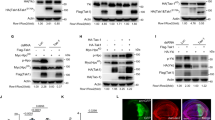
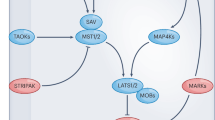
Abstract
Deregulation of the evolutionarily conserved Hippo pathway has been implicated in abnormal development of animals and in several types of cancer. One mechanism of Hippo pathway regulation is achieved by controlling the stability of its regulatory components. However, the executive E3 ligases that are involved in this process, and how the process is regulated, remain poorly defined. In this study, we identify, through a genetic candidate screen, the SCFSlmb E3 ligase as a novel negative regulator of the Hippo pathway in Drosophila imaginal tissues via mediation of the degradation of Expanded (Ex). Mechanistic study shows that Slmb-mediated degradation of Ex is inhibited by the Hippo signaling. Considering the fact that Hippo signaling suppresses the transcription of ex, we propose that the Hippo pathway employs a double security mechanism to ensure fine-tuned homeostasis during development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Hpo:
-
Hippo
- Wts:
-
Warts
- Yki:
-
Yorkie
- Ft:
-
Fat
- Mer:
-
Merlin
- Ex:
-
Expanded
- D:
-
Dachs
- Fj:
-
Four-jointed
- Ds:
-
Dachsous
References
Harvey KF, Pfleger CM, Hariharan IK . The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell 2003; 114:457–467.
Udan RS, Kango-Singh M, Nolo R, Tao C, Halder G . Hippo promotes proliferation arrest and apoptosis in the Salvador/Warts pathway. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5:914–920.
Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D . Hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with salvador and warts. Cell 2003; 114:445–456.
Lai ZC, Wei X, Shimizu T, et al. Control of cell proliferation and apoptosis by mob as tumor suppressor, mats. Cell 2005; 120:675–685.
Staley BK, Irvine KD . Hippo signaling in Drosophila: recent advances and insights. Dev Dyn 2012; 241:3–15.
Jia J, Zhang W, Wang B, Trinko R, Jiang J . The Drosophila Ste20 family kinase dMST functions as a tumor suppressor by restricting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. Genes Dev 2003; 17:2514–2519.
Pan D . The Hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell 2010; 19:491–505.
Harvey KF, Zhang X, Thomas DM . The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2013; 13:246–257.
Yu FX, Guan KL . The Hippo pathway: regulators and regulations. Genes Dev 2013; 27:355–371.
Thompson BJ, Cohen SM . The Hippo pathway regulates the bantam microRNA to control cell proliferation and apoptosis in Drosophila. Cell 2006; 126:767–774.
Hamaratoglu F, Willecke M, Kango-Singh M, et al. The tumour-suppressor genes NF2/Merlin and Expanded act through Hippo signalling to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8:27–36.
Genevet A, Wehr MC, Brain R, Thompson BJ, Tapon N . Kibra is a regulator of the Salvador/Warts/Hippo signaling network. Dev Cell 2010; 18:300–308.
Baumgartner R, Poernbacher I, Buser N, Hafen E, Stocker H . The WW domain protein Kibra acts upstream of Hippo in Drosophila. Dev Cell 2010; 18:309–316.
Yu J, Zheng Y, Dong J, et al. Kibra functions as a tumor suppressor protein that regulates Hippo signaling in conjunction with Merlin and Expanded. Dev Cell 2010; 18:288–299.
Boggiano JC, Fehon RG . Growth control by committee: intercellular junctions, cell polarity, and the cytoskeleton regulate Hippo signaling. Dev Cell 2012; 22:695–702.
Cho E, Feng Y, Rauskolb C, et al. Delineation of a Fat tumor suppressor pathway. Nat Genet 2006; 38:1142–1150.
Rauskolb C, Pan G, Reddy BV, Oh H, Irvine KD . Zyxin links fat signaling to the hippo pathway. PLoS Biol 2011; 9:e1000624.
Bennett FC, Harvey KF . Fat cadherin modulates organ size in Drosophila via the Salvador/Warts/Hippo signaling pathway. Curr Biol 2006; 16:2101–2110.
Silva E, Tsatskis Y, Gardano L, Tapon N, McNeill H . The tumor-suppressor gene fat controls tissue growth upstream of expanded in the hippo signaling pathway. Curr Biol 2006; 16:2081–2089.
