Abstract
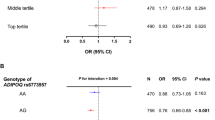
Adiponectin is an adipocyte-derived protein that is down-regulated in obesity-linked disorders. Variants of the adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) have been shown to affect adiponectin level. We have now examined the relation of polymorphisms of ADIPOQ to adiponectin concentration and to metabolic disorders in the Kita-Nagoya Genomic Epidemiology study, a population-based study of elderly Japanese. The genomic region including ADIPOQ was genotyped for 30 single nucleotide polymorphisms in 500 subjects of a screening population with the use of a fluorescence- or colorimetry-based allele-specific DNA primer–probe assay system. Four polymorphisms were then selected for genotyping in an additional 2797 subjects. Serum adiponectin level was negatively associated with metabolic abnormalities after adjustment for age and sex. The minor alleles of the rs1656930, Ile164Thr, and rs9882205 polymorphisms were associated with a low serum adiponectin level. Whereas the minor alleles of rs1656930 and rs9882205 were common (minor allele frequency of 6.2 and 38.5%, respectively), that of Ile164Thr was rare (0.9%). The minor allele of rs1656930 was positively associated with systolic blood pressure and the prevalence of hypertension. The association of rs1656930 with adiponectin level was replicated in an independent population. A subject with the 164Thr/Thr genotype had an extremely low serum adiponectin level (0.6 μg/ml) and the phenotype of metabolic syndrome. Our results suggest that a common variant of ADIPOQ, the minor allele of rs1656930, is associated with hypoadiponectinemia and hypertension. Screening for a common genetic background underlying low adiponectin levels might provide important information for assessment and management of metabolic disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Alberti KGMM, Zimmet P, Shaw J : Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A Consensus Statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 2006; 23: 469–480.
Lakka H-M, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA et al: The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 2002; 288: 2709–2716.
Yoshiike N, Seino F, Tajima S et al: Twenty-year changes in the prevalence of overweight in Japanese adults: the National Nutrition Survey 1976-95. Obes Rev 2002; 3: 183–190.
Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Shimomura I : Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 29–33.
Vettor R, Milan G, Rossato M, Federspil G : Review article: adipocytokines and insulin resistance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 3–10.
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S et al: Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1930–1935.
Hotta K, Funahashi T, Arita Y et al: Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000; 20: 1595–1599.
Lindsay RS, Funahashi T, Hanson RL et al: Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population. Lancet 2002; 360: 57–58.
Spranger J, Kroke A, Möhlig M et al: Adiponectin and protection against type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2003; 361: 226–228.
Li S, Shin HJ, Ding EL, van Dam RM : Adiponectin levels and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2009; 302: 179–188.
Ryo M, Nakamura T, Kihara S et al: Adiponectin as a biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. Circ J 2004; 68: 975–981.
Iwashima Y, Katsuya T, Ishikawa K et al: Hypoadiponectinemia is an independent risk factor for hypertension. Hypertension 2004; 43: 1318–1323.
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y et al: Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999; 100: 2473–2476.
Kumada M, Kihara S, Sumitsuji S et al: Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery disease in men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 85–89.
Otsuka F, Sugiyama S, Kojima S et al: Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with impaired glucose tolerance and coronary artery disease in non-diabetic men. Circ J 2007; 71: 1703–1709.
Snijder MB, Heine RJ, Seidell JC et al: Associations of adiponectin levels with incident impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes in older men and women: the Hoorn Study. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 2498–2503.
Ouchi N, Ohishi M, Kihara S et al: Association of hypoadiponectinemia with impaired vasoreactivity. Hypertension 2003; 42: 231–234.
Francischetti EA, Celoria BMJ, Duarte SFP et al: Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with blood pressure increase in obese insulin-resistant individuals. Metabolism 2007; 56: 1464–1469.
Huang K-C, Chen C-L, Chuang L-M, Ho S-R, Tai T-Y, Yang W-S : Plasma adiponectin levels and blood pressures in nondiabetic adolescent females. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003; 88: 4130–4134.
Iwashima Y, Horio T, Suzuki Y et al: Adiponectin and inflammatory markers in peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Atherosclerosis 2006; 188: 384–390.
Pischon T, Girman CJ, Hotamisligil GS, Rifai N, Hu FB, Rimm EB : Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. JAMA 2004; 291: 1730–1737.
Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM : AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 10697–10703.
Gable DR, Hurel SJ, Humphries SE : Adiponectin and its gene variants as risk factors for insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2006; 188: 231–244.
Kondo H, Shimomura I, Matsukawa Y et al: Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes : a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 2002; 51: 2325–2328.
