Abstract
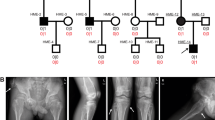
Spondylocostal dysostosis (SCD) is an inherited disorder with abnormal vertebral segmentation that results in extensive hemivertebrae, truncal shortening and abnormally aligned ribs. It arises during embryonic development by a disruption of formation of somites (the precursor tissue of the vertebrae, ribs and associated tendons and muscles). Four genes causing a subset of autosomal recessive forms of this disease have been identified: DLL3 (SCDO1: MIM 277300), MESP2 (SCDO2: MIM 608681), LFNG (SCDO3: MIM609813) and HES7 (SCDO4). These genes are all essential components of the Notch signalling pathway, which has multiple roles in development and disease. Previously, only a single SCD-causative missense mutation was described in HES7. In this study, we have identified two new missense mutations in the HES7 gene in a single family, with only individuals carrying both mutant alleles being affected by SCD. In vitro functional analysis revealed that one of the mutant HES7 proteins was unable to repress gene expression by DNA binding or protein heterodimerization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Turnpenny PD, Alman B, Cornier AS et al: Abnormal vertebral segmentation and the notch signaling pathway in man. Dev Dyn 2007; 236: 1456–1474.
Bulman MP, Kusumi K, Frayling TM et al: Mutations in the human delta homologue, DLL3, cause axial skeletal defects in spondylocostal dysostosis. Nat Genet 2000; 24: 438–441.
Sparrow DB, Clements M, Withington SL et al: Diverse requirements for Notch signalling in mammals. Int J Dev Biol 2002; 46: 365–374.
Whittock NV, Sparrow DB, Wouters MA et al: Mutated MESP2 causes spondylocostal dysostosis in humans. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 1249–1254.
Sparrow DB, Chapman G, Wouters MA et al: Mutation of the LUNATIC FRINGE gene in humans causes spondylocostal dysostosis with a severe vertebral phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 78: 28–37.
Sparrow DB, Guillen-Navarro E, Fatkin D, Dunwoodie SL : Mutation of HAIRY-AND-ENHANCER-OF-SPLIT-7 in humans causes spondylocostal dysostosis. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 3761–3766.
Bessho Y, Sakata R, Komatsu S, Shiota K, Yamada S, Kageyama R : Dynamic expression and essential functions of Hes7 in somite segmentation. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 2642–2647.
Dunwoodie SL, Clements M, Sparrow DB, Sa X, Conlon RA, Beddington RS : Axial skeletal defects caused by mutation in the spondylocostal dysplasia/pudgy gene Dll3 are associated with disruption of the segmentation clock within the presomitic mesoderm. Development 2002; 129: 1795–1806.
Evrard YA, Lun Y, Aulehla A, Gan L, Johnson RL : Lunatic fringe is an essential mediator of somite segmentation and patterning. Nature 1998; 394: 377–381.
Forsberg H, Crozet F, Brown NA : Waves of mouse lunatic fringe expression, in four-hour cycles at two-hour intervals, precede somite boundary formation. Curr Biol 1998; 8: 1027–1030.
Saga Y, Hata N, Koseki H, Taketo MM : Mesp2: a novel mouse gene expressed in the presegmented mesoderm and essential for segmentation initiation. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 1827–1839.
Sparrow DB, Chapman G, Turnpenny PD, Dunwoodie SL : Disruption of the somitic molecular clock causes abnormal vertebral segmentation. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 2007; 81: 93–110.
Davis RL, Turner DL : Vertebrate hairy and enhancer of split related proteins: transcriptional repressors regulating cellular differentiation and embryonic patterning. Oncogene 2001; 20: 8342–8357.
Fischer A, Gessler M : Delta-Notch—and then? Protein interactions and proposed modes of repression by Hes and Hey bHLH factors. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 4583–4596.
Bessho Y, Hirata H, Masamizu Y, Kageyama R : Periodic repression by the bHLH factor Hes7 is an essential mechanism for the somite segmentation clock. Genes Dev 2003; 17: 1451–1456.
Collins JS, Schwartz CE : Detecting polymorphisms and mutations in candidate genes. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 1251–1252.
Bessho Y, Miyoshi G, Sakata R, Kageyama R : Hes7: a bHLH-type repressor gene regulated by Notch and expressed in the presomitic mesoderm. Genes Cells 2001; 6: 175–185.
Longo A, Guanga GP, Rose RB : Crystal structure of E47-NeuroD1/beta2 bHLH domain-DNA complex: heterodimer selectivity and DNA recognition. Biochemistry 2008; 47: 218–229.
Atchley WR, Terhalle W, Dress A : Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain. J Mol Evol 1999; 48: 501–516.
Acknowledgements
We thank the family for their cooperation, and Wendy Chua for technical assistance. We are extremely grateful to Ryoichiro Kageyama and Diane Fatkin for providing reagents. This work was funded by National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Project Grants 404804 and 635500 (SLD and DBS), a Pfizer Foundation Australia Senior Research Fellowship (SLD) and a NHMRC Senior Research Fellowship (SLD). This research was approved by St Vincent's Hospital Human Research Ethics Committee (H05/057), Darlinghurst, Sydney, NSW 2010, Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sparrow, D., Sillence, D., Wouters, M. et al. Two novel missense mutations in HAIRY-AND-ENHANCER-OF-SPLIT-7 in a family with spondylocostal dysostosis. Eur J Hum Genet 18, 674–679 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.241
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.241
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Whole genome sequencing in cats, identifies new models for blindness in AIPL1 and somite segmentation in HES7
BMC Genomics (2016)
-
Whole Genome Sequencing Identifies a Missense Mutation in HES7 Associated with Short Tails in Asian Domestic Cats
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Whole exome sequencing in an Indian family links Coats plus syndrome and dextrocardia with a homozygous novel CTC1 and a rare HES7 variation
BMC Medical Genetics (2015)
-
ptk7 mutant zebrafish models of congenital and idiopathic scoliosis implicate dysregulated Wnt signalling in disease
Nature Communications (2014)
-
The role of notch signaling in bone development and disease
Hormones (2014)