Abstract
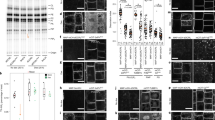
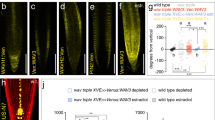
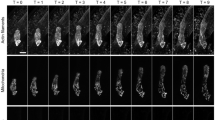
Within a multicellular tissue cells may coordinately form a singular or multiple polar axes, but it is unclear whether a common mechanism governs different types of polar axis formation. The phosphorylation status of PIN proteins, which is directly affected by the PINOID (PID) protein kinase and the PP2A protein phosphatase, is known to regulate the apical-basal polarity of PIN localization in bipolar cells of roots and shoot apices. Here, we provide evidence that the phosphorylation status-mediated PIN polarity switch is widely used to modulate cellular processes in Arabidopsis including multipolar pavement cells (PC) with interdigitated lobes and indentations. The degree of PC interdigitation was greatly reduced either when the FYPP1 gene, which encodes a PP2A called phytochrome-associated serine/threonine protein phosphatase, was knocked out or when the PID gene was overexpressed (35S::PID). These genetic modifications caused PIN1 localization to switch from lobe to indentation regions. The PP2A and PID mediated switching of PIN1 localization is strikingly similar to their regulation of the apical-basal polarity switch of PIN proteins in other cells. Our findings suggest a common mechanism for the regulation of PIN1 polarity formation, a fundamental cellular process that is crucial for pattern formation both at the tissue/organ and cellular levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
McEwen DG, Peifer M . Wnt signaling: the naked truth? Curr Biol 2001; 11:R524–R526.
Goto T, Davidson L, Asashima M, Keller R . Planar cell polarity genes regulate polarized extracellular matrix deposition during frog gastrulation. Curr Biol 2005; 15:787–793.
Klein TJ, Mlodzik M . Planar cell polarization: an emerging model points in the right direction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2005; 21:155–176.
Settleman J . Intercalating Arabidopsis leaf cells: a jigsaw puzzle of lobes, necks, ROPs, and RICs. Cell 2005; 120:570–572.
Price MH, Roberts DM, McCartney BM, Jezuit E, Peifer M . Cytoskeletal dynamics and cell signaling during planar polarity establishment in the Drosophila embryonic denticle. J Cell Sci 2006; 119(Pt 3):403–415.
Fu Y, Li H, Yang Z . The ROP2 GTPase controls the formation of cortical fine F-actin and the early phase of directional cell expansion during Arabidopsis organogenesis. Plant Cell 2002; 14:777–794.
Smith LG . Cytoskeletal control of plant cell shape: getting the fine points. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2003; 6:63–73.
Li S, Blanchoin L, Yang Z, Lord EM . The putative Arabidopsis arp2/3 complex controls leaf cell morphogenesis. Plant Physiol 2003; 132:2034–2044.
Fu Y, Gu Y, Zheng Z, Wasteneys G, Yang Z . Arabidopsis interdigitating cell growth requires two antagonistic pathways with opposing action on cell morphogenesis. Cell 2005; 120:687–700.
Yang Z . Cell polarity signaling in Arabidopsis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2008; 24:551–575.
Fu Y, Xu T, Zhu L, Wen M, Yang Z . A ROP GTPase signaling pathway controls cortical microtubule ordering and cell expansion in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 2009; 19:1827–1832.
Xu T, Wen M, Nagawa S, et al. Cell surface- and rho GTPase-based auxin signaling controls cellular interdigitation in Arabidopsis. Cell 2010; 143:99–110.
Wisniewska J, Xu J, Seifertova D, et al. Polar PIN localization directs auxin flow in plants. Science 2006; 312:883.
Michniewicz M, Zago MK, Abas L, et al. Antagonistic regulation of PIN phosphorylation by PP2A and PINOID directs auxin flux. Cell 2007; 130:1044–1056.
Huang F, Zago MK, Abas L, et al. Phosphorylation of conserved PIN motifs directs Arabidopsis PIN1 polarity and auxin transport. Plant Cell 2010; 22:1129–1142.
Friml J, Yang X, Michniewicz M, et al. A PINOID-dependent binary switch in apical-basal PIN polar targeting directs auxin efflux. Science 2004; 306:862–865.