Ohashi K, Ouchi N, Kihara S et al: Adiponectin I164T mutation is associated with the metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 43: 1195–1200.
Vasseur F, Helbecque N, Dina C et al: Single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes in the both proximal promoter and exon 3 of the APM1 gene modulate adipocyte-secreted adiponectin hormone levels and contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. Hum Mol Genet 2002; 11: 2607–2614.
Schwarz PEH, Towers GW, Fischer S et al: Hypoadiponectinemia is associated with progression toward type 2 diabetes and genetic variation in the ADIPOQ gene promoter. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 1645–1650.
Hara K, Boutin P, Mori Y et al: Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 2002; 51: 536–540.
Filippi E, Sentinelli F, Trischitta V et al: Association of the human adiponectin gene and insulin resistance. Eur J Hum Genet 2003; 12: 199–205.
Asano H, Izawa H, Nagata K et al: Plasma resistin concentration determined by common variants in the resistin gene and associated with metabolic traits in an aged Japanese population. Diabetologia 2009; 53: 234–246.
Yamada Y, Izawa H, Ichihara S et al: Prediction of the risk of myocardial infarction from polymorphisms in candidate genes. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 1916–1923.
Heid IM, Wagner SA, Gohlke H et al: Genetic architecture of the APM1 gene and its influence on adiponectin plasma levels and parameters of the metabolic syndrome in 1727 healthy Caucasians. Diabetes 2006; 55: 375–384.
Menzaghi C, Ercolino T, Di Paola R et al: A haplotype at the adiponectin locus is associated with obesity and other features of the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 2002; 51: 2306–2312.
Sutton BS, Weinert S, Langefeld CD et al: Genetic analysis of adiponectin and obesity in Hispanic families: the IRAS family study. Hum Genet 2005; 117: 107–118.
Hivert M-F, Manning AK, McAteer JB et al: Common variants in the adiponectin gene (ADIPOQ) associated with plasma adiponectin levels, type 2 diabetes, and diabetes-related quantitative traits: the Framingham Offspring study. Diabetes 2008; 57: 3353–3359.
Heid IM, Henneman P, Hicks A et al: Clear detection of ADIPOQ locus as the major gene for plasma adiponectin: results of genome-wide association analyses including 4659 European individuals. Atherosclerosis 2010; 208: 412–420.
Gu HF, Abulaiti A, Ostenson C-G et al: Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the proximal promoter region of the adiponectin (APM1) gene are associated with type 2 diabetes in Swedish Caucasians. Diabetes 2004; 53: S31–S35.
Mackevics V, Heid IM, Wagner SA et al: The adiponectin gene is associated with adiponectin levels but not with characteristics of the insulin resistance syndrome in healthy Caucasians. Eur J Hum Genet 2006; 14: 349–356.
Chow W-S, Cheung BMY, Tso AWK et al: Hypoadiponectinemia as a predictor for the development of hypertension: a 5-Year prospective study. Hypertension 2007; 49: 1455–1461.
Furuhashi M, Ura N, Higashiura K et al: Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system increases adiponectin concentrations in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 2003; 42: 76–81.
Ohashi K, Kihara S, Ouchi N et al: Adiponectin replenishment ameliorates obesity-related hypertension. Hypertension 2006; 47: 1108–1116.
Acknowledgements
We thank the study participants as well as Masakazu Kobayashi, Ken Harada, Takashi Yamada, Kazumasa Unno, Hiroki Kataoka, Hidehito Funahashi, Kousuke Arai, Yasutsugu Morimoto, Mayo Sukegawa, and especially Takao Nishizawa for their assistance. This study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research to MY including those of Categories (A) and (B) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (17209021 and 21390209) and of Priority Area ‘Applied Genomics’ (1601223, 17019028, 18018020, and 20018026) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers
KING study: NCT00262691(http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00262691).
Replication study: NCT00408824 (http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00408824).
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanimura, D., Shibata, R., Izawa, H. et al. Relation of a common variant of the adiponectin gene to serum adiponectin concentration and metabolic traits in an aged Japanese population. Eur J Hum Genet 19, 262–269 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.201
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.201
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ADIPOQ gene is linked to emotional eating behaviour in young Nigerian adults independent of psychological traits
Bulletin of the National Research Centre (2020)
-
Epigenome-wide association of myocardial infarction with DNA methylation sites at loci related to cardiovascular disease
Clinical Epigenetics (2017)
-
Polymorphisms of the adiponectin gene in gestational hypertension and pre-eclampsia
Journal of Human Hypertension (2014)
-
Combinational risk factors of metabolic syndrome identified by fuzzy neural network analysis of health-check data
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making (2012)