Abstract
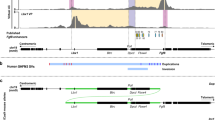
Split-hand/foot malformation with long-bone deficiency (SHFLD) is a relatively rare autosomal-dominant skeletal disorder, characterized by variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance. Although several chromosomal loci for SHFLD have been identified, the molecular basis and pathogenesis of most SHFLD cases are unknown. In this study we describe three unrelated kindreds, in which SHFLD segregated with distinct but overlapping duplications in 17p13.3, a region previously linked to SHFLD. In a large three-generation family, the disorder was found to segregate with a 254 kb microduplication; a second microduplication of 527 kb was identified in an affected female and her unaffected mother, and a 430 kb microduplication versus microtriplication was identified in three affected members of a multi-generational family. These findings, along with previously published data, suggest that one locus responsible for this form of SHFLD is located within a 173 kb overlapping critical region, and that the copy gains are incompletely penetrant.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Majewski F, Kuster W, ter Haar B, Goecke T : Aplasia of tibia with split-hand/split-foot deformity. Report of six families with 35 cases and considerations about variability and penetrance. Hum Genet 1985; 70: 136–147.
Basel D, Kilpatrick MW, Tsipouras P : The expanding panorama of split hand foot malformation. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 1359–1365.
Ugur SA, Tolun A : Homozygous WNT10b mutation and complex inheritance in split-Hand/Foot malformation. Hum Mol Genet 2008; 17: 2644–2653.
Celli J, Duijf P, Hamel BC et al: Heterozygous germline mutations in the p53 homolog p63 are the cause of EEC syndrome. Cell 1999; 99: 143–153.
Kjaer KW, Hansen L, Schwabe GC et al: Distinct CDH3 mutations cause ectodermal dysplasia, ectrodactyly, macular dystrophy (EEM syndrome). J Med Genet 2005; 42: 292–298.
Scherer SW, Poorkaj P, Massa H et al: Physical mapping of the split hand/split foot locus on chromosome 7 and implication in syndromic ectrodactyly. Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3: 1345–1354.
de Mollerat XJ, Gurrieri F, Morgan CT et al: A genomic rearrangement resulting in a tandem duplication is associated with split hand-split foot malformation 3 (SHFM3) at 10q24. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12: 1959–1971.
Lyle R, Radhakrishna U, Blouin JL et al: Split-hand/split-foot malformation 3 (SHFM3) at 10q24, development of rapid diagnostic methods and gene expression from the region. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 1384–1395.
Goodman FR, Majewski F, Collins AL, Scambler PJ : A 117-kb microdeletion removing HOXD9-HOXD13 and EVX2 causes synpolydactyly. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 70: 547–555.
Babbs C, Heller R, Everman DB et al: A new locus for split hand/foot malformation with long bone deficiency (SHFLD) at 2q14.2 identified from a chromosome translocation. Hum Genet 2007; 122: 191–199.
Naveed M, Al-Ali MT, Murthy SK et al: Ectrodactyly with aplasia of long bones (OMIM; 119 100) in a large inbred arab family with an apparent autosomal dominant inheritance and reduced penetrance: Clinical and genetic analysis. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 1440–1446.
Naveed M, Nath SK, Gaines M et al: Genomewide linkage scan for split-hand/foot malformation with long-bone deficiency in a large arab family identifies two novel susceptibility loci on chromosomes 1q42.2-q43 and 6q14.1. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 80: 105–111.
Lezirovitz K, Maestrelli SR, Cotrim NH, Otto PA, Pearson PL, Mingroni-Netto RC : A novel locus for split-hand/foot malformation associated with tibial hemimelia (SHFLD syndrome) maps to chromosome region 17p13.1-17p13.3. Hum Genet 2008; 123: 625–631.
Schwartz CE, Ulmer J, Brown A, Pancoast I, Goodman HO, Stevenson RE : Allan-herndon syndrome. II. linkage to DNA markers in Xq21. Am J Hum Genet 1990; 47: 454–458.
Barch MJ, Knutsen T, Spurbeck JL (eds).: Cytogenetics Laboratory Manual, 3rd edn. New York: Lippincott-Raven, 1997, pp 127–130.
Armour CM, McCready ME, Baig A, Hunter AG, Bulman DE : A novel locus for brachydactyly type A1 on chromosome 5p13.3-p13.2. J Med Genet 2002; 39: 186–188.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD : Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001; 25: 402–408.
Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Frazer KA et al: PipMaker – a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 2000; 10: 577–586.
Jarinova O, Hatch G, Poitras L et al: Functional resolution of duplicated hoxb5 genes in teleosts. Development 2008; 135: 3543–3553.
Ianakiev P, Kilpatrick MW, Toudjarska I, Basel D, Beighton P, Tsipouras P : Split-hand/split-foot malformation is caused by mutations in the p63 gene on 3q27. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 67: 59–66.
Rinne T, Hamel B, van Bokhoven H, Brunner HG : Pattern of p63 mutations and their phenotypes – update. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140: 1396–1406.
Agarwala R, Schaffer AA, Tomlin JF : Towards a complete North American Anabaptist genealogy II: Analysis of inbreeding. Hum Biol 2001; 73: 533–545.
Berg JS, Potocki L, Bacino CA : Common recurrent microduplication syndromes: Diagnosis and management in clinical practice. Am J Med Genet A 2010; 152A: 1066–1078.
Vissers LE, de Vries BB, Veltman JA : Genomic microarrays in mental retardation: From copy number variation to gene, from research to diagnosis. J Med Genet 2010; 47: 289–297.
Bruno DL, Anderlid BM, Lindstrand A et al: Further molecular and clinical delineation of co-locating 17p13.3 microdeletions and microduplications that show distinctive phenotypes. J Med Genet 2010; 47: 299–311.
Bi W, Sapir T, Shchelochkov OA et al: Increased LIS1 expression affects human and mouse brain development. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 168–177.
Roos L, Jonch AE, Kjaergaard S et al: A new microduplication syndrome encompassing the region of the Miller-Dieker (17p13 deletion) syndrome. J Med Genet 2009; 46: 703–710.
Klopocki E, Ott CE, Benatar N, Ullmann R, Mundlos S, Lehmann K : A microduplication of the long range SHH limb regulator (ZRS) is associated with triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome. J Med Genet 2008; 45: 370–375.
Sun M, Ma F, Zeng X et al: Triphalangeal thumb-polysyndactyly syndrome and syndactyly type IV are caused by genomic duplications involving the long range, limb-specific SHH enhancer. J Med Genet 2008; 45: 589–595.
Dathe K, Kjaer KW, Brehm A et al: Duplications involving a conserved regulatory element downstream of BMP2 are associated with brachydactyly type A2. Am J Hum Genet 2009; 84: 483–492.
Sidow A, Bulotsky MS, Kerrebrock AW et al: A novel member of the F-box/WD40 gene family, encoding dactylin, is disrupted in the mouse dactylaplasia mutant. Nat Genet 1999; 23: 104–107.
Chuang TH, Xu X, Kaartinen V, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J, Bokoch GM : Abr and bcr are multifunctional regulators of the rho GTP-binding protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 10282–10286.
Kaartinen V, Nagy A, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N : Vestibular dysgenesis in mice lacking abr and bcr Cdc42/RacGAPs. Dev Dyn 2002; 223: 517–525.
Park TJ, Boyd K, Curran T : Cardiovascular and craniofacial defects in crk-null mice. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 6272–6282.
Funato Y, Michiue T, Terabayashi T et al: Nucleoredoxin regulates the Wnt/planar cell polarity pathway in xenopus. Genes Cells 2008; 13: 965–975.
Verma RS, Conte RA, Pitter JH : Tandem duplication of the terminal band of the long arm of chromosome 7 (dir dup (7)(q36----qter)). J Med Genet 1992; 29: 344–345.
Kent WJ, Sugnet CW, Furey TS et al: The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res 2002; 12: 996–1006.
Rhead B, Karolchik D, Kuhn RM et al: The UCSC genome browser database: Update 2010. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38 (Database issue): D613–D619.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge the participation of the families, without whom this work would not have been possible. We also thank Cindy Skinner, RN for assistance with sample coordination. This work was funded by a grant from the Children's Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, the Clinical Teachers’ Association of Queen's University, and support from the South Carolina Birth Defects Foundation, the Genetics Endowment of South Carolina, and the South Carolina Department of Disabilities and Special Needs. OJ holds HSF/Pfizer Postdoctoral fellowship.
Note added in proof
The nonpenetrant mother with the duplication in Family 2 has bilateral hearing loss and has worn hearing aids since 3 years of age.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armour, C., Bulman, D., Jarinova, O. et al. 17p13.3 microduplications are associated with split-hand/foot malformation and long-bone deficiency (SHFLD). Eur J Hum Genet 19, 1144–1151 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.97
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2011.97
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Split hand/foot malformation with long bone deficiency associated with BHLHA9 gene duplication: a case report and review of literature
BMC Medical Genetics (2019)
-
Multiple occurrence of psychomotor retardation and recurrent miscarriages in a family with a submicroscopic reciprocal translocation t(7;17)(p22;p13.2)
BMC Medical Genomics (2018)
-
17p13.3 genomic rearrangement in a Chinese family with split-hand/foot malformation with long bone deficiency: report of a complicated duplication with marked variation in phenotype
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018)
-
Deletions of exons with regulatory activity at the DYNC1I1 locus are associated with split-hand/split-foot malformation: array CGH screening of 134 unrelated families
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2014)
-
Japanese founder duplications/triplications involving BHLHA9 are associated with split-hand/foot malformation with or without long bone deficiency and Gollop-Wolfgang complex
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2014)