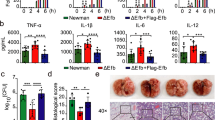
Abstract
Type I interferon (IFN) production plays pivotal roles in host antiviral innate immune responses, but an excessive production of type I IFN leads to the development of immunopathological conditions. Investigations on the regulatory mechanisms underlying host type I IFN production are currently of great interest. Here, we found that the expression of lectin family member Siglec1 was upregulated by viral infection in macrophages, which was dependent on the IFN/JAK/STAT1 signaling pathway. Siglec1 was found to negatively regulate viral infection-triggered type I IFN production. Mechanistically, Siglec1 associates with DAP12 to recruit and activate the scaffolding function of SHP2; SHP2 then recruits E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM27, which induces TBK1 degradation via K48-linked ubiquitination at Lys251 and Lys372. Therefore, viral infection-induced upregulation of Siglec1 feedback loop inhibits type I IFN production and suppresses antiviral innate immune responses. Our study outlines a novel mechanism of negative regulation of type I IFN production, which may help virus to escape immune elimination.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Liu SY, Aliyari R, Chikere K, et al. Interferon-inducible cholesterol-25-hydroxylase broadly inhibits viral entry by production of 25-hydroxycholesterol. Immunity 2013; 38:92–105.
Ivashkiv LB, Donlin LT . Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; 14:36–49.
Schneider WM, Chevillotte MD, Rice CM . Interferon-stimulated genes: a complex web of host defenses. Annu Rev Immunol 2014; 32:513–545.
Hertzog PJ, Williams BR . Fine tuning type I interferon responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2013; 24:217–225.
O'Neill LA, Golenbock D, Bowie AG . The history of Toll-like receptors — redefining innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol, 2013; 13:453–460.
Broz P, Monack DM . Newly described pattern recognition receptors team up against intracellular pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13:551–565.
Yoo JS, Kato H, Fujita T . Sensing viral invasion by RIG-I like receptors. Curr Opin Microbiol 2014; 20C:131–138.
Cui J, Zhu L, Xia X, et al. NLRC5 negatively regulates the NF-kappaB and type I interferon signaling pathways. Cell 2010; 141:483–496.
Cui J, Li Y, Zhu L, et al. NLRP4 negatively regulates type I interferon signaling by targeting the kinase TBK1 for degradation via the ubiquitin ligase DTX4. Nat Immunol 2012; 13:387–395.
Chen W, Han C, Xie B, et al. Induction of Siglec-G by RNA viruses inhibits the innate immune response by promoting RIG-I degradation. Cell 2013; 152:467–478.
Pillai S, Netravali IA, Cariappa A, Mattoo H . Siglecs and immune regulation. Annu Rev Immunol 2012; 30:357–392.
Yu X, Feizpour A, Ramirez NG, et al. Glycosphingolipid-functionalized nanoparticles recapitulate CD169-dependent HIV-1 uptake and trafficking in dendritic cells. Nat Commun 2014; 5:4136.
Delputte PL, Breedam VW, Delrue I, et al. Porcine arterivirus attachment to the macrophage-specific receptor sialoadhesin is dependent on the sialic acid-binding activity of the N-terminal immunoglobulin domain of sialoadhesin. J Virol 2007; 81:9546–9550.
Martinez-Pomares L, Gordon S . CD169+ macrophages at the crossroads of antigen presentation. Trends Immunol 2012; 33:66–70.
Kawasaki N, Vela JL, Nycholat CM, et al. Targeted delivery of lipid antigen to macrophages via the CD169/sialoadhesin endocytic pathway induces robust invariant natural killer T cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110:7826–7831.
Zhao W . Negative regulation of TBK1-mediated antiviral immunity. FEBS Lett 2013; 587:542–548.
Li S, Wang L, Berman M, Kong YY, Dorf ME . Mapping a dynamic innate immunity protein interaction network regulating type I interferon production. Immunity 2011; 35:426–440.
Ye JS, Kim N, Lee KJ, et al. Lysine 63-linked TANK-binding kinase 1 ubiquitination by mindbomb E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 is mediated by the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein. J Virol 2014; 88:12765–12776.
Wang C, Chen T, Zhang J, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Nrdp1 'preferentially' promotes TLR-mediated production of type I interferon. Nat Immunol 2009; 10:744–752.
Zhang M, Wang L, Zhao X, et al. TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) negatively regulates IFN-beta production and antiviral response by promoting proteasomal degradation of TANK-binding kinase 1. J Exp Med 2012; 209:1703–1711.
Chung HY, Gu M, Buehler E, MacDonald ER, Rice CM . Seed sequence-matched controls reveal limitations of small interfering RNA knockdown in functional and structural studies of hepatitis C virus NS5A-MOBKL1B interaction. J Virol 2014; 88:11022–11033.
Mori M, Yoneyama M, Ito T, et al. Identification of Ser-386 of interferon regulatory factor 3 as critical target for inducible phosphorylation that determines activation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:9698–9702.
Blasius AL, Cella M, Maldonado J, Takai T, Colonna M . Siglec-H is an IPC-specific receptor that modulates type I IFN secretion through DAP12. Blood 2006; 107:2474–2476.
Taylor VC, Buckley CD, Douglas M, et al. The myeloid-specific sialic acid-binding receptor, CD33, associates with the protein-tyrosine phosphatases, SHP-1 and SHP-2. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:11505–11512.