Kleine-Vehn J, Huang F, Naramoto S, et al. PIN auxin efflux carrier polarity is regulated by PINOID kinase-mediated recruitment into GNOM-independent trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009; 21:3839–3849.
Kim DH, Kang JG, Yang SS, et al. A phytochrome-associated protein phosphatase 2A modulates light signals in flowering time control in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2002; 14:3043–3056.
Benjamins R, Quint A, Weijers D, Hooykaas P, Offringa R . The PINOID protein kinase regulates organ development in Arabidopsis by enhancing polar auxin transport. Development 2001; 128:4057–4067.
Christensen SK, Dagenais N, Chory J, Weigel D . Regulation of auxin response by the protein kinase PINOID. Cell 2000; 100:469–478.
Sukumar P, Edwards KS, Rahman A, Delong A, Muday GK . PINOID kinase regulates root gravitropism through modulation of PIN2-dependent basipetal auxin transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 2009; 150:722–735.
Zourelidou M, Muller I, Willige BC, et al. The polarly localized D6 PROTEIN KINASE is required for efficient auxin transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 2009; 136:627–636.
Zhang J, Nodzynski T, Pencik A, Rolcik J, Friml J . PIN phosphorylation is sufficient to mediate PIN polarity and direct auxin transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107:918–922.
Dhonukshe P, Huang F, Galvan-Ampudia CS, et al. Plasma membrane-bound AGC3 kinases phosphorylate PIN auxin carriers at TPRXS(N/S) motifs to direct apical PIN recycling. Development 2010; 137:3245–3255.
Jaillais Y, Santambrogio M, Rozier F, et al. The retromer protein VPS29 links cell polarity and organ initiation in plants. Cell 2007; 130:1057–1070.
Hazak O, Bloch D, Poraty L, et al. A rho scaffold integrates the secretory system with feedback mechanisms in regulation of auxin distribution. PLoS Biol 2010; 8:e1000282.
Li L, Xu J, Xu ZH, Xue HW . Brassinosteroids stimulate plant tropisms through modulation of polar auxin transport in Brassica and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005; 17:2738–2753.
Robert S, Kleine-Vehn J, Barbez E, et al. ABP1 mediates auxin inhibition of clathrin-dependent endocytosis in Arabidopsis. Cell 2010; 143:111–121.
Garbers C, DeLong A, Deruere J, Bernasconi P, Soll D . A mutation in protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit A affects auxin transport in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 1996; 15:2115–2124.
Rashotte AM, DeLong A, Muday GK . Genetic and chemical reductions in protein phosphatase activity alter auxin transport, gravity response, and lateral root growth. Plant Cell 2001; 13:1683–1697.
Wasteneys GO, Willingale-Theune J, Menzel D . Freeze shattering: a simple and effective method for permeabilizing higher plant cell walls. J Microsc 1997; 188 (Part 1):51–61.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to members of the Yang group for stimulating discussions during the course of this work. This work is supported by grants from the US National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM081451 and GM081451-03S2). HL was partly supported by Chinese Scholarship Council. PD was supported by Netherlands Scientific Organization NWO-VENI grant and BS by NWO Spinoza prize.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
( Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
Short lobe phenotype of fypp1 can be rescued by 35S::FYPP1. (PDF 625 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
Pavement cell shapes of cotyledons from WT and pp2aa1 pp2aa3 double mutant. (PDF 433 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S3
PIN1 localization in guard cells was also switched in 35S::PID plants. (PDF 151 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Lin, D., Dhonukshe, P. et al. Phosphorylation switch modulates the interdigitated pattern of PIN1 localization and cell expansion in Arabidopsis leaf epidermis. Cell Res 21, 970–978 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2011.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2011.49
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Involvement of differentially accumulated proteins and endogenous auxin in adventitious root formation in micropropagated shoot cuttings of Cedrela fissilis Vellozo (Meliaceae)
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) (2022)
-
Auxin-induced signaling protein nanoclustering contributes to cell polarity formation
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Mining and expression analysis of candidate genes involved in regulating the chilling requirement fulfillment of Paeonia lactiflora ‘Hang Baishao’
BMC Plant Biology (2017)
-
Cytokinin signaling regulates pavement cell morphogenesis in Arabidopsis
Cell Research (2013)