Abstract
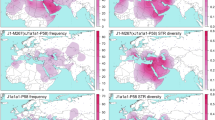
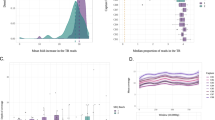
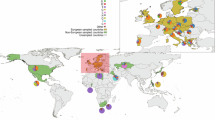
The present day distribution of Y chromosomes bearing the haplogroup J1 M267*G variant has been associated with different episodes of human demographic history, the main one being the diffusion of Islam since the Early Middle Ages. To better understand the modes and timing of J1 dispersals, we reconstructed the genealogical relationships among 282 M267*G chromosomes from 29 populations typed at 20 YSTRs and 6 SNPs. Phylogenetic analyses depicted a new genetic background consistent with climate-driven demographic dynamics occurring during two key phases of human pre-history: (1) the spatial expansion of hunter gatherers in response to the end of the late Pleistocene cooling phases and (2) the displacement of groups of foragers/herders following the mid-Holocene rainfall retreats across the Sahara and Arabia. Furthermore, J1 STR motifs previously used to trace Arab or Jewish ancestries were shown unsuitable as diagnostic markers for ethnicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Karafet TM, Mendez FL, Meilerman MB, Underhill PA, Zegura SL, Hammer MF : New binary polymorphisms reshape and increase resolution of the human Y chromosomal haplogroup tree. Genome Res 2008; 18: 830–838.
Nebel A, Landau-Tasseron E, Filon D, Oppenheim A, Faerman M : Genetic evidence for the expansion of Arabian tribes into the Southern Levant and North Africa. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 1594–1596.
Semino O, Magri C, Benuzzi G et al: Origin, diffusion and differentiation of Y-chromosome haplogroups E and J: inferences on the neolithization of Europe and later migratory events in the Mediterranean area. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 1023–1034.
Thomas MG, Skorecki K, Ben-Ami H, Parfitt T, Bradman N, Goldstein DB : Origins of Old Testament priests. Nature 1998; 394: 138–140.
Di Giacomo F, Luca F, Popa LO et al: Y chromosomal haplogroup J as a signature of the post-neolithic colonization of Europe. Hum Genet 2004; 115: 357–371.
Arredi B, Poloni ES, Paracchini S et al: A predominantly Neolithic origin for Y-chromosomal DNA variation in North Africa. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 338–345.
Cadenas AM, Zhivotovsky LA, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Underhill PA, Herrera RJ : Y-chromosome diversity characterizes the Gulf of Oman. Eur J Hum Genet 2008; 16: 374–386.
Zalloua PA, Xue Y, Khalife J et al: Y-chromosomal diversity in Lebanon is structured by recent historical events. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 82: 873–882.
Chiaroni J, King RJ, Underhill P : Correlation of annual precipitation with human Y chromosome diversity and the emergence of Neolithic agriculture and pastoral economies in the fertile crescent. Antiquity 2008; 82: 281–289.
Nebel A, Filon D, Weiss D et al: High-resolution Y chromosome haplotypes of Israeli and Palestinian Arabs reveal geographic substructure and substantial overlap with haplotypes of Jews. Hum Genet 2000; 107: 630–641.
Harpending HC : Signature of ancient population growth in a low-resolution mitochondrial DNA mismatch distribution. Hum Biol 1994; 66: 591–600.
Rogers A : Genetic evidence for a Pleistocene population explosion. Evolution 1995; 49: 608–615.
Sturrock K, Rocha J : A multidimensional scaling stress evaluation table. Field methods 2000; 12: 49–60.
Wilson IJ, Balding DJ : Genealogical inference from microsatellite data. Genetics 1998; 150: 499–510.
Cheddadi R, Lamb HF, Guiot J, van der Kaars S : Holocene climatic change in Morocco: a quantitative reconstruction from pollen data. Clim Dyn 1998; 14: 883–890.
Kuper R, Kröpelin S : Climate-controlled Holocene occupation in the Sahara: motor of Africa's evolution. Science 2006; 313: 803–807.
Edens C, Wilkinson TJ : Southwest Arabia during the Holocene: recent archaeological developments. J World Prehist 1998; 12: 55–119.
Cruciani F, LaFratta R, Santolamazza P et al: Phylogeographic analysis of haplogroup E3b (E-M215) Y chromosomes reveals multiple migratory events within and out of Africa. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 74: 1014–1022.
Maca-Meyer N, González AM, Pestano J, Flores C, Larruga JM, Cabrera VM : Mitochondrial DNA transit between West Asia and North Africa inferred from U6 phylogeography. BMC Genet 2003; 16: 4–15.
Firestone RB, West A, Kennett JP et al: Evidence for an extraterrestrial impact 12,900 years ago that contributed to the megafaunal extinction and the Younger Dryas cooling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 16016–16021.
Acknowledgements
We thank Davide Merlitti for his precious support in the computational design. Publication of this study was made possible by the 60% grants to GP and ST by the University of Pisa. CC is a RCUK academic fellow. The collaboration with the University of Gezira is within the framework of the activities developed by the Center of Excellence on Aging (CeSI) of Chieti, Italy, as Special Consultant of ECOSOC of the United Nations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tofanelli, S., Ferri, G., Bulayeva, K. et al. J1-M267 Y lineage marks climate-driven pre-historical human displacements. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 1520–1524 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.58
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.58
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Insights into the Middle Eastern paternal genetic pool in Tunisia: high prevalence of T-M70 haplogroup in an Arab population
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Origin and diffusion of human Y chromosome haplogroup J1-M267
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A finely resolved phylogeny of Y chromosome Hg J illuminates the processes of Phoenician and Greek colonizations in the Mediterranean
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
The Connection of the Genetic, Cultural and Geographic Landscapes of Transoxiana
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Y-chromosome phylogeographic analysis of the Greek-Cypriot population reveals elements consistent with Neolithic and Bronze Age settlements
Investigative Genetics (2016)