Willecke M, Hamaratoglu F, Kango-Singh M, et al. The fat cadherin acts through the hippo tumor-suppressor pathway to regulate tissue size. Curr Biol 2006; 16:2090–2100.
Feng Y, Irvine KD . Fat and expanded act in parallel to regulate growth through warts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104:20362–20367.
Chen CL, Gajewski KM, Hamaratoglu F, et al. The apical-basal cell polarity determinant Crumbs regulates Hippo signaling in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107:15810–15815.
Grzeschik NA, Parsons LM, Allott ML, Harvey KF, Richardson HE . Lgl, aPKC, and Crumbs regulate the Salvador/Warts/Hippo pathway through two distinct mechanisms. Curr Biol 2010; 20:573–581.
Ling C, Zheng Y, Yin F, et al. The apical transmembrane protein Crumbs functions as a tumor suppressor that regulates Hippo signaling by binding to Expanded. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107:10532–10537.
Robinson BS, Huang J, Hong Y, Moberg KH . Crumbs regulates Salvador/Warts/Hippo signaling in Drosophila via the FERM-domain protein Expanded. Curr Biol 2010; 20:582–590.
Yue T, Tian A, Jiang J . The cell adhesion molecule echinoid functions as a tumor suppressor and upstream regulator of the Hippo signaling pathway. Dev Cell 2012; 22:255–267.
Dui W, Lu W, Ma J, Jiao R . A systematic phenotypic screen of F-box genes through a tissue-specific RNAi-based approach in Drosophila. J Genet Genomics 2012; 39:397–413.
Rogers GC, Rusan NM, Roberts DM, Peifer M, Rogers SL . The SCF Slimb ubiquitin ligase regulates Plk4/Sak levels to block centriole reduplication. J Cell Biol 2009; 184:225–239.
Ho MS, Ou C, Chan YR, Chien CT, Pi H . The utility F-box for protein destruction. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008; 65:1977–2000.
Wu S, Liu Y, Zheng Y, Dong J, Pan D . The TEAD/TEF family protein Scalloped mediates transcriptional output of the Hippo growth-regulatory pathway. Dev Cell 2008; 14:388–398.
Miletich I, Limbourg-Bouchon B . Drosophila null slimb clones transiently deregulate Hedgehog-independent transcription of wingless in all limb discs, and induce decapentaplegic transcription linked to imaginal disc regeneration. Mech Dev 2000; 93:15–26.
Herranz H, Hong X, Cohen SM . Mutual repression by bantam miRNA and Capicua links the EGFR/MAPK and Hippo pathways in growth control. Curr Biol 2012; 22:651–657.
Oh H, Irvine KD . In vivo regulation of Yorkie phosphorylation and localization. Development 2008; 135:1081–1088.
Jiang J, Struhl G . Regulation of the Hedgehog and Wingless signalling pathways by the F-box/WD40-repeat protein Slimb. Nature 1998; 391:493–496.
McCartney BM, Kulikauskas RM, LaJeunesse DR, Fehon RG . The neurofibromatosis-2 homologue, Merlin, and the tumor suppressor expanded function together in Drosophila to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Development 2000; 127:1315–1324.
Clark HF, Brentrup D, Schneitz K, et al. Dachsous encodes a member of the cadherin superfamily that controls imaginal disc morphogenesis in Drosophila. Genes Dev 1995; 9:1530–1542.
Villano JL, Katz FN . four-jointed is required for intermediate growth in the proximal-distal axis in Drosophila. Development 1995; 121:2767–2777.
Brodsky MH, Steller H . Positional information along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila eye: graded expression of the four-jointed gene. Dev Biol 1996; 173:428–446.
Rogulja D, Rauskolb C, Irvine KD . Morphogen control of wing growth through the Fat signaling pathway. Dev Cell 2008; 15:309–321.
Zecca M, Struhl G . A feed-forward circuit linking wingless, fat-dachsous signaling, and the warts-hippo pathway to Drosophila wing growth. PLoS Biol 2010; 8:e1000386.
Schwank G, Tauriello G, Yagi R, et al. Antagonistic growth regulation by Dpp and Fat drives uniform cell proliferation. Dev Cell 2011; 20:123–130.
Simon MA, Xu A, Ishikawa HO, Irvine KD . Modulation of fat:dachsous binding by the cadherin domain kinase four-jointed. Curr Biol 2010; 20:811–817.
