Abstract
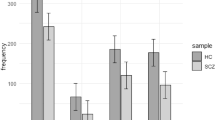
Associations have been reported between the variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) polymorphisms in the exon 3 of dopamine D4 receptor gene gene and multiple psychiatric illnesses/traits. We examined the distribution of VNTR alleles of different length in a Japanese cohort and found that, as reported earlier, the size of allele ‘7R’ was much rarer (0.5%) in Japanese than in Caucasian populations (∼20%). This presents a challenge to an earlier proposed hypothesis that positive selection favoring the allele 7R has contributed to its high frequency. To further address the issue of selection, we carried out sequencing of the VNTR region not only from human but also from chimpanzee samples, and made inference on the ancestral repeat motif and haplotype by use of a phylogenetic analysis program. The most common 4R variant was considered to be the ancestral haplotype as earlier proposed. However, in a gene tree of VNTR constructed on the basis of this inferred ancestral haplotype, the allele 7R had five descendent haplotypes in relatively long lineage, where genetic drift can have major influence. We also tested this length polymorphism for association with schizophrenia, studying two Japanese sample sets (one with 570 cases and 570 controls, and the other with 124 pedigrees). No evidence of association between the allele 7R and schizophrenia was found in any of the two data sets. Collectively, this study suggests that the VNTR variation does not have an effect large enough to cause either selection or a detectable association with schizophrenia in a study of samples of moderate size.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Prasad S, Semwal P, Deshpande S, Bhatia T, Nimgaonkar VL, Thelma BK : Molecular genetics of schizophrenia: past, present and future. J Biosci 2002; 27: 35–52.
Petronis A, Van Tol HH, Lichter JB, Livak KJ, Kennedy JL : The D4 dopamine receptor gene maps on 11p proximal to HRAS. Genomics 1993; 18: 161–163.
Gelernter J, Kennedy JL, Van Tol HH, Civelli O, Kidd KK : The D4 dopamine receptor (DRD4) maps to distal 11p close to HRAS. Genomics 1992; 13: 208–210.
Sanyal S, Van Tol HH : Review the role of dopamine D4 receptors in schizophrenia and antipsychotic action. J Psychiatr Res 1997; 31: 219–232.
Van Tol HH, Bunzow JR, Guan HC et al: Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature 1991; 350: 610–614.
Stefanis NC, Bresnick JN, Kerwin RW, Schofield WN, McAllister G : Elevation of D4 dopamine receptor mRNA in postmortem schizophrenic brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1998; 53: 112–119.
Sumiyoshi T, Stockmeier CA, Overholser JC, Thompson PA, Meltzer HY : Dopamine D4 receptors and effects of guanine nucleotides on [3H]raclopride binding in postmortem caudate nucleus of subjects with schizophrenia or major depression. Brain Res 1995; 681: 109–116.
Murray AM, Hyde TM, Knable MB et al: Distribution of putative D4 dopamine receptors in postmortem striatum from patients with schizophrenia. J Neurosci 1995; 15: 2186–2191.
Seeman P, Guan HC, Van Tol HH : Dopamine D4 receptors elevated in schizophrenia. Nature 1993; 365: 441–445.
Van Tol HH, Wu CM, Guan HC et al: Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature 1992; 358: 149–152.
Schoots O, Van Tol HH : The human dopamine D4 receptor repeat sequences modulate expression. Pharmacogenomics J 2003; 3: 343–348.
Asghari V, Sanyal S, Buchwaldt S, Paterson A, Jovanovic V, Van Tol HH : Modulation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels by different human dopamine D4 receptor variants. J Neurochem 1995; 65: 1157–1165.
Jonsson E, Brene S, Geijer T et al: A search for association between schizophrenia and dopamine-related alleles. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1996; 246: 297–304.
Ebstein RP, Novick O, Umansky R et al: Dopamine D4 receptor (D4DR) exon III polymorphism associated with the human personality trait of Novelty Seeking. Nat Genet 1996; 12: 78–80.
Faraone SV, Doyle AE, Mick E, Biederman J : Meta-analysis of the association between the 7-repeat allele of the dopamine D(4) receptor gene and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2001; 158: 1052–1057.
LaHoste GJ, Swanson JM, Wigal SB et al: Dopamine D4 receptor gene polymorphism is associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1996; 1: 121–124.
Sanak M, Zelek-Molik A, Nalepa I, Wegrzyn J, Wciorka J : The dopamine D4 receptor VNTR in Polish schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 2005; 73: 129–131.
Ambrosio AM, Kennedy JL, Macciardi F et al: No evidence of association or linkage disequilibrium between polymorphisms in the 5′ upstream and coding regions of the dopamine D4 receptor gene and schizophrenia in a Portuguese population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2004; 125: 20–24.
Segman RH, Goltser T, Heresco-Levy U et al: Association of dopaminergic and serotonergic genes with tardive dyskinesia in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Pharmacogenomics J 2003; 3: 277–283.
Tang Y, Wang Y, Cai Z : [Schizophrenia and dopamine D4 gene polymorphism in Chinese population: association analysis]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2001; 81: 995–998.
Serretti A, Lilli R, Lorenzi C, Lattuada E, Smeraldi E : DRD4 exon 3 variants associated with delusional symptomatology in major psychoses: a study on 2,011 affected subjects. Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 283–290.
Kaiser R, Konneker M, Henneken M et al: Dopamine D4 receptor 48-bp repeat polymorphism: no association with response to antipsychotic treatment, but association with catatonic schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 418–424.
Serretti A, Lilli R, Di Bella D et al: Dopamine receptor D4 gene is not associated with major psychoses. Am J Med Genet 1999; 88: 486–491.
Hwu HG, Hong CJ, Lee YL, Lee PC, Lee SF : Dopamine D4 receptor gene polymorphisms and neuroleptic response in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 1998; 44: 483–487.
Kohn Y, Ebstein RP, Heresco-Levy U et al: Dopamine D4 receptor gene polymorphisms: relation to ethnicity, no association with schizophrenia and response to clozapine in Israeli subjects. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1997; 7: 39–43.
Hong CJ, Lee YL, Sim CB, Hwu HG : Dopamine D4 receptor variants in Chinese sporadic and familial schizophrenics. Am J Med Genet 1997; 74: 412–415.
Weiss J, Magert HJ, Cieslak A, Forssmann WG : Association between different psychotic disorders and the DRD4 polymorphism, but no differences in the main ligand binding region of the DRD4 receptor protein compared to controls. Eur J Med Res 1996; 1: 439–445.
Petronis A, Macciardi F, Athanassiades A et al: Association study between the dopamine D4 receptor gene and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 1995; 60: 452–455.
Daniels J, Williams J, Mant R, Asherson P, McGuffin P, Owen MJ : Repeat length variation in the dopamine D4 receptor gene shows no evidence of association with schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 1994; 54: 256–258.
Sommer SS, Lind TJ, Heston LL, Sobell JL : Dopamine D4 receptor variants in unrelated schizophrenic cases and controls. Am J Med Genet 1993; 48: 90–93.
Nanko S, Hattori M, Ikeda K, Sasaki T, Kazamatsuri H, Kuwata S : Dopamine D4 receptor polymorphism and schizophrenia. Lancet 1993; 341: 689–690.
Iwata Y, Matsumoto H, Minabe Y et al: Early-onset schizophrenia and dopamine-related gene polymorphism. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2003; 116: 23–26.
Tanaka T, Igarashi S, Onodera O et al: Lack of association between dopamine D4 receptor gene and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 1995; 60: 580–582.
Wang E, Ding YC, Flodman P et al: The genetic architecture of selection at the human dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene locus. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 931–944.
Ding YC, Chi HC, Grady DL et al: Evidence of positive selection acting at the human dopamine receptor D4 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 309–314.
Bandelt HJ : Phylogenetic networks. Verh Naturewiss Ver Hamburg (NF) 1994; 34: 51–71.
Saitou N, Yamamoto F : Evolution of primate ABO blood group genes and their homologous genes. Mol Biol Evol 1997; 14: 399–411.
Shimizu H, Iwayama Y, Yamada K et al: Genetic and expression analyses of the STOP (MAP6) gene in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2006; 84: 244–252.
Aoki-Suzuki M, Yamada K, Meerabux J et al: A family-based association study and gene expression analyses of netrin-G1 and -G2 genes in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 57: 382–393.
Sham PC, Curtis D : Monte Carlo tests for associations between disease and alleles at highly polymorphic loci. Ann Hum Genet 1995; 59 (Pt 1): 97–105.
Martin ER, Monks SA, Warren LL, Kaplan NL : A test for linkage and association in general pedigrees: the pedigree disequilibrium test. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 146–154.
Kim YS, Leventhal BL, Kim SJ et al: Family-based association study of DAT1 and DRD4 polymorphism in Korean children with ADHD. Neurosci Lett 2005; 390: 176–181.
Livak KJ, Rogers J, Lichter JB : Variability of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene sequence within and among nonhuman primate species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 427–431.
Gelernter J, Kranzler H, Coccaro E, Siever L, New A, Mulgrew CL : D4 dopamine-receptor (DRD4) alleles and novelty seeking in substance-dependent, personality-disorder, and control subjects. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 61: 1144–1152.
Nakajima T, Wooding S, Sakagami T et al: Natural selection and population history in the human angiotensinogen gene (AGT): 736 complete AGT sequences in chromosomes from around the world. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 898–916.
Glatt SJ, Faraone SV, Tsuang MT : Schizophrenia is not associated with DRD4 48-base-pair-repeat length or individual alleles: results of a meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 2003; 54: 629–635.
Nakajima M, Hattori E, Yamada K et al: Association and synergistic interaction between promoter variants of the DRD4 gene in Japanese schizophrenics. J Hum Genet 2007; 52: 86–91.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P : Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000; 155: 945–959.
Purcell S, Cherny SS, Sham PC : Genetic Power Calculator: design of linkage and association genetic mapping studies of complex traits. Bioinformatics 2003; 19: 149–150.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the patients and their families who participated in this study. This study was supported by RIKEN BSI Funds, Grant-in-aid for scientific studies from the MEXT of Japan to NS and EH, NARSAD Young Investigator Award to EH, and CREST funds from the Japan Science and Technology Agency, Japan to TY. We wish to thank the members of the Research Resource Center at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute for sequencing and genotyping services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hattori, E., Nakajima, M., Yamada, K. et al. Variable number of tandem repeat polymorphisms of DRD4: re-evaluation of selection hypothesis and analysis of association with schizophrenia. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 793–801 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.247
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.247
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Ancient DNA Reveals That the Variability of the DRD4 -521 C/T SNP Associated with Novelty Seeking Behavior is Influenced by Selection in Western South American Populations
Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology (2016)
-
Is there a role for rare variants in DRD4 gene in the susceptibility for ADHD? Searching for an effect of allelic heterogeneity
Molecular Psychiatry (2012)