2785–2792.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81373218, 81302239, 81300426) and the Foundation for Scientific and Technological Achievements of Jinan (Grant No. 201302046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Song, G., Zheng, Y. et al. miR-573 is a negative regulator in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Immunol 13, 839–849 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.63
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.63
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases
European Journal of Medical Research (2022)
-
E2F2 directly regulates the STAT1 and PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathways to exacerbate the inflammatory phenotype in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and mouse embryonic fibroblasts
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018)
-
TXNDC5 synergizes with HSC70 to exacerbate the inflammatory phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis through NF-κB signaling
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
Expression of Semaphorin 4A and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2015)