Abstract
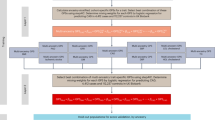
A new understanding of the genetic basis of coronary artery disease (CAD) has recently emerged from genome-wide association (GWA) studies of common single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), thus far performed mostly in European-descent populations. To identify novel susceptibility gene variants for CAD and confirm those previously identified mostly in populations of European descent, a multistage GWA study was performed in the Japanese. In the discovery phase, we first genotyped 806 cases and 1337 controls with 451 382 SNP markers and subsequently assessed 34 selected SNPs with direct genotyping (541 additional cases) and in silico comparison (964 healthy controls). In the replication phase, involving 3052 cases and 6335 controls, 12 SNPs were tested; CAD association was replicated and/or verified for 4 (of 12) SNPs from 3 loci: near BRAP and ALDH2 on 12q24 (P=1.6 × 10−34), HLA-DQB1 on 6p21 (P=4.7 × 10−7), and CDKN2A/B on 9p21 (P=6.1 × 10−16). On 12q24, we identified the strongest association signal with the strength of association substantially pronounced for a subgroup of myocardial infarction cases (P=1.4 × 10−40). On 6p21, an HLA allele, DQB1*0604, could show one of the most prominent association signals in an ∼8-Mb interval that encompasses the LTA gene, where an association with myocardial infarction had been reported in another Japanese study. CAD association was also identified at CDKN2A/B, as previously reported in different populations of European descent and Asians. Thus, three loci confirmed in the Japanese GWA study highlight the likely presence of risk alleles with two types of genetic effects – population specific and common – on susceptibility to CAD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Schunkert H, Erdmann J, Samani NJ : Genetics of myocardial infarction: a progress report. Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 918–925.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium: Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007; 447: 661–978.
Trégouët DA, König IR, Erdmann J et al: Genome-wide haplotype association study identifies the SLC22A3-LPAL2-LPA gene cluster as a risk locus for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 283–285.
Erdmann J, Grosshennig A, Braund PS et al: New susceptibility locus for coronary artery disease on chromosome 3q22.3. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 280–282.
Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium: Genome-wide association of early-onset myocardial infarction with single nucleotide polymorphisms and copy number variants. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 334–341.
Gudbjartsson DF, Bjornsdottir US, Halapi E et al: Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 342–347.
Schunkert H, König IR, Kathiresan S et al: Large-scale association analysis identifies 13 new susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 333–338.
Coronary Artery Disease (C4D) Genetics Consortium: A genome-wide association study in Europeans and South Asians identifies five new loci for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 339–344.
Soranzo N, Spector TD, Mangino M et al: A genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 22 loci associated with eight hematological parameters in the HaemGen consortium. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1182–1190.
Shen GQ, Li L, Rao S et al: Four SNPs on chromosome 9p21 in a South Korean population implicate a genetic locus that confers high cross-race risk for development of coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008; 28: 360–365.
Saleheen D, Alexander M, Rasheed A et al: Association of the 9p21.3 locus with risk of first-ever myocardial infarction in Pakistanis: case-control study in South Asia and updated meta-analysis of Europeans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2010; 30: 1467–1473.
Moriyama Y, Okamura T, Inazu A et al: A low prevalence of coronary heart disease among subjects with increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, including those with plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein deficiency. Prev Med 1998; 27: 659–667.
Okamura T : Dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease: a series of epidemiologic studies in Japanese populations. J Epidemiol 2010; 20: 259–265.
Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M : Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 209–213.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al: PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Takeuchi F, Serizawa M, Yamamoto K et al: Confirmation of multiple risk loci and genetic impacts by a genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1690–1699.
Devlin B, Roeder K : Genomic control for association studies. Biometrics 1999; 55: 997–1004.
Kang HM, Sul JH, Service SK et al: Variance component model to account for sample structure in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 348–354.
Browning BL, Browning SR : A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 84: 210–223.
Ozaki K, Sato H, Inoue K et al: SNPs in BRAP associated with risk of myocardial infarction in Asian populations. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 329–333.
Ozaki K, Ohnishi Y, Iida A et al: Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-alpha gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 650–654.
Ozaki K, Inoue K, Sato H et al: Functional variation in LGALS2 confers risk of myocardial infarction and regulates lymphotoxin-alpha secretion in vitro. Nature 2004; 429: 72–75.