An H, Zhao W, Hou J, et al. SHP-2 phosphatase negatively regulates the TRIF adaptor protein-dependent type I interferon and proinflammatory cytokine production. Immunity 2006; 25:919–928.
Radivojac P, Vacic V, Haynes C, et al. Identification, analysis, and prediction of protein ubiquitination sites. Proteins 2010; 78:365–380.
Crocker PR, Paulson JC, Varki A . Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7:255–266.
Crow MK, Olferiev M, Kirou KA . Targeting of type I interferon in systemic autoimmune diseases. Transl Res 2015; 165:296–305.
Zou Z, Chastain A, Moir S, et al. Siglecs facilitate HIV-1 infection of macrophages through adhesion with viral sialic acids. PLoS One 2011; 6:e 24559.
Delputte PL, Van Gorp H, Favoreel HW, et al. Porcine sialoadhesin (CD169/Siglec-1) is an endocytic receptor that allows targeted delivery of toxins and antigens to macrophages. PLoS One 2011; 6:e 16827.
Asano K, Nabeyama A, Miyake Y, et al. CD169-positive macrophages dominate antitumor immunity by crosspresenting dead cell-associated antigens. Immunity 2011; 34:85–95.
Versteeg GA, Rajsbaum R, Sanchez-Aparicio MT, et al. The E3-ligase TRIM family of proteins regulates signaling pathways triggered by innate immune pattern-recognition receptors. Immunity 2013; 38:384–398.
Gack MU, Shin YC, Joo CH, et al. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature 2007; 446:916–920.
Tsuchida T, Zou J, Saitoh T, et al. The ubiquitin ligase TRIM56 regulates innate immune responses to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Immunity 2010; 33:765–776.
Zhang Z, Bao M, Lu N, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 negatively regulates the innate immune response to intracellular double-stranded DNA. Nat Immunol 2013; 14:172–178.
Zurek B, Schoultz I, Neerincx A, et al. TRIM27 negatively regulates NOD2 by ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. PLoS One 2012; 7:e 41255.
Neel BG, Gu H, Pao L . The 'Shp'ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 2003; 28:284–293.
Chen T, Yang M, Yu Z, et al. Small GTPase RBJ mediates nuclear entrapment of MEK1/MEK2 in tumor progression. Cancer Cell 2014; 25:682–696.
Hou J, Zhou Y, Zheng Y, et al. Hepatic RIG-I predicts survival and interferon-alpha therapeutic response in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014; 25:49–63.
Wang P, Xue Y, Han Y, et al. The STAT3-binding long noncoding RNA lnc-DC controls human dendritic cell differentiation. Science 2014; 344:310–313.
Liu J, Han C, Xie B, et al. Rhbdd3 controls autoimmunity by suppressing the production of IL-6 by dendritic cells via K27-linked ubiquitination of the regulator NEMO. Nat Immunol 2014; 15:612–622.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Tingting Fang, Mei Jin, and Yan Li for technical assistance, Drs Chaofeng Han, Xingguang Liu, Sheng Xu, Yanmei Han, and Taoyong Chen for valuable discussions. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB530502 and 2012CB518900), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81123006, 31300718, 31370864, and 81422037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
( Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, Figure S1
Siglec1's promoter has ISRE binding site (Related to Figure 1). (PDF 100 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S2
Siglec1 suppresses VSV-triggered type I IFN production in cDC (Related to Figure 2). (PDF 64 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S3
Human Siglec1-mediated inhibition of type I IFN production is dependent on TBK1 and upstream of IRF3 (Related to Figure 3). (PDF 102 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S4
Siglec1 associates with DAP12 and TRIM27 in cells upon viral infection (Related to Figure 4). (PDF 31 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S5
Recruitment of TRIM27 by SHP2 inhibits VSV-triggered type I IFN production in macrophages (Related to Figure 5). (PDF 99 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S6
TRIM27 directly binds SHP2 and TBK1, and TRIM27 mediates TBK1 degradation (Related to Figure 6). (PDF 295 kb)
Supplementary information, Figure S7
Mutant of TBK1(K372/251R) binds TRIM27 (Related to Figure 7). (PDF 34 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S1
siRNA sequences used for RNA interference (PDF 40 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S2
Primers used for Q-PCR (PDF 39 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S3
PCR primers used for gene cloning (PDF 44 kb)
Supplementary information, Table S4
PCR primers used for TBK1 mutants (PDF 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Q., Hou, J., Zhou, Y. et al. Siglec1 suppresses antiviral innate immune response by inducing TBK1 degradation via the ubiquitin ligase TRIM27. Cell Res 25, 1121–1136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.108
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of genomic characteristics and selective signals in Guizhou black goat
BMC Genomics (2024)
-
TRIM18 is a critical regulator of viral myocarditis and organ inflammation
Journal of Biomedical Science (2022)
-
Early innate immune response triggered by the human respiratory syncytial virus and its regulation by ubiquitination/deubiquitination processes
Journal of Biomedical Science (2022)
-
USP7 accelerates FMR1-mediated ferroptosis by facilitating TBK1 ubiquitination and DNMT1 deubiquitination after renal ischemia–reperfusion injury
Inflammation Research (2022)
-
TRIM31 facilitates K27-linked polyubiquitination of SYK to regulate antifungal immunity
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)