Abstract
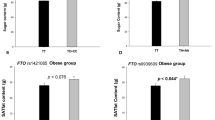
As shown by genome-wide association studies single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within intron 1 of the FTO gene are associated with the body mass index and type II diabetes, although the functional significance of these SNPs has remained unclear. Using primer extension assays, we have determined the ratio of allelic FTO transcript levels in unspliced heterogeneous nuclear RNA preparations from blood of individuals heterozygous for SNP rs9939609. Allelic expression ratios of the neighboring RPGRIP1L gene were investigated in individuals who were heterozygous for SNP rs4784319 and heterozygous or homozygous for rs9939609. In each of five individuals, the FTO transcripts containing the A (risk) allele of rs9939609 were more abundant than those with T allele (mean 1.38; 95% confidence interval 1.31–1.44). Similar results were obtained in a fibroblast sample. We also observed skewed allelic expression of the RPGRIP1L gene in blood, but skewing was independent of the FTO genotype. Our data suggest that increased expression of FTO is associated with increased body mass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon NM et al: A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 2007; 316: 889–892.
Dina C, Meyre D, Gallina S et al: Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 724–726.
Gerken T, Girard ChA, Tung YL et al: The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science 2007; 318: 1469–1474.
Boissel S, Reish O, Proulx K et al: Loss-of-Function mutation in the dioxygenase-encoding FTO gene causes severe growth retardation and multiple malformations. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 85: 106–111.
Meyre D, Proulx K, Kawagoe-Takaki H et al: Prevalence of loss of function FTO mutations in lean and obese individuals. Diabetes 2010; 59: 311–318.
Delous M, Lekbir Baala L, Salomon R et al: The ciliary gene RPGRIP1L is mutated in cerebello-oculo-renal syndrome (Joubert syndrome type B) and Meckel syndrome. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 875–881.
Fischer J, Koch L, Emmerling Ch et al: Inactivation of the Fto gene protects from obesity. Nature 2009; 458: 894–898.
Church C, Lee S, Bagg EAL et al: A mouse model for the metabolic effects of the human fat mass and obesity associated FTO gene. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000599.
Stratigopoulos G, Padilla SL, LeDuc CA et al: Regulation of Fto/Ftm gene expression in mice and humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2008; 294: 1185–1196.
Klöting N, Schleinitz D, Ruschke K et al: Inverse relationship between obesity and FTO gene expression in visceral adipose tissue in humans. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 641–647.
Wåhlén K, Sjölin E, Hoffstedt J : The common rs9939609 gene variant of the fat mass- and obesity-associated gene FTO is related to fat cell lypolisis. J Lipid Res 2008; 49: 607–611.
Louise GG, Nilsson E, Ling C et al: Regulation and function of FTO mRNA expression in human skeletal muscle and subcutaneous adipose tissue. Diabetes 2009; 58: 2402–2408.
Jowett BMJ, Curran JE, Johnson MP et al: Genetic variation at the FTO locus influences RBL2 gene expression. Diabetes 2010; 59: 726–732.
Sansregret L, Nepveu A : The multiple roles of CUX1: insights from mouse models and cell-based assays. Gene 2008; 412: 84–94.
Yan H, Yuan W, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW : Allelic variation in human gene expression. Science 2002; 297: 1143.
Lo HS, Wang Z, Hu Y et al: Allelic variation in gene expression is common in the human genome. Genome Res 2003; 13: 1855–1862.
Pastinen T, Sladek R, Gurd S et al: A survey of genetic and epigenetic variation affecting human gene expression. Physiol Genomics 2004; 16: 184–193.
Serre D, Gurd S, Ge B et al: Differential allelic expression in the human genome: a robust approach to identify genetic and epigenetic cis-acting mechanisms regulating gene expression. PLoS Genet 2008; 4: e1000006.
Kanber D, Berulava T, Ammerpohl O et al: The human retinoblastoma gene is impinted. PLoS Genet 2009; 5: e1000790.
Jacobsson JA, Danielsson P, Svensson V et al: Major gender difference in association of FTO gene variant among several obese children with obesity and obesity related phenotypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 368: 476–482.
Acknowledgements
We thank all individuals for donating blood and skin biopsies, physicians for drawing blood, Regina Kubica for technical assistance with fibroblast cultures and the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (NGFN plus 01GS0820) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
WEB RESOURCES
The URLs used for this study are as follows: UCSC Human Genome Browser Gateway at http://genome.ucsc.edu/NCBI Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP/HapMap Genome Browser at http://hapmap.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-perl/gbrowse/hapmap3r2_B36/.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berulava, T., Horsthemke, B. The obesity-associated SNPs in intron 1 of the FTO gene affect primary transcript levels. Eur J Hum Genet 18, 1054–1056 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.71
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.71
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association of FTO gene variant rs9939609 with polycystic ovary syndrome from Gujarat, India
BMC Medical Genomics (2023)
-
FTO-mediated m6A demethylation regulates GnRH expression in the hypothalamus via the PLCβ3/Ca2+/CAMK signalling pathway
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Long-term exercise training down-regulates m6A RNA demethylase FTO expression in the hippocampus and hypothalamus: an effective intervention for epigenetic modification
BMC Neuroscience (2022)
-
Association of ADIPOQ-rs2241766 and FTO-rs9939609 genetic variants with body mass index trajectory in women of reproductive age over 6 years of follow-up: the PREDI study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2022)
-
Altered m6A RNA methylation contributes to hippocampal memory deficits in Huntington’s disease mice
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)