Pickrell JK, Coop G, Novembre J et al: Signals of recent positive selection in a worldwide sample of human populations. Genome Res 2009; 19: 826–837.
de Bakker PI, McVean G, Sabeti PC et al: A high-resolution HLA and SNP haplotype map for disease association studies in the extended human MHC. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 1166–1172.
Iwakawa M, Goto M, Noda S et al: DNA repair capacity measured by high throughput alkaline comet assays in EBV-transformed cell lines and peripheral blood cells from cancer patients and healthy volunteers. Mutat Res 2005; 588: 1–6.
Takagi S, Iwai N, Yamauchi R et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene is a risk factor for myocardial infarction in Japanese men. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 677–681.
Kato N, Takeuchi F, Tabara Y et al: Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies common variants associated with blood pressure variation in east Asians. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 531–538.
Chen CH, Budas GR, Churchill EN, Disatnik MH, Hurley TD, Mochly-Rosen D : Activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 reduces ischemic damage to the heart. Science 2008; 321: 1493–1495.
Li W, Xu J, Wang X et al: Lack of association between lymphotoxin-alpha, galectin-2 polymorphisms and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2010; 208: 433–436.
Zollner S, Pritchard JK : Overcoming the winner's curse: estimating penetrance parameters from case-control data. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 605–615.
Deitiker PR, Oshima M, Smith RG, Mosier DR, Atassi MZ : Subtle differences in HLA DQ haplotype-associated presentation of AChR alpha-chain peptides may suffice to mediate myasthenia gravis. Autoimmunity 2006; 39: 277–288.
Björkbacka H, Lavant EH, Fredrikson GN et al: Weak associations between human leucocyte antigen genotype and acute myocardial infarction. J Intern Med 2010; 268: 50–58.
Reilly MP, Li M, He J et al: Identification of ADAMTS7 as a novel locus for coronary atherosclerosis and association of ABO with myocardial infarction in the presence of coronary atherosclerosis: two genome-wide association studies. Lancet 2011; 377: 383–392.
Hao K, Chudin E, Greenawalt D, Schadt EE : Magnitude of stratification in human populations and impacts on genome wide association studies. PLoS One 2010; 5: e8695.
Karvanen J, Silander K, Kee F et al: The impact of newly identified loci on coronary heart disease, stroke and total mortality in the MORGAM prospective cohorts. Genet Epidemiol 2009; 33: 237–246.
Ripatti S, Tikkanen E, Orho-Melander M et al: A multilocus genetic risk score for coronary heart disease: case-control and prospective cohort analyses. Lancet 2010; 376: 1393–1400.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the people who have continuously supported the Hospital-based Cohort Study at the National Center for Global Health and Medicine, the Amagasaki Study and the Kyushu University Fukuoka Cohort Study, and the KING Study. We also thank Drs Suminori Kono, Ken Sugimoto, Kei Kamide, and Chikanori Makibayashi, and the many physicians of the participating hospitals and medical institutions for their assistance in collecting the DNA samples and accompanying clinical information. This work was supported by grants for the Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) from the Japan Science Technology Agency; the Program for Promotion of Fundamental Studies in Health Sciences, National Institute of Biomedical Innovation Organization (NIBIO); and KAKENHI (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research) on Priority Areas ‘Applied Genomics’ from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeuchi, F., Yokota, M., Yamamoto, K. et al. Genome-wide association study of coronary artery disease in the Japanese. Eur J Hum Genet 20, 333–340 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.184
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.184
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Genetic associations of cardiovascular risk genes in European patients with coronary artery spasm
Clinical Research in Cardiology (2024)
-
East Asian variant aldehyde dehydrogenase type 2 genotype exacerbates ischemia/reperfusion injury with ST-elevation myocardial infarction in men: possible sex differences
Heart and Vessels (2022)
-
Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Polymorphisms and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease: Evidence From Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis
Biochemical Genetics (2022)
-
The role of MTHFR C677T and ALDH2 Glu504Lys polymorphism in acute coronary syndrome in a Hakka population in southern China
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2020)
-
Blood levels of microRNAs associated with ischemic heart disease differ between Austrians and Japanese: a pilot study
Scientific Reports (2020)