- TECHNOLOGY FEATURE
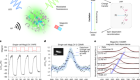
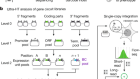
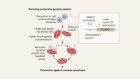
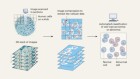
How to build a genome
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 578, 633-635 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-00511-9
References
Fredens, J. et al. Nature 569, 514–518 (2019).
Hutchison, C. A. et al. Science 351, aad6253 (2016).
Palluk, S. et al. Nature Biotechnol. 36, 645–650 (2018).
Engler, C., Kandzia, R. & Marillonnet, S. PLoS ONE 3, e3647 (2008).
Shao, Y. et al. Nature 560, 331–335 (2018).
Ostrov, N. et al. Science 353, 819–822 (2016).
Ostrov, N. et al. Science 366, 310–312 (2019).

 Synthetic yeast genome reveals its versatility
Synthetic yeast genome reveals its versatility
 Scientists downsize bold plan to make human genome from scratch
Scientists downsize bold plan to make human genome from scratch
 How to hack the genome
How to hack the genome
 NatureTech hub
NatureTech hub