Abstract
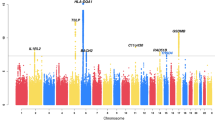
Genome-wide association studies followed by replication provide a powerful approach to map genetic risk factors for asthma. We sought to search for new variants associated with asthma and attempt to replicate the association with four loci reported previously (ORMDL3, PDE4D, DENND1B and IL1RL1). Genome-wide association analyses of individual single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), rare copy number variants (CNVs) and overall CNV burden were carried out in 986 asthma cases and 1846 asthma-free controls from Australia. The most-associated locus in the SNP analysis was ORMDL3 (rs6503525, P=4.8 × 10−7). Five other loci were associated with P<10−5, most notably the chemokine CXC motif ligand 14 (CXCL14) gene (rs31263, P=7.8 × 10−6). We found no evidence for association with the specific risk variants reported recently for PDE4D, DENND1B and ILR1L1. However, a variant in IL1RL1 that is in low linkage disequilibrium with that reported previously was associated with asthma risk after accounting for all variants tested (rs10197862, gene wide P=0.01). This association replicated convincingly in an independent cohort (P=2.4 × 10−4). A 300-kb deletion on chromosome 17q21 was associated with asthma risk, but this did not reach experiment-wide significance. Asthma cases and controls had comparable CNV rates, length and number of genes affected by deletions or duplications. In conclusion, we confirm the association between asthma risk and variants in ORMDL3 and identify a novel risk variant in IL1RL1. Follow-up of the 17q21 deletion in larger cohorts is warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Australian Centre for Asthma Monitoring. Asthma in Australia 2008. AIHW Asthma Series No. 3. Cat. No. ACM 14. Canberra: AIHW, 2008.
Lemanske Jr RF, Busse WW : Asthma: clinical expression and molecular mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 125: S95–102.
Altshuler D, Daly MJ, Lander ES : Genetic mapping in human disease. Science 2008; 322: 881–888.
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA et al: Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 9362–9367.
Rioux JD, Xavier RJ, Taylor KD et al: Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 596–604.
Fellay J, Shianna KV, Ge D et al: A whole-genome association study of major determinants for host control of HIV-1. Science 2007; 317: 944–947.
Moffatt MF, Kabesch M, Liang L et al: Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature 2007; 448: 470–473.
Choudhry S, Taub M, Mei R et al: Genome-wide screen for asthma in Puerto Ricans: evidence for association with 5q23 region. Hum Genet 2008; 123: 455–468.
Himes BE, Hunninghake GM, Baurley JW et al: Genome-wide association analysis identifies PDE4D as an asthma-susceptibility gene. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 84: 581–593.
Hancock DB, Romieu I, Shi M et al: Genome-wide association study implicates chromosome 9q21.31 as a susceptibility locus for asthma in Mexican children. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000623.
Sleiman PM, Flory J, Imielinski M et al: Variants of DENND1B associated with asthma in children. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 36–44.
Mathias RA, Grant AV, Rafaels N et al: A genome-wide association study on African-ancestry populations for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 125: 336–346.e4.
Li X, Howard TD, Zheng SL et al: Genome-wide association study of asthma identifies RAD50-IL13 and HLA-DR/DQ regions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 125: 328–335.e11.
Ober C, Tan Z, Sun Y et al: Effect of variation in CHI3L1 on serum YKL-40 level, risk of asthma, and lung function. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1682–1691.
Weidinger S, Gieger C, Rodriguez E et al: Genome-wide scan on total serum IgE levels identifies FCER1A as novel susceptibility locus. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e1000166.
Gudbjartsson DF, Bjornsdottir US, Halapi E et al: Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 342–347.
Scherer SW, Lee C, Birney E et al: Challenges and standards in integrating surveys of structural variation. Nat Genet 2007; 39: S7–15.
The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium: Genome-wide association study of CNVs in 16 000 cases of eight common diseases and 3000 shared controls. Nature 2010; 464: 713–720.
Bochukova EG, Huang N, Keogh J et al: Large, rare chromosomal deletions associated with severe early-onset obesity. Nature 2010; 463: 666–670.