Ribeiro P, Holder M, Frith D, Snijders AP, Tapon N . Crumbs promotes expanded recognition and degradation by the SCFSlimb/beta-TrCP ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111:E1980–E1989.
Liu CY, Zha ZY, Zhou X, et al. The hippo tumor pathway promotes TAZ degradation by phosphorylating a phosphodegron and recruiting the SCF{beta}-TrCP E3 ligase. J Biol Chem 2010; 285:37159–37169.
Zhao B, Li L, Tumaneng K, Wang CY, Guan KL . A coordinated phosphorylation by Lats and CK1 regulates YAP stability through SCF(beta-TRCP). Genes Dev 2010; 24:72–85.
Frescas D, Pagano M . Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and beta-TrCP: tipping the scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8:438–449.
Fuchs SY, Spiegelman VS, Kumar KG . The many faces of beta-TrCP E3 ubiquitin ligases: reflections in the magic mirror of cancer. Oncogene 2004; 23:2028–2036.
Aza-Blanc P, Ramirez-Weber FA, Laget MP, Schwartz C, Kornberg TB . Proteolysis that is inhibited by hedgehog targets Cubitus interruptus protein to the nucleus and converts it to a repressor. Cell 1997; 89:1043–1053.
Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K . The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J 2012; 31:2714–2736.
Genevet A, Polesello C, Blight K, et al. The Hippo pathway regulates apical-domain size independently of its growth-control function. J Cell Sci 2009; 122(Part 14):2360–2370.
Swarup S, Verheyen EM . Drosophila homeodomain-interacting protein kinase inhibits the Skp1-Cul1-F-box E3 ligase complex to dually promote Wingless and Hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108:9887–9892.
Xie G, Zhang H, Du G, et al. Uif, a large transmembrane protein with EGF-like repeats, can antagonize Notch signaling in Drosophila. PLoS One 2012; 7:e36362.
Boggiano JC, Vanderzalm PJ, Fehon RG . Tao-1 phosphorylates Hippo/MST kinases to regulate the Hippo-Salvador-Warts tumor suppressor pathway. Dev Cell 2011; 21:888–895.
Simcox A, Mitra S, Truesdell S, et al. Efficient genetic method for establishing Drosophila cell lines unlocks the potential to create lines of specific genotypes. PLoS Genet 2008; 4:e1000142.
Dui W, Wei B, He F, et al. The Drosophila F-box protein dSkp2 regulates cell proliferation by targeting Dacapo for degradation. Mol Biol Cell 2013; 24:1676–1687, S1–S7.
Li C, Andrake M, Dunbrack R, Enders GH . A bifunctional regulatory element in human somatic Wee1 mediates cyclin A/Cdk2 binding and Crm1-dependent nuclear export. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30:116–130.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs E Knust, E Verheyen, Z Wang and Y Zhao for fly stocks; Drs I Edery, H McNeill, X Lin, D Pan and Z Yuan for plasmids; Drs R Fehon and K Irvine for anitibodies; William H Palmer, Jennifer Kennedy and Nick Contreras for critical reading of the manuscript. We thank all the Jiao lab members and members from Dr Li Liu and Yan Zhu's lab for stimulating discussions at the joint fly meetings. We are particularly grateful to Xuehong Liang for her technical assistance. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31228015, 31271573, 81470846), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program; 2012CB825504) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA04020413-02). W-M D is supported by NIH R01GM072562 and NSF IOS-1052333. C L is supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (5122027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
( Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
slmb negatively regulates Hippo pathway activity. (PDF 330 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
Genetic interaction between slmb and Hippo signaling components. (PDF 108 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S3
Slmb specifically degrades Ex in imaginal discs. (PDF 337 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S4
Wts antagonizes the Slmb-mediated Ex degradation. (PDF 252 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S5
In vivo effects of crbIntra and ft on Ex stability are dependent on slmb. (PDF 443 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Li, C., Chen, H. et al. SCFSlmb E3 ligase-mediated degradation of Expanded is inhibited by the Hippo pathway in Drosophila. Cell Res 25, 93–109 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.166
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.166
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
E2 enzyme Bruce negatively regulates Hippo signaling through POSH-mediated expanded degradation
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Shaggy regulates tissue growth through Hippo pathway in Drosophila
Science China Life Sciences (2022)
-
CRB3 regulates contact inhibition by activating the Hippo pathway in mammary epithelial cells
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
A Drosophila RNAi library modulates Hippo pathway-dependent tissue growth
Nature Communications (2016)