Abstract
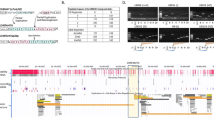
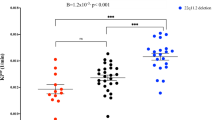
The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene (CHRNA7) is located at 15q13–q14 in a region that is strongly linked to the P50 sensory gating deficit, an endophenotype of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Part of the gene is a copy number variant, due to a duplication of exons 5–10 and 3′ sequence in CHRFAM7A, which is present in many but not all humans. Maps of this region show that the two genes are in opposite orientation in the individual mainly represented in the public access human DNA sequence database (Build 36), suggesting that an inversion had occurred since the duplication. We have used fluorescent in situ hybridization to investigate this putative inversion. Analysis of interphase chromosomes in 12 individuals confirms the occurrence of an inversion and indicates that CHRFAM7A exists in both orientations with similar frequency. We showed that the 2 bp deletion polymorphism in exon 6 of CHRFAM7A is in strong linkage disequilibrium with the inversion polymorphism (r2=0.82, CI 0.53–1.00, P=0.00003), which can therefore be used as a surrogate marker. Previous associations of endophenotypes of schizophrenia with the 2 bp deletion might therefore be due to the orientation of the duplicon containing CHRFAM7A.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Freedman R, Coon H, Myles-Worsley M et al: Linkage of a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia to a chromosome 15 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 587–592.
Leonard S, Gault J, Moore T et al: Further investigation of a chromosome 15 locus in schizophrenia: analysis of affected sibpairs from the NIMH Genetics Initiative. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 308–312.
Olincy A, Martin L : Diminished suppression of the P50 auditory evoked potential in bipolar disorder subjects with a history of psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 2005; 162: 43–49.
Schulze KK, Hall MH, McDonald C et al: P50 auditory evoked potential suppression in bipolar disorder patients with psychotic features and their unaffected relatives. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 62: 121–128.
Weiland S, Bertrand D, Leonard S : Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from the gene to the disease. Behav Brain Res 2000; 113: 43–56.
Turecki G, Grof P, Grof E et al: Mapping susceptibility genes for bipolar disorder: a pharmacogenetic approach based on excellent response to lithium. Mol Psychiatry 2001; 6: 570–578.
Kaufmann CA, Suarez B, Malaspina D et al: NIMH Genetics Initiative Millenium Schizophrenia Consortium: linkage analysis of African-American pedigrees. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 282–289.
Riley BP, Makoff A, Mogudi-Carter M et al: Haplotype transmission disequilibrium and evidence for linkage of the CHRNA7 gene region to schizophrenia in Southern African Bantu families. Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 196–201.
Stassen HH, Bridler R, Hagele S et al: Schizophrenia and smoking: evidence for a common neurobiological basis? Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 173–177.
Elmslie FV, Rees M, Williamson MP et al: Genetic mapping of a major susceptibility locus for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy on chromosome 15q. Hum Mol Genet 1997; 6: 1329–1334.
Neubauer BA, Fiedler B, Himmelein B et al: Centrotemporal spikes in families with rolandic epilepsy: linkage to chromosome 15q14. Neurology 1998; 51: 1608–1612.
Gault J, Robinson M, Berger R et al: Genomic organization and partial duplication of the human alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene (CHRNA7). Genomics 1998; 52: 173–185.
Riley BP, Williamson M, Collier DA, Wilkie H, Makoff AJ : A 3Mb map of a large segmental duplication overlapping a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene (CHRNA7) at human 15q13–q14. Genomics 2002; 79: 197–209.
Makoff A, Flomen RH : Detailed analysis of 15q11–q14 sequence fully reveals large segmental duplications at breakpoints for Prader–Willi and Angelman syndromes and other 15q genomic disorders. Genome Biol 2007; 8: R114.1–R114.16.
Locke DP, Archidiacono N, Misceo D et al: Refinement of a chimpanzee pericentric inversion breakpoint to a segmental duplication cluster. Genome Biol 2003; 4: R50.1–R50.9.
Flomen RH, Breen G, Collier D, St Clair D, Makoff AJ : Association study of CHRFAM7A copy number and 2 bp deletion polymorphisms with schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2006; 141: 571–575.
Clouston HJ : Lymphocyte culture; in Rooney ED (ed): Human Cytogenetics, a practical approach, Oxford University Press, 2001; 1: Constitutional analysis Chapter 3, pp33–53.
Davies AF, Mirza G, Sekhon G et al: Delineation of two distinct 6p deletion syndromes. Hum Genet 1999; 104: 64–72.
Curtis D, Knight J, Sham PC : Program report: GENECOUNTING support programs. Ann Hum Genet 2006; 70: 277–279.
Zhao JH : 2LD, GENECOUNTING and HAP: computer programs for linkage disequilibrium analysis. Bioinformatics 2004; 20: 1325–1326.
Eichler EE : Recent duplication domain accretion and the dynamic mutation of the human genome. Trends Genet 2001; 17: 661–669.
Zody MC, Garber M, Sharpe T et al: Analysis of the DNA sequence and duplication history of human chromosome 15. Nature 2006; 440: 671–675.
Stefansson H, Helgason A, Thorleifsson G et al: A common inversion under selection in Europeans. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 129–137.
Locke DP, Sharp AJ, McCarroll SA et al: Linkage disequilibrium and heritability of copy-number polymorphisms within duplicated regions of the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 275–290.
McCarroll SA, Hadnott TN, Perry GH et al: Common deletion polymorphisms in the human genome. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 86–92.
Hinds DA, Kloek AP, Jen M, Chen X, Frazer KA : Common deletions and SNPs are in linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 82–85.
Newman TL, Rieder MJ, Morrison VA et al: High-throughput genotyping of intermediate-size structural variation. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 1159–1167.
Gimelli G, Pujana MA, Patricelli MG et al: Genomic inversions of human chromosome 15q11–q13 in mothers of Angelman syndrome patients with class II (BP2/3) deletions. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 849–858.
Sharp AJ, Cheng Z, Eichler EE : Structural variation of the human genome. Annu Rev Hum Genet 2006; 7: 407–442.
Battaglia A : The inv dup(15) or idic(15) syndrome: a clinically recognisable neurogenetic disorder. Brain Dev 2005; 27: 365–369.
Wang NJ, Liu D, Parokonny AS, Schanen NC : High-resolution molecular characterization of 15q11–q13 rearrangements by array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) with detection of gene dosage. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 267–281.
Sharp AJ, Mefford HC, Li K et al: A recurrent 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome associated with mental retardation and seizures. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 322–328.
Orr-Urtreger A, Goldner FM, Saeki M et al: Mice deficient in the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor lack alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites and hippocampal fast nicotinic currents. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 9165–9171.
Sahoo T, Bacino CA, German JR et al: Identification of novel deletions of 15q11q13 in Angelman syndrome by array-CGH: molecular characterization and genotype–phenotype correlations. Eur J Hum Genet 2007; 15: 943–949.
Sharp AJ, Hansen S, Selzer RR et al: Discovery of previously unidentified genomic disorders from the duplication architecture of the human genome. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 1038–1042.
Redon R, Ishikawa S, Fitch KR et al: Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature 2006; 444: 444–454.
Raux G, Bonnet-Brilhault F, Louchart S et al: The −2 bp deletion in exon 6 of the ‘alpha 7-like’ nicotinic receptor subunit gene is a risk factor for the P50 sensory gating deficit. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 1006–1011.
Dempster EL, Toulopoulou T, McDonald C et al: Episodic memory performance predicted by the 2 bp deletion in exon 6 of the ‘alpha 7-like’ nicotinic receptor subunit gene. Am J Psychiatry 2006; 163: 1832–1834.
Lai IC, Hong CJ, Tsai SJ : Association study of a nicotinic receptor variant with schizophrenic disorders. Neuropsychobiology 2001; 43: 15–18.
Hong CJ, Lai IC, Liou LL, Tsai SJ : Association study of the human partially duplicated alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genetic variant with bipolar disorder. Neurosci Lett 2004; 355: 69–72.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a NARSAD Young Investigator Award to RF. We thank Professor Brien Riley for useful discussions during the conceptual phase of the project and Professor Cathryn Lewis for a helpful discussion on estimating r2 in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flomen, R., Davies, A., Di Forti, M. et al. The copy number variant involving part of the α7 nicotinic receptor gene contains a polymorphic inversion. Eur J Hum Genet 16, 1364–1371 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.112
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.112
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association between the 2-bp deletion polymorphism in the duplicated version of the alpha7 nicotinic receptor gene and P50 sensory gating
European Journal of Human Genetics (2013)
-
Deletions flanked by breakpoints 3 and 4 on 15q13 may contribute to abnormal phenotypes
European Journal of Human Genetics (2011)
-
Common inversion polymorphisms and rare microdeletions at 15q13.3
European Journal of Human Genetics (2009)