Abstract
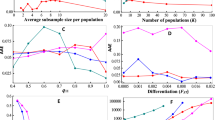
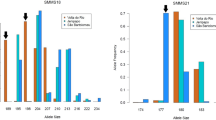
Algorithms for inferring population structure from genetic data (ie, population assignment methods) have shown to effectively recognize genetic clusters in human populations. However, their performance in identifying groups of genealogically related individuals, especially in scanty-differentiated populations, has not been tested empirically thus far. For this study, we had access to both genealogical and genetic data from two closely related, isolated villages in southern Italy. We found that nearly all living individuals were included in a single pedigree, with multiple inbreeding loops. Despite Fst between villages being a low 0.008, genetic clustering analysis identified two clusters roughly corresponding to the two villages. Average kinship between individuals (estimated from genealogies) increased at increasing values of group membership (estimated from the genetic data), showing that the observed genetic clusters represent individuals who are more closely related to each other than to random members of the population. Further, average kinship within clusters and Fst between clusters increases with increasingly stringent membership threshold requirements. We conclude that a limited number of genetic markers is sufficient to detect structuring, and that the results of genetic analyses faithfully mirror the structuring inferred from detailed analyses of population genealogies, even when Fst values are low, as in the case of the two villages. We then estimate the impact of observed levels of population structure on association studies using simulated data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Peltonen L : Positional cloning of disease genes: advantages of genetic isolates. Hum Hered 2000; 50: 66–75.
Shifman S, Darvasi A : The value of isolated populations. Nat Genet 2001; 28: 309–310.
Wright AF, Carothers AD, Pirastu M : Population choice in mapping genes for complex diseases. Nat Genet 1999; 23: 397–404.
Kristiansson K, Naukkarinen J, Peltonen L : Isolated populations and complex disease gene identification. Genome Biol 2008; 9: 109.
Helgason A, Yngvadottir B, Hrafnkelsson B, Gulcher J, Stefansson K : An Icelandic example of the impact of population structure on association studies. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 90–95.
Madrigal L, Melendez-Obando M : Grandmothers' longevity negatively affects daughters' fertility. Am J Phys Anthropol 2008; 136: 223–229.
Helgason A, Palsson S, Gudbjartsson DF, Kristjansson T, Stefansson K : An association between the kinship and fertility of human couples. Science 2008; 319: 813–816.
Chen C, Durands E, Forbes F, Francois O : Bayesian clustering algorithms ascertaining spatial population structure: a new computer program and a comparison study. Mol Ecol Notes 2007; 7: 747–756.
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P : Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000; 155: 945–959.
Corander J, Waldmann P, Marttinen P, Sillanpaa MJ : BAPS 2: enhanced possibilities for the analysis of genetic population structure. Bioinformatics 2004; 20: 2363–2369.
Dawson KJ, Belkhir K : A Bayesian approach to the identification of panmictic populations and the assignment of individuals. Genet Res 2001; 78: 59–77.
Guillot G, Estoup A, Mortier F, Cosson JF : A spatial statistical model for landscape genetics. Genetics 2005; 170: 1261–1280.
Huelsenbeck JP, Andolfatto P : Inference of population structure under a Dirichlet process model. Genetics 2007; 175: 1787–1802.
Rosenberg NA, Pritchard JK, Weber JL et al: Genetic structure of human populations. Science 2002; 298: 2381–2385.
Li JZ, Absher DM, Tang H et al: Worldwide human relationships inferred from genome-wide patterns of variation. Science 2008; 319: 1100–1104.
Jakobsson M, Scholz SW, Scheet P et al: Genotype, haplotype and copy-number variation in worldwide human populations. Nature 2008; 451: 998–1003.
Vitart V, Biloglav Z, Hayward C et al: 3000 years of solitude: extreme differentiation in the island isolates of Dalmatia, Croatia. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 478–487.
Latch EK, Dharmarajan G, Glaubitz JC, Rhodes OE : Relative performance of Bayesian clustering software for inferring population substructure and individual assignment at low levels of population differentiation. Conservation Genetics 2006; 7: 295–302.
Abney M, Ober C, McPeek MS : Quantitative-trait homozygosity and association mapping and empirical genomewide significance in large, complex pedigrees: fasting serum-insulin level in the Hutterites. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 920–934.
Bourgain C, Genin E : Complex trait mapping in isolated populations: are specific statistical methods required? Eur J Hum Genet 2005; 13: 698–706.
Newman DL, Abney M, McPeek MS, Ober C, Cox NJ : The importance of genealogy in determining genetic associations with complex traits. Am J Hum Genet 2001; 69: 1146–1148.
Devlin B, Roeder K : Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 1999; 55: 997–1004.
Bourgain C, Hoffjan S, Nicolae R et al: Novel case-control test in a founder population identifies P-selectin as an atopy-susceptibility locus. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 612–626.
Thornton T, McPeek MS : Case-control association testing with related individuals: a more powerful quasi-likelihood score test. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 321–337.
Ciullo M, Nutile T, Dalmasso C et al: Identification and replication of a novel obesity locus on chromosome 1q24 in isolated populations of Cilento. Diabetes 2008; 57: 783–790.
Colonna V, Nutile T, Astore M et al: Campora: a young genetic isolate in South Italy. Hum Hered 2007; 64: 123–135.
Ciullo M, Bellenguez C, Colonna V et al: New susceptibility locus for hypertension on chromosome 8q by efficient pedigree-breaking in an Italian isolate. Hum Mol Genet 2006; 15: 1735–1743.
Karigl G : A recursive algorithm for the calculation of identity coefficients. Ann Hum Genet 1981; 45: 299–305.
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK : Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 2003; 164: 1567–1587.
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J : Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 2005; 14: 2611–2620.
Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA : CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics 2007; 23: 1801–1806.
Rosenberg NA : DISTRUCT: a program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol Ecol Notes 2004; 4: 137–138.
Excoffier L, Laval LG, Schneider S : Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinformatics Online 2005; 1: 47–50.
Bacanu SA, Devlin B, Roeder K : Association studies for quantitative traits in structured populations. Genet Epidemiol 2002; 22: 78–93.
Wijsman EM, Rothstein JH, Thompson EA : Multipoint linkage analysis with many multiallelic or dense diallelic markers: Markov chain-Monte Carlo provides practical approaches for genome scans on general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet 2006; 79: 846–858.
Pritchard JK : WW: Documentation for structure software:version 2. available on line athttp://pritch.bsd.uchicago.edu/software/readme_2_1/readme.html, 2004.
Lao O, Lu TT, Nothnagel M et al: Correlation between genetic and geographic structure in Europe. Curr Biol 2008; 18: 1241–1248.
Novembre J, Johnson T, Bryc K et al: Genes mirror geography within Europe. Nature 2008; 456: 98–101.
Abney M, McPeek MS, Ober C : Estimation of variance components of quantitative traits in inbred populations. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 629–650.
Falchi M, Forabosco P, Mocci E et al: A genomewide search using an original pairwise sampling approach for large genealogies identifies a new locus for total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in two genetically differentiated isolates of Sardinia. Am J Hum Genet 2004; 75: 1015–1031.
Leutenegger AL, Prum B, Genin E et al: Estimation of the inbreeding coefficient through use of genomic data. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 516–523.
Liu F, Elefante S, van Duijn CM, Aulchenko YS : Ignoring distant genealogic loops leads to false-positives in homozygosity mapping. Ann Hum Genet 2006; 70: 965–970.
Long JC : The allelic correlation structure of Gainj- and Kalam-speaking people. I. The estimation and interpretation of Wright's F-statistics. Genetics 1986; 112: 629–647.
Wood JW, Johnson PL, Kirk RL, McLoughlin K, Blake NM, Matheson FA : The genetic demography of the Gainj of Papua New Guinea. I. Local differentiation of blood group, red cell enzyme, and serum protein allele frequencies. Am J Phys Anthropol 1982; 57: 15–25.
Rosenberg NA, Mahajan S, Ramachandran S, Zhao C, Pritchard JK, Feldman MW : Clines, clusters, and the effect of study design on the inference of human population structure. PLoS Genet 2005; 1: e70.
Acknowledgements
We thank the populations of Gioi and Cardile for their kind cooperation. We thank Don Guglielmo Manna and Dr Leopoldo Errico for helping in the interaction with the populations; Raffaella Romano and Teresa Rizzo for the organization of the study in the villages; Valerio Di Vico for providing us with historical information; Agnar Helgason, Giorgio Bertorelle, and Catherine Bourgain for several important suggestions and comments. This study was supported by funds of the Italian Ministry of Universities (PRIN 2006 and FIRB 2008) to G.B, (FIRB -RBIN064YAT) and the Fondazione Banco di Napoli to MC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website (http://www.nature.com/ejhg)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colonna, V., Nutile, T., Ferrucci, R. et al. Comparing population structure as inferred from genealogical versus genetic information. Eur J Hum Genet 17, 1635–1641 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.97
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2009.97
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Emerging patterns of genetic diversity in the critically endangered Malayan tiger (Panthera tigris jacksoni)
Biodiversity and Conservation (2024)
-
Characterization of Danube Swabian population samples on a high-resolution genome-wide basis
BMC Genomics (2023)
-
Genetics of PlGF plasma levels highlights a role of its receptors and supports the link between angiogenesis and immunity
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Close inbreeding and low genetic diversity in Inner Asian human populations despite geographical exogamy
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Fine-scale human genetic structure in Western France
European Journal of Human Genetics (2015)