Weiss LA, Shen Y, Korn JM et al: Association between microdeletion and microduplication at 16p11.2 and autism. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 667–675.
The International Schizophrenia Consortium: Rare chromosomal deletions and duplications increase risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2008; 455: 237–241.
Ionita-Laza I, Perry GH, Raby BA et al: On the analysis of copy-number variations in genome-wide association studies: a translation of the family-based association test. Genet Epidemiol 2008; 32: 273–284.
Medland SE, Nyholt DR, Painter JN et al: Common variants in the trichohyalin gene are associated with straight hair in Europeans. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 85: 750–755.
Blangero J, Almasy L : Multipoint oligogenic linkage analysis of quantitative traits. Genet Epidemiol 1997; 14: 959–964.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al: PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Frazer KA, Ballinger DG, Cox DR et al: A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 2007; 449: 851–861.
Colella S, Yau C, Taylor JM et al: QuantiSNP: an Objective Bayes Hidden-Markov Model to detect and accurately map copy number variation using SNP genotyping data. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 2013–2025.
Shurin GV, Ferris RL, Tourkova IL et al: Loss of new chemokine CXCL14 in tumor tissue is associated with low infiltration by dendritic cells (DC), while restoration of human CXCL14 expression in tumor cells causes attraction of DC both in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 2005; 174: 5490–5498.
Dubois PC, Trynka G, Franke L et al: Multiple common variants for celiac disease influencing immune gene expression. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 295–302.
Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium (TASC) Reveille JD, Sims AM, Danoy P et al: Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 123–127.
Barrett JC, Hansoul S, Nicolae DL et al: Genome-wide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn's disease. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 955–962.
Stefansson H, Helgason A, Thorleifsson G et al: A common inversion under selection in Europeans. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 129–137.
Ferreira MA, Mangino M, Brumme CJ et al: Quantitative trait loci for CD4: CD8 lymphocyte ratio are associated with risk of type 1 diabetes and HIV-1 immune control. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 86: 88–92.
Tantisira KG, Lazarus R, Litonjua AA, Klanderman B, Weiss ST : Chromosome 17: association of a large inversion polymorphism with corticosteroid response in asthma. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2008; 18: 733–737.
Acknowledgements
We thank the twins and their families for their participation; Dixie Statham, Ann Eldridge, Marlene Grace and Kerrie McAloney for sample collection; Lisa Bowdler and Steven Crooks for DNA processing; David Smyth, Harry Beeby and Daniel Park for IT support. Funding was provided by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (241944, 339462, 389927, 389875, 389891, 389892, 389938, 442915, 442981, 496739, 552485, 552498, 613627), the Australian Research Council (A7960034, A79906588, A79801419, DP0770096, DP0212016, DP0343921), the FP-5 GenomEUtwin Project (QLG2-CT-2002-01254) and the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Grants AA07728, AA07535, AA10248, AA11998, AA13320, AA13321, AA13326, AA14041, DA12854, MH66206). A portion of the genotyping on which this study was based (Illumina 370k scans on 4300 individuals) was carried out at the Center for Inherited Disease Research, Baltimore (CIDR) through an access award to our late colleague Dr Richard Todd (Psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis). SEM, DRN, MARF, GWM and PMV are supported by the NHMRC Fellowship Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, M., McRae, A., Medland, S. et al. Association between ORMDL3, IL1RL1 and a deletion on chromosome 17q21 with asthma risk in Australia. Eur J Hum Genet 19, 458–464 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.191
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.191
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Exome-wide analysis of copy number variation shows association of the human leukocyte antigen region with asthma in UK Biobank
BMC Medical Genomics (2022)
-
Reconstructing recent population history while mapping rare variants using haplotypes
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Lessons from ten years of genome‐wide association studies of asthma
Clinical & Translational Immunology (2017)
-
Genetic and epigenetic studies of FOXP3 in asthma and allergy
Asthma Research and Practice (2015)
-
Functional analysis of the impact of ORMDL3 expression on inflammation and activation of the unfolded protein response in human airway epithelial cells
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology (2013)