Abstract
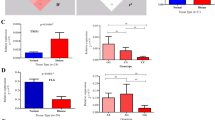
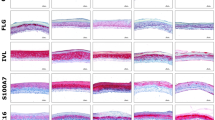
Family-based analysis has revealed several loci for psoriasis and the locus, PSORS5, on chromosome 3q21 has been found in two independent studies. In this region, cystatin A (CSTA) encodes a skin barrier cystein protease inhibitor found in human sweat and it is over-expressed in psoriatic skin. Three CSTA markers at positions –190 (g.−190T>C), +162 (c.162T>C) and +344 (c.344C>T) were analysed in 107 unrelated patients and 216 matched controls. There was a significant trend for association with CSTA c.162T>C and psoriasis (odds ratio (OR)=3.45, P<0.001). Analysis of constructed haplotypes showed a highly significant association between disease and CSTA –190T/+162C/+344C (CSTA TCC) (P=10−6). In independent study, a TDT analysis in 126 nuclear families confirmed the over-transmission of CSTA TCC (P=0.0001). The presence of statistical interaction between CSTA TCC haplotype and HLA-Cw6 at PSORS1 locus was detected by performing TDT analysis on CSTA haplotypes stratified by the presence or absence of the risk allele at HLA-Cw6 locus. To estimate the disease risk we employed conditional logistic regression on the family data. The CSTA TCC haplotype is only associated with psoriasis in those individuals carrying the risk allele at the HLA-Cw6 locus (OR=2.22, P=0.0004, 95% CI= 1.42, 3.49). These results represent a major step towards the dissection of genetic factors involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Accession codes
References
Stern RS : Psoriasis. Lancet 1997; 350: 349–353.
Barker JN : Pathogenesis of psoriasis. J Dermatol 1998; 25: 778–781.
Nevitt GJ, Hutchinson PE : Psoriasis in the community: prevalence, severity and patient's belief and attitudes towards the disease. Br J Dermatol 1996; 135: 533–537.
Simons RD : Additional studies on psoriasis in the tropics and in the starvation camps. J Invest Dermatol 1949; 12: 285–294.
Yui Yip S : The prevalence of psoriasis in the mongoloid race. J Am Acad Dermatol 1984; 10: 965–968.
Lomholt G : Psoriasis, Prevalence, Spontaneous Course and Genetics. Copenhagen: G.E.C. Gad, 1963, pp 31–33.
Brandrup F, Hauge M, Henningsen J, Eriksen B : Psoriasis in an unselected series of twins. Arch Dermatol 1978; 114: 874–878.
Elder JT, Nair RP, Guo SW et al: The genetics of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol 2001; 130: 216–224.
Swanbeck G, Inerot A, Martinsson T, Wahlström J : A population genetic study of psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 1994; 131: 32–39.
Tagami H : Triggering factors. Clin Dermatol 1997; 15: 677–685.
Sagoo GS, Cork MJ, Patel R, Tazi-Ahnini R : Genome-wide studies of psoriasis susceptibility loci: a review. J Dermatol Sci 2004; 35: 171–179.
Sagoo GS, Tazi-Ahnini R, Barker JW et al: Meta-analysis of genome-wide studies of psoriasis susceptibility reveals linkage to chromosome 6p21 and 4q28-q31 in Caucasian and Chinese Hans population. J Invest Dermatol 2004; 122: 1401–1405.
Mallon E, Newson R, Bunker CB : HLA-Cw6 and the genetic predisposition to psoriasis: a meta-analysis of published serologic studies. J Invest Dermatol 1999; 113: 693–695.
Nair RP, Stuart PE, Nistor I et al: Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 78: 827–851.
Samuelsson L, Enlun F, Torinsson A et al: A genome-wide search for genes predisposing to familial psoriasis by using a stratification approach. Hum Genet 1999; 105: 523–529.
Enlund F, Samuelsson L, Enerback C et al: Psoriasis susceptibility locus in chromosome region 3q21 identified in patients from southwest Sweden. Eur J Hum Genet 1999; 7: 783–790.
Takahashi M, Tezuka T, Katunuma N : Phosphorylated cystatin α is a natural substrate of epidermal transglutaminase for formation of skin cornified envelope. FEBS Lett 1992; 308: 79–82.
Barret AJ : The cystatins: a new class of peptide inhibitor. Trends Biochem Sci 1987; 12: 193–196.
Takeda A, Kaji H, Nakaya Y et al: Comparative studies on the primary structure of human cystatin As from epidermis, liver, spleen and leukocytes. J Biochem 1989; 105: 986–991.
Tsushima H, Ueki A, Mine H et al: Purification and characterization of a cystatin-type cysteine protease inhibitor in the human hair shaft. Arch Dermatol Res 1992; 284: 380–385.
Yamazaki M, Ishidoh K, Kominami E, Ogawa H : Genomic structure of human cystatin A. DNA Seq 1997; 8: 71–76.
Takahashi H, Asano K, Kinouchi M et al: Structure and transcriptional regulation of the human cystatin A gene. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 17375–17380.
Samuelsson L, Stiller C, Friberg C et al: Association analysis of cystatin A and zinc finger protein 148, two genes located at the psoriasis susceptibility locus PSORS5. J Invest Dermatol 2004; 122: 1399–1400.
Bowcock AM, Shannon W, Du F et al: Insights into psoriasis and other inflammatory diseases from large-scale gene expression studies. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 1793–1805.
Kulski JK, Kenworthy W, Bellgard M et al: Gene expression profiling of Japanese psoriatic skin reveals an increased activity in molecular stress and immune response signals. J Mol Med 2005; 83: 964–975.
Steinle A, Nossner E, Schendel DJ : Isolation and characterization of a genomic HLA-Cw6 clone. Tissue Antigens 1992; 39: 134–137.
Tazi-Ahnini R, Camp NJ, Cork MJ et al: Novel genetic association between the corneodesmosin (MHC S) gene and susceptibility to psoriasis. Hum Mol Genet 1999; 8: 1135–1140.
Zhao JH, Curtis D, Sham PC : Model-free analysis and permutation tests for allelic associations. Hum Hered 2000; 50: 133–139.
Clayton DA : A generalization of the transmission disequilibrium test for uncertain haplotypes transmission. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 65: 1170–1177.
Cordell HJ, Barratt BJ, Clayton DG : Case/pseudocontrol analysis in genetic association studies: a unified framework for detection of genotype and haplotype associations, gene–gene and gene–environment interactions, and parent-of-origin effects. Genet Epidemiol 2004; 26: 167–185.
Hewett D, Samuelsson L, Polding J et al: Identification of a psoriasis susceptibility candidate gene by linkage disequilibrium mapping with a localized single nucleotide polymorphism map. Genomics 2002; 79: 305–314.
Huffmeier U, Lascorz J, Traupe H et al: Systematic linkage disequilibrium analysis of SLC12A8 at PSORS5 confirms a role in susceptibility to psoriasis vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol 2005; 125: 906–912.
Bowcock AM, Cookson WO : The genetics of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 1: R43–R55.
Zettergren JG, Peterson L, Wuepper KD : Keratolinin: the soluble substrate of epidermal transglutaminase for human and bovine tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1984; 81: 238–242.
Capon F, Semprini S, Dallapiccola B, Novelli G : Evidence for interaction between psoriasis-susceptibility loci on chromosomes 6p21 and 1q21. Am J Hum Genet 1999; 65: 1798–1800.
Lee YA, Wahn U, Kehrt R et al: A major susceptibility locus for atopic dermatitis maps to chromosome 3q21. Nat Genet 2000; 26: 470–473.
Vasilopoulos Y, Cork MJ, Teare D et al: A nonsynonymous substitution of cystatin A, a cysteine protease inhibitor of house dust mite protease, leads to decreased mRNA stability and shows a significant association with atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2007; 62: 514–519.
Cookson WO, Ubhi B, Lawrence R et al: Genetic linkage of childhood atopic dermatitis to psoriasis susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 372–373.
Kashlev M, Komissarova N : Transcription termination: primary intermediates and secondary adducts. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 14501–14508.
Reeder TC, Hawley DK : Promoter proximal sequences modulate RNA polymerase II elongation by a novel mechanism. Cell 1996; 87: 767–777.
Ujvari A, Pal M, Luse DS : RNA polymerase II transcription complexes may become arrested if the nascent RNA is shortened to less than 50 nucleotides. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 32527–32537.
Capon F, Allen MH, Ameen M et al: A synonymous SNP of the corneodesmosin gene leads to increased mRNA stability and demonstrates association with psoriasis across diverse ethnic groups. Hum Mol Genet 2004; 13: 2361–2368.
Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Oh JM, Kim IW et al: A ‘silent’ polymorphism in the MDR1 gene changes substrate specificity. Science 2007; 315: 525–528.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families who took part in this study. This work was supported by funding from RTA's DC7559, The Psoriasis Association, The Cecil Kind Memorial Fund and Molecular SkinCare Ltd (now York Pharma). YV was supported by a University of Sheffield PhD studentship. We are grateful to Dr Andrew McDonagh for his helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasilopoulos, Y., Walters, K., Cork, M. et al. Association analysis of the skin barrier gene cystatin A at the PSORS5 locus in psoriatic patients: evidence for interaction between PSORS1 and PSORS5. Eur J Hum Genet 16, 1002–1009 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.40
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Global genetic diversity, introgression, and evolutionary adaptation of indicine cattle revealed by whole genome sequencing
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Skin chronological aging drives age-related bone loss via secretion of cystatin-A
Nature Aging (2022)
-
Review Update on Topical Therapy for Psoriasis
Current Dermatology Reports (2018)
-
HLA-C, CSTA and DS12346 susceptibility alleles confer over 100-fold increased risk of developing psoriasis: evidence of gene interaction
Journal of Human Genetics (